Disaster Management: Volcanoes | UPSC Mains: Internal Security & Disaster Management PDF Download
A volcano is an opening in the earth’s crust through which gases, molten rocks materials (lava), ash, steam etc. are emitted outward in the course of an eruption. Such vents or openings occur in those parts of the earth’s crust where the rock strata are relatively weak. Volcanic activity is an example of endogenic process. Depending upon the explosive nature of the volcano, different land forms can be formed such as a plateau (if the volcano is not explosive) or a mountain (if the volcano is explosive in nature).
Magma vs Lava: The difference
- Magma is the term used to denote the molten rocks and related materials seen inside earth. A weaker zone of the mantle called asthenosphere, usually is the source of magma.
- Once this magma came out to the earth surface through the vent of a volcano, it is called as the Lava. Therefore, Lava is nothing but the magma on earth surface.
- The process by which solid, liquid and gaseous material escape from the earth’s interior to the surface of the earth is called as Volcanism.
Types of Volcanoes
Volcanoes are classified on the basis of nature of eruption and the form developed at the surface.
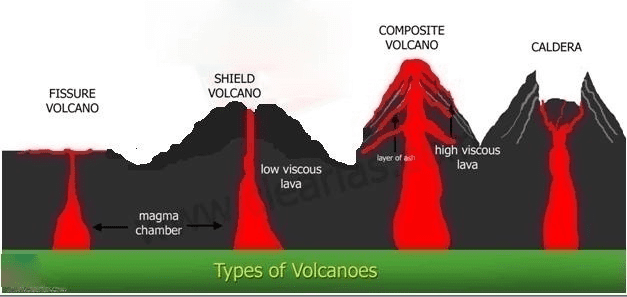
Shield Volcanoes
- How to identify: They are not very steep but are far and wider. They extend to great height as well as distance.
- They are the largest of all volcanoes in the world as the lava flows to a far distance. The Hawaiian volcanoes are the most famous examples.
- Shield volcanoes have low slopes and consist almost entirely of frozen lavas.
- If you were to fly over top of a shield volcano, it would resemble a warrior’s shield, hence the name.
- These volcanoes are mostly made up of basalt (less viscous), a type of lava that is very fluid when erupted. For this reason, these volcanoes are not steep.
- They are of low explosive in general, but if somehow water gets into the vent they may turn explosive.
- The upcoming lava moves in the form of a fountain and throws out the cone at the top of the vent and develops into cinder cone
Cinder Cone Volcanoes:
- Cinders are extrusive igneous rocks. A more modern name for cinder is Scoria.
- Small volcanoes.
- These volcanoes consist almost entirely of loose, grainy cinders and almost no lava.
- They have very steep sides and usually have a small crater on top.
Composite Volcanoes:
- Shape: Cone shaped with moderately steep sides and sometimes have small craters in their summits.
- Volcanologists call these “strato-” or composite volcanoes because they consist of layers of solid lava flows mixed with layers of sand- or gravel-like volcanic rock called cinders or volcanic ash.
- They are characterized by the eruption of a cooler and more viscous lavas than basalt.
- These volcanoes often result in explosive eruptions.
- Along with lava, large quantities of pyroclastic materials and ashes find their way to the ground.
- This material accumulates in the vicinity of the vent openings and leading to the formation of layers, and this makes the mount appears as composite volcanoes.
Caldera:
- These are the most explosive of the earth’s volcanoes.
- They are usually so explosive that when they erupt they tend to collapse on themselves rather than building any tall structure. The collapsed depressions are called calderas.
- Their explosiveness indicates that its magma chamber is large and in close vicinity.
- A caldera differs from a crater in such a way that a caldera is a huge depression caused by a collapse after a large-scale eruption, whereas a crater is a small, steep side, volcanic depression bored out by an eruptive plume.
Flood Basalt Provinces
- These volcanoes outpour highly fluid lava that flows for long distances.
- The Deccan Traps from India, presently covering most of the Maharashtra plateau, are a much larger flood basalt province.
Mid-Ocean Ridge Volcanoes
- These volcanoes occur in the oceanic areas.
- There is a system of mid-ocean ridges more than 70,000 km long that stretches through all the ocean basins.
- The central portion of this ridge experiences frequent eruptions.
- Volcanoes can also be classified based on the frequency of eruption, mode of eruption and characteristic of lava.
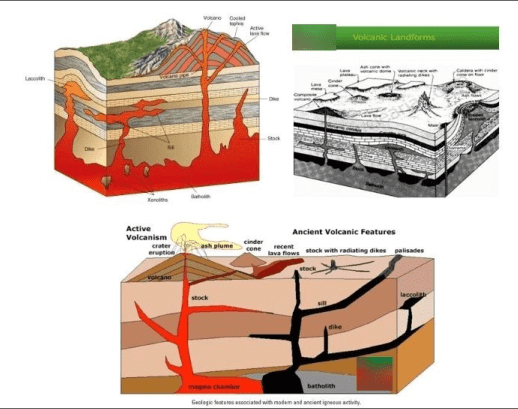
Volcanic Landforms:
The lava that is released during volcanic eruptions on cooling develops into igneous rocks.
The cooling may take place either on reaching the surface or from the inside itself.
Depending on the location of the cooling of lava, igneous rocks are classified as:
Volcanic Igneous rocks (Extrusive igneous rocks):
Cooling of the rock occurs at the surface of the earth. E.g. Basalt, Andesite etc.
Plutonic Igneous rocks (Intrusive igneous rocks):
Cooling takes place in the crust and not over the surface. E.g. Granite, Gabbro, Diorite etc. Intrusive igneous rocks are classed into the following types according to their forms.
- Batholiths: A large body of magmatic material that cools in the deeper depth in the form of a large dome. These are granitic bodies. They sometimes appear on the earth surface when the denudation processes remove the overlying materials.
- Laccoliths: Large dome shaped intrusive bodies with a level base and pipe-like conduit from below. Resembles a composite volcano structure, but beneath the earth. (Eg: Karnataka Plateau)
- Lapoliths: They are saucer shaped, concave to the sky.
- Phacoliths: Wavy materials which have a definite conduit to source beneath.
- Sheets/ sills: They are the near horizontal bodies of intrusive igneous rocks. Thinner ones are called as sheets and while thick horizontal deposits are called sills.
- Dykes: When the lava comes out through cracks and fissures, they solidify almost perpendicular to the ground to form wall like structures called dykes. (Eg: Deccan traps in Maharastra region).
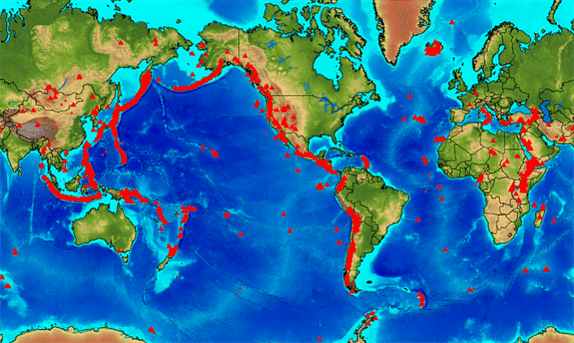
Distribution of Volcanoes:
Most of the volcanoes in the world are found in three well defined belts:
- The Circum-Pacific Belt (The Pacific Ring of Fire).
- The Mid-World Mountain Belt.
- The African Rift Valley Belt.
Volcanic Activity – Points to note down:
- Volcanoes are closely related to the regions of intense folding and faulting.
- They occur along coastal mountain ranges, on islands and in the mid oceans.
- Interior parts of the continent are generally free from their activity.
- Most of the active volcanoes are found in the pacific region which is thus called as the Pacific Ring of Fire.
|
63 videos|114 docs|22 tests
|





















