Determination of Moisture Content | Agriculture Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Determination of moisture content
Objective
The objective is to determine the moisture content of seeds using methods suitable for routine use.
Definition
Seed moisture content is the percentage of weight loss when a seed sample is dried and is expressed as a percentage of the original sample weight. It is a crucial factor in maintaining seed quality.
Methods of Moisture Determination
- Air Oven Method: In this method, seed moisture is eliminated by drying the seed sample at a specified temperature for a set duration.
- Moisture Meters: Moisture meters provide quick estimates of seed moisture, but the accuracy is not as high as that achieved through the air oven method.
Weight of the Submitted Sample
- 100 grams for species that require grinding.
- 50 grams for all other species.
- The sample should be placed in a polythene bag with a thickness of 700 gauge.
Air Oven Method for Seed Moisture Estimation
Materials Required
Grinding Mill
It should be constructed of non-absorbent material. It should grind evenly and should be operated at such a speed that during grinding, it should not cause heating of the ground material. Air currents that might cause loss of moisture must be reduced to a minimum. The fineness of grinding should be adjustable.
Container
Glass or non-corrosive metal (e.g., stainless steel).
Oven
- High-quality electric air oven with thermostatic electronic temperature control to maintain temperature within ±1°C.
- Desiccator, Analytical balance, Sieves. A set of wire mesh sieves with meshes of 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm and 4.0 mm.
Grinding
For some seeds (e.g. Cereals and Cotton) fine grinding is essential before the moisture content is determined. In such cases, at least 50% of the ground material should pass through a wire sieve with meshes of 0.5 mm and not more than 10% remain on a wire sieve with a mesh of 1.0 mm. For leguminous seeds, coarse grinding is recommended; at least 50% of the ground material shall pass through a wire sieve with meshes of 4.0 mm.
Pre-Drying
If the species is one for which grinding is necessary and the moisture content is more than 17%. (or 10% in the case of soy bean and 13% in rice) pre drying before grinding is necessary. For this purpose, two 50 g portions are weighed and placed on open trays at 130°C for 5-10 min. If seed moisture content is about 25% or more it should be pre-dried at 70° C for 2-5 hours, depending on the initial water content. The pre dried seeds should be kept in a closed desiccator for cooling. Then each of the duplicate quantities is weighed separately and about 20 g is ground. The ground material is then subjected to moisture testing using a hot air-oven as described below.
Moisture Estimation
It should be carried out in duplicate on two independently drawn 5-10 g working samples, weighed with an accuracy of 1 mg. Most species are dried for 1 hr at 130° C, cereals for 2 hours (130°C) and maize for 4 hours (130°C). Seeds containing high percentage of oil should be dried at 103°C for 17 hours.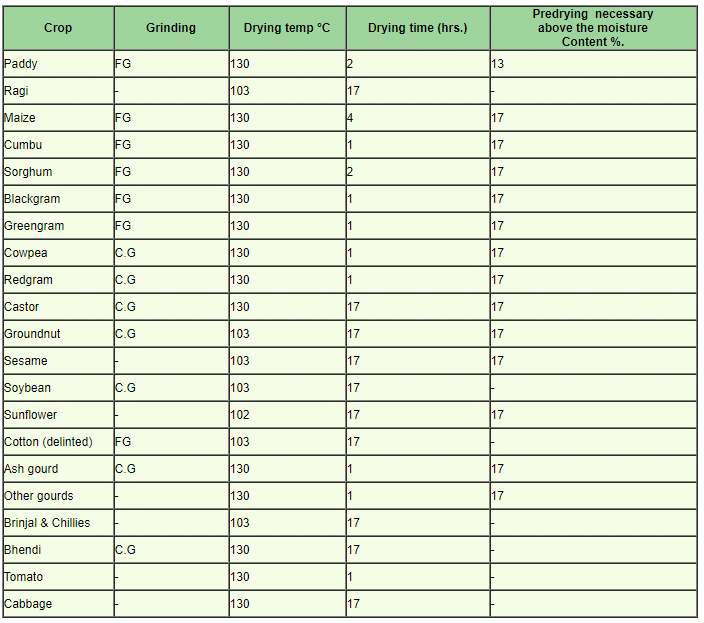
Steps:
- Empty container along with its cover should be weighed
- The submitted sample should be mixed thoroughly and two small portions or seed sample are to be drawn and it should be ground as per the requirements.
- Then fill the container with 5 grams of ground sample and weigh it.
- After weighing, remove the cover or lid of the container and the open container should be kept in the oven which has already been heated to the prescribed drying temperature.
- At the end of the drying period, container should be closed with its cover or lid. The container should be transferred into a Desiccator. The Desiccator should be closed and the sample should be allowed to cool for 30 minutes.
- The sample should be weighed again and the moisture content may be calculated to one decimal place by the following formula.
 Where, m = Seed moisture contentm1 = Weight of the empty container with its cover
Where, m = Seed moisture contentm1 = Weight of the empty container with its cover
m2 = Weight of the container with its cover and seeds before drying
m3 = Weight of the container with its cover and seeds after drying
The duplicate result of the determination may not differ by more than 0.2% otherwise the analysis should be repeated.
If pre dried, the moisture content is calculated from the results obtained in the first (pre-drying) and second stages of the procedure. If S1 is the moisture lost in the first stage and S2 is the moisture lost in the second stage, each calculated as above and expressed as a percentage, the original moisture content of the sample is calculated as below.
m = moisture content
S1 =Moisture percentage lost in predrying stage
S2 = Moisture percentage lost in drying stage
Moisture meters: Universal (OSAW) digital moisture meters
Moisture meters work based on the principle that wet grains are better conductors of electricity, while dry grains are less conductive. Therefore, the moisture content of seeds is directly proportional to their electrical conductivity.
These meters include a compression unit to compress the sample to a predetermined thickness. The thickness setting can be easily read on a vertical and circular scale. The seed material to be tested is placed in a test cup and compressed. Then, a push-type switch is pressed until the reading appears on the display. There is no need for temperature readings and correlated dials. In the computer version of digital moisture meters, temperature corrections are automatically compensated for.
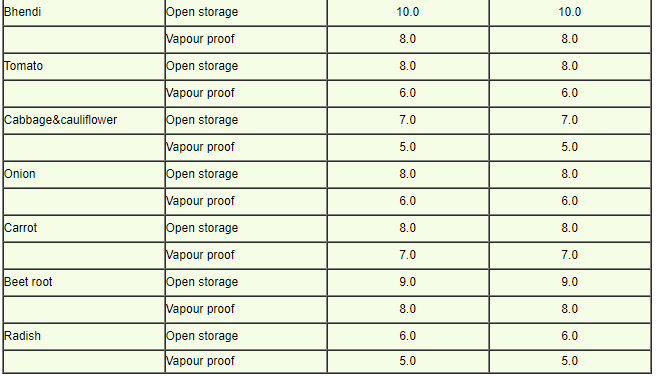
Seed standards for moisture content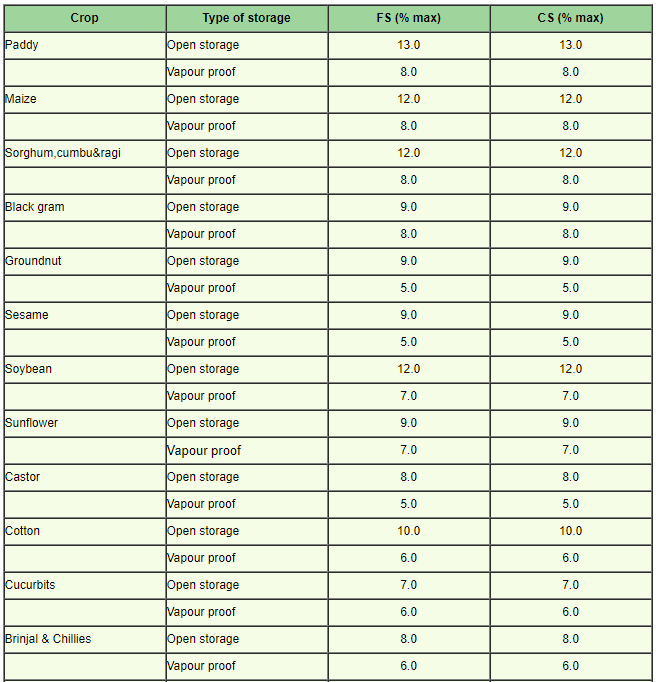
FAQs on Determination of Moisture Content - Agriculture Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is moisture content? |  |
| 2. Why is the determination of moisture content important? |  |
| 3. How is moisture content determined? |  |
| 4. What are the factors that affect moisture content determination? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of moisture content determination? |  |

 Where, m = Seed moisture contentm1 = Weight of the empty container with its cover
Where, m = Seed moisture contentm1 = Weight of the empty container with its cover





















