Diagram Based Questions: How do Organisms Reproduce? | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Q1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
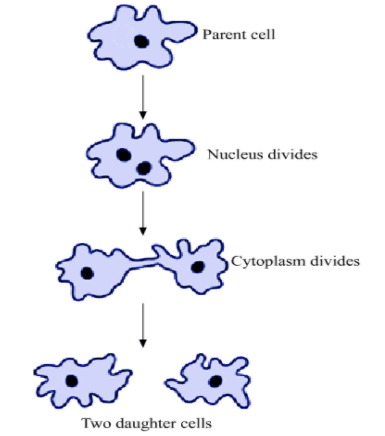 Binary Fission in Amoeba(i) What is binary fission in Amoeba?
Binary Fission in Amoeba(i) What is binary fission in Amoeba?
Ans: Binary fission in Amoeba is a process where a single Amoeba cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It's a form of asexual reproduction.
(ii) Describe the key stages of binary fission in Amoeba.
Ans: In binary fission, the Amoeba goes through several key stages:
- Elongation: The cell stretches to prepare for division.
- Nucleus division: The nucleus splits into two.
- Cell membrane formation: A new membrane forms between the two nuclei.
- Separation: The cell divides into two daughter cells.
(iii) How does binary fission differ from sexual reproduction in Amoeba?
Ans: Binary fission is asexual reproduction, producing genetically identical offspring, while sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two different gametes, leading to genetic variation in offspring.
(iv) What is the significance of binary fission in the life of Amoeba?
Ans: Binary fission is vital for the survival and propagation of Amoeba because it helps in rapid reproduction and population growth under favorable conditions.
(v) Explain how environmental factors can influence the frequency of binary fission in Amoeba.
Ans: Environmental factors such as temperature, food availability, and water quality can affect the frequency of binary fission in Amoeba. Warmer temperatures and ample food resources often lead to more frequent reproduction, while adverse conditions may slow it down or halt it altogether.
Q2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
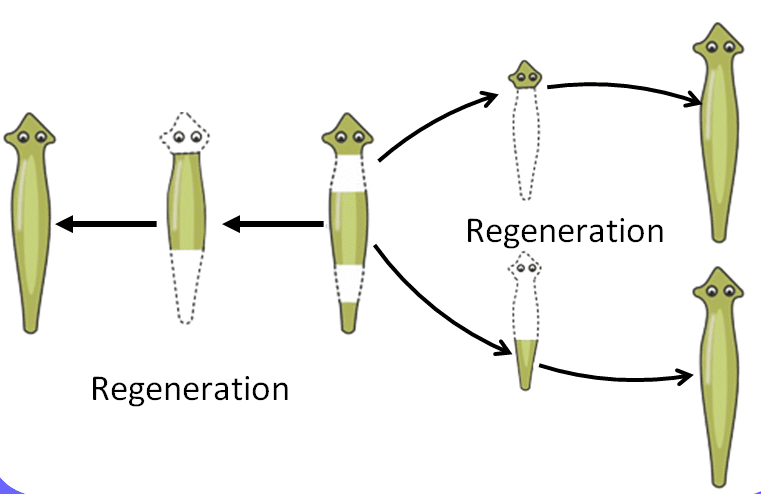
(i) What is the organism shown in the diagram, and why is it important for the study of regeneration?
Ans: The organism in the diagram is a Planaria, a type of flatworm. It is important for the study of regeneration because it has the remarkable ability to regrow lost body parts.
(ii) In the diagram, what body part of the Planaria is being cut or removed for the experiment, and why?
Ans: In the diagram, a portion of the Planaria's body, usually the tail or head, is being cut or removed. This is done to observe the process of regeneration, where the Planaria can regrow the missing body part.
(iii) What do you expect to happen after the Planaria's body part is removed, based on the experiment?
Ans: In the diagram, a portion of the Planaria's body, usually the tail or head, is being cut or removed. This is done to observe the process of regeneration, where the Planaria can regrow the missing body part.After the body part is removed, we expect the Planaria to regenerate or grow back the missing body part over time.
(iv) How does the ability of Planaria to regenerate its body parts relate to the concept of asexual reproduction?
Ans: The ability of Planaria to regenerate its body parts is a form of asexual reproduction. When it regrows a missing body part, it essentially creates a new individual that is genetically identical to the original.
(v) What is the significance of studying regeneration in Planaria for scientific research and potential medical applications?
Ans: Studying regeneration in Planaria can provide insights into the regenerative capabilities of living organisms. This knowledge may have applications in fields such as regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and the development of treatments for injuries and diseases in humans.
Q3: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
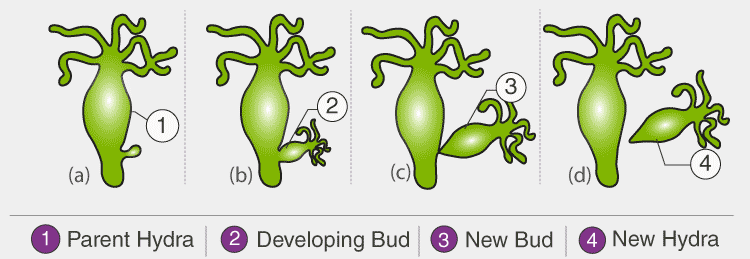
(i) What is budding in Hydra, and how does it differ from other forms of reproduction in animals?
Ans: Budding in Hydra is a form of asexual reproduction where a small outgrowth or bud develops on the body of the parent Hydra and eventually detaches to form a new individual. This is different from sexual reproduction, where offspring are produced by the fusion of gametes (sperm and egg).
(ii) Explain the process of budding in Hydra using a labeled diagram.
Ans: Budding in Hydra starts with the formation of a small bud on the body of the parent Hydra. The bud grows in size and eventually detaches from the parent to become a new Hydra. The process involves the development of tentacles, a mouth, and a foot in the bud.
(iii) What advantages does budding offer to Hydra as a mode of reproduction?
Ans: Budding allows Hydra for rapid reproduction without needing a mate. This facilitates quick colonisation of new environments and ensures species continuity even when mates are scarce.
(iv) Can you name another organism besides Hydra that reproduces through budding?
Ans: Yeast is another organism that reproduces through budding. In yeast, a small bud forms on the parent cell, grows, and eventually separates to become a new yeast cell.
Q4: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
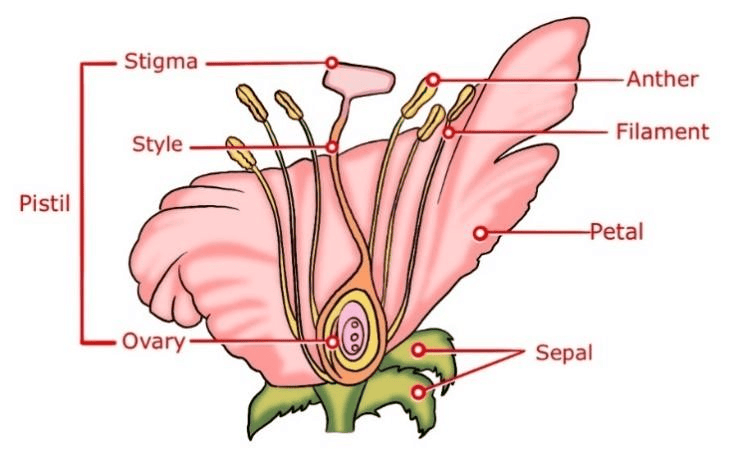 (i) What is the main purpose of a longitudinal section of a flower?
(i) What is the main purpose of a longitudinal section of a flower?
Ans: A longitudinal section of a flower is prepared to study the internal structures of a flower, such as its reproductive parts, to understand how pollination and fertilization occur.
(ii) Name the male and female reproductive parts of a flower seen in the longitudinal section.
Ans: In a typical flower's longitudinal section, the male reproductive part is called the stamen, consisting of anther and filament, while the female reproductive part is called the pistil, which includes the stigma, style, and ovary.
(iii) What is the function of the anther in a flower's reproductive process?
Ans: The anther is the part of the stamen that produces pollen grains. Its function is to release pollen, which contains male gametes, into the environment for the purpose of fertilizing the female reproductive organ (ovule) of another flower.
(iv) Explain why the stigma is an essential part of the pistil in a flower.
Ans: The stigma is a sticky structure at the top of the pistil. Its role is crucial as it captures pollen grains from other flowers. This sticky surface allows pollen grains to adhere to it, facilitating the process of pollination.
(v) What is the ultimate aim of the fertilization process in a flower?
Ans: The main goal of fertilization in a flower is to combine the male and female gametes, resulting in the formation of a fertilized egg (zygote). This fertilized egg eventually develops into a seed within the ovary, ensuring the continuation of the plant's life cycle.
Q5: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
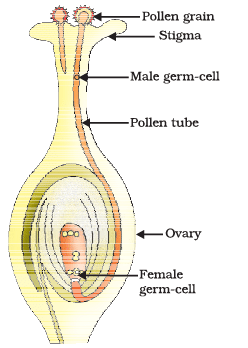
(i) What is the process called when pollen lands on the stigma of a flower?
Ans: The process is called "pollination" when pollen lands on the stigma of a flower.
(ii) What is the main purpose of the pollen grain in the process of germination on the stigma?
Ans: The main purpose of the pollen grain is to deliver male gametes (sperm cells) to the female part of the flower, known as the stigma and facilitate fertilisation by ensuring the male and female gametes meet.
(iii) How does the pollen grain reach the stigma of a flower?
Ans:The pollen grain is carried to the stigma either by the wind (wind pollination) or by pollinators such as insects, birds, or bats (animal pollination).
(iv) What happens to the pollen grain once it lands on the stigma?
Ans: Once the pollen grain lands on the stigma, it germinates. The pollen tube begins to grow down through the style towards the ovule, carrying male gametes to fertilize the egg cell.
(v) Why is germination of pollen on the stigma essential for plant reproduction?
Ans: Germination of pollen on the stigma is essential for plant reproduction because it is the first step in the fertilization process. It allows the male gametes from the pollen grain to reach the female gametes in the ovule, leading to the formation of seeds and the continuation of the plant species.
Q6: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
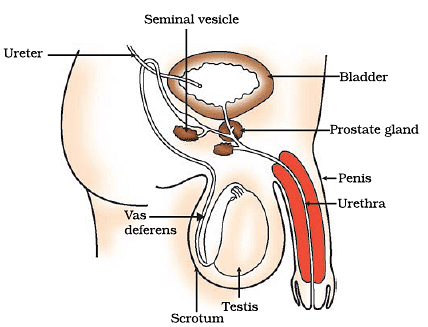
(i) What are the primary organs of the male reproductive system?
Ans: The primary organs of the male reproductive system are the testes, vas deferens, and penis.
(ii) What is the function of the testes in the male reproductive system?
Ans: The testes are responsible for producing sperm cells and secreting the male sex hormone, testosterone.
(iii) How does sperm move from the testes to the urethra?
Ans: Sperm move from the testes to the urethra through a tube called the vas deferens, which connects the testes to the urethra.
(iv) Why are the testes located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum?
Ans: The testes are located in the scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature.
(v) What is the function of the penis in the male reproductive system?
Ans: The penis is the external organ that delivers sperm into the female reproductive system during sexual intercourse.
Q7: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
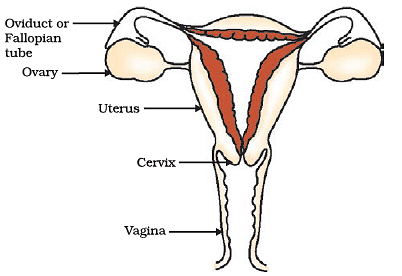
(i) What are the main organs of the female reproductive system, and what are their functions?
Ans: The main organs of the female reproductive system are the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
- Ovaries: Produce eggs and hormones.
- Fallopian Tubes: Transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
- Uterus: Nurtures a developing embryo.
- Cervix: Connects the uterus to the vagina.
- Vagina: The passage through which sperm enters.
(ii) What is menstruation, and what is its significance in the female reproductive system?
Ans: Menstruation is the monthly shedding of the uterine lining. It is significant because it prepares the uterus for potential pregnancy and is a crucial part of the female reproductive cycle.
(iii) Where is the embryo implanted during pregnancy?
Ans: The embryo is implanted in the lining of the uterus, where it continues to grow and develop.
(iv) What is fertilization, and where does it usually occur in the female reproductive system?
Ans: Fertilization is the fusion of a sperm cell and an egg cell, resulting in the formation of a zygote. It typically occurs in the fallopian tubes, shortly after ovulation.
(v) How does the embryo receive nutrition from the mother's blood?
Ans: The embryo gets nutrition from the mother's blood through a special tissue called the placenta, embedded in the uterine wall.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Diagram Based Questions: How do Organisms Reproduce? - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the two main types of reproduction in organisms? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of asexual reproduction? |  |
| 3. How does sexual reproduction contribute to genetic diversity? |  |
| 4. What role do gametes play in sexual reproduction? |  |
| 5. Why is it important for organisms to reproduce? |  |

















