Ecosystem: Introduction & Types | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Global Ecosystem |

|
| Natural Ecosystems |

|
| (i) Terrestrial Ecosystems |

|
| (ii) Aquatic Ecosystems |

|
| Artificial Ecosystem |

|
An ecosystem can be understood as a functional unit of nature where living organisms, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, interact with each other and with the physical environment in which they exist. It's like a community of organisms and their surrounding environment working together as a cohesive system.

Definition: Total living factor (biotic) and total non living factor (abiotic) of the environment present in a particular area is called ecosystem.
Note:
- The boundaries of ecosystem are indistinct and have a overlapping character over each other.
- Ecosystem is the smallest structural and functional unit of nature or environment. It is a self regulatory and self sustaining unit.
- Ecosystem may be large or small. Single drop of water may be an ecosystem.
- Ecosystem may be temporary or permanent.
Example of Ecosystem:
Let us consider an example of puddle which can be shown in the figure below. In it, we can find several living things (such as frog, tadpole, flies, fish and snail) and non – living things (such as sun, water, temperature, weather, humidity, etc.)
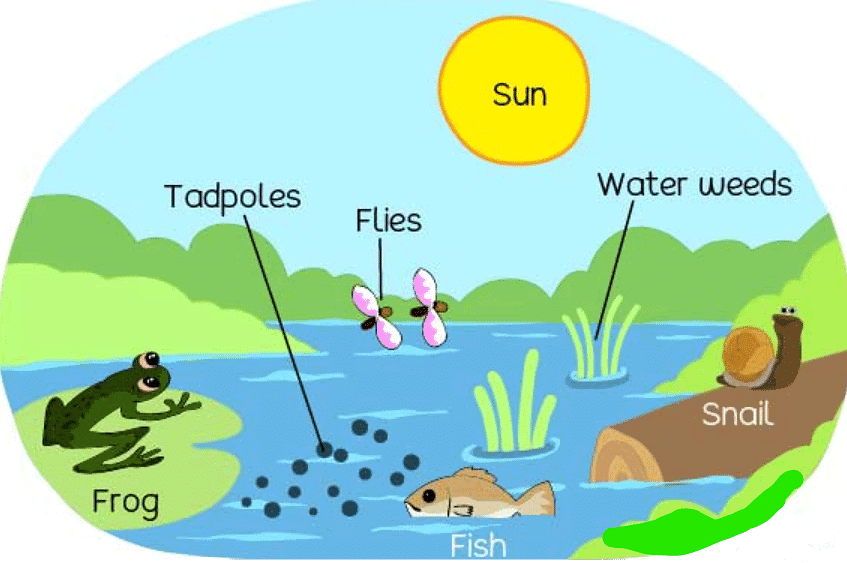
Global Ecosystem
Ecosystems can vary greatly in size, ranging from small ponds to vast forests or expansive seas. In fact, some ecologists even consider the entire biosphere, which encompasses all the ecosystems on Earth, as a global ecosystem. However, studying the entire biosphere as one unit is impractical due to its immense size and complexity.
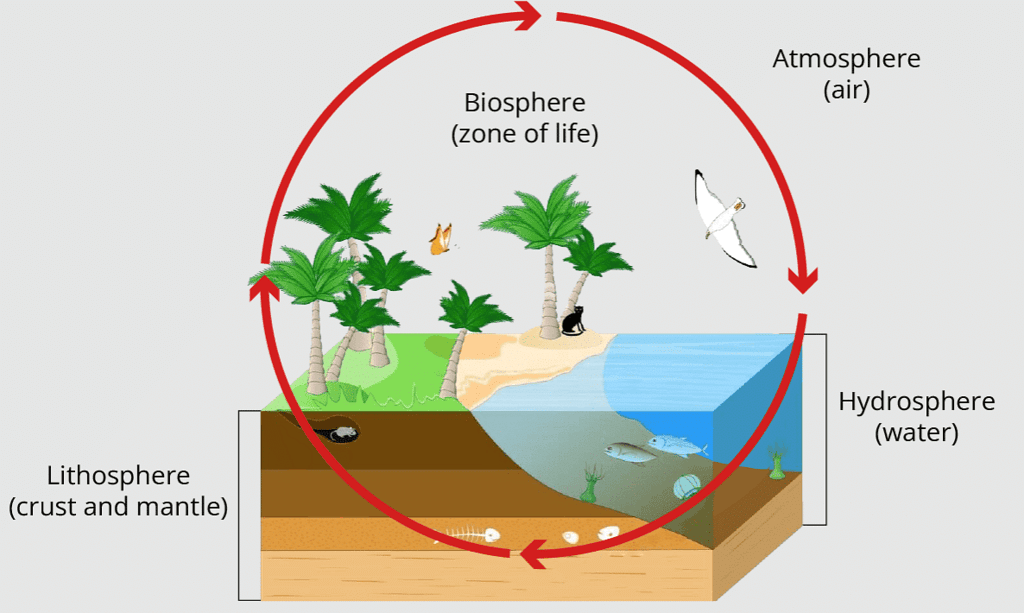 Global Ecosystem: Biosphere
Global Ecosystem: Biosphere
Therefore, ecologists often divide the biosphere into two main categories: terrestrial ecosystems and aquatic ecosystems which comes under Natural Ecosystem.
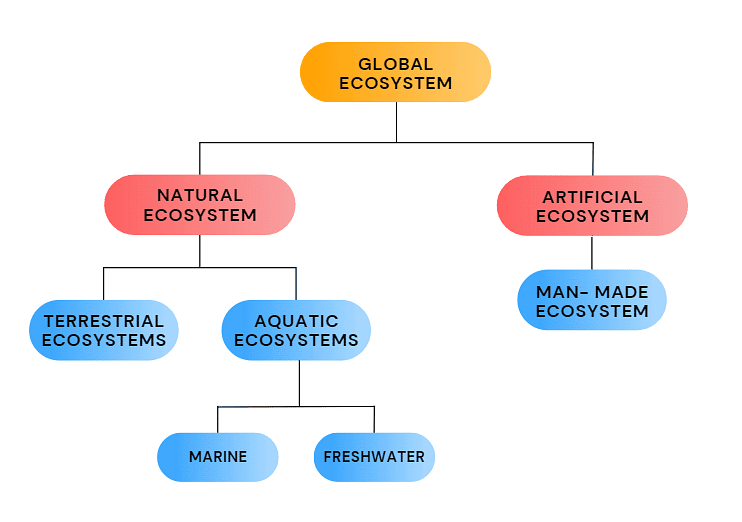
Natural Ecosystems
(i) Terrestrial Ecosystems
- Terrestrial ecosystems refer to those found on land. Examples of terrestrial ecosystems include forests, grasslands, and deserts.

- These ecosystems are characterized by the presence of diverse plant and animal species that have adapted to survive in specific climatic and environmental conditions.
- Forests are home to a variety of trees, shrubs, and animals, while grasslands are dominated by grasses and support grazing animals.
- Deserts, on the other hand, are arid regions with sparse vegetation and specialized animals and plants adapted to survive in water-scarce conditions.
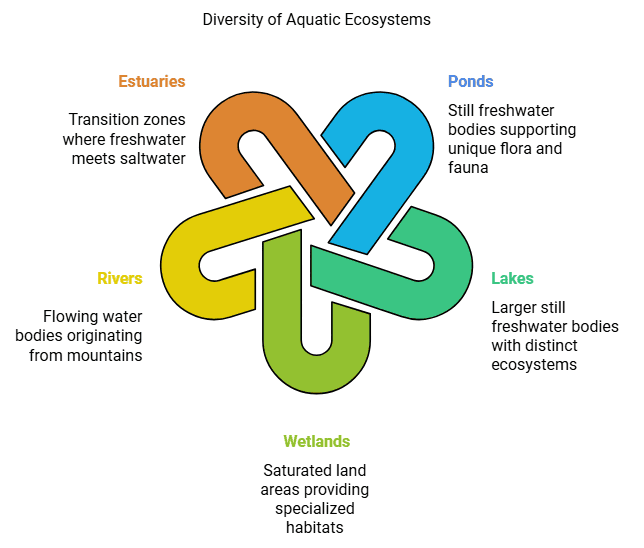
(ii) Aquatic Ecosystems
- Aquatic ecosystems, as the name suggests, are found in water bodies.
- They encompass various types of ecosystems such as ponds, lakes, wetlands, rivers, and estuaries.
- Each of these aquatic ecosystems has unique characteristics and supports a specific set of plant and animal life.
- Ponds and lakes are still bodies of freshwater, while rivers are flowing water bodies that often originate from mountains and flow towards seas or oceans.
- Wetlands are areas where the land is saturated with water, creating specific habitats for specialized species.
- Estuaries are unique ecosystems where freshwater and saltwater mix, creating a transition zone between rivers and oceans.
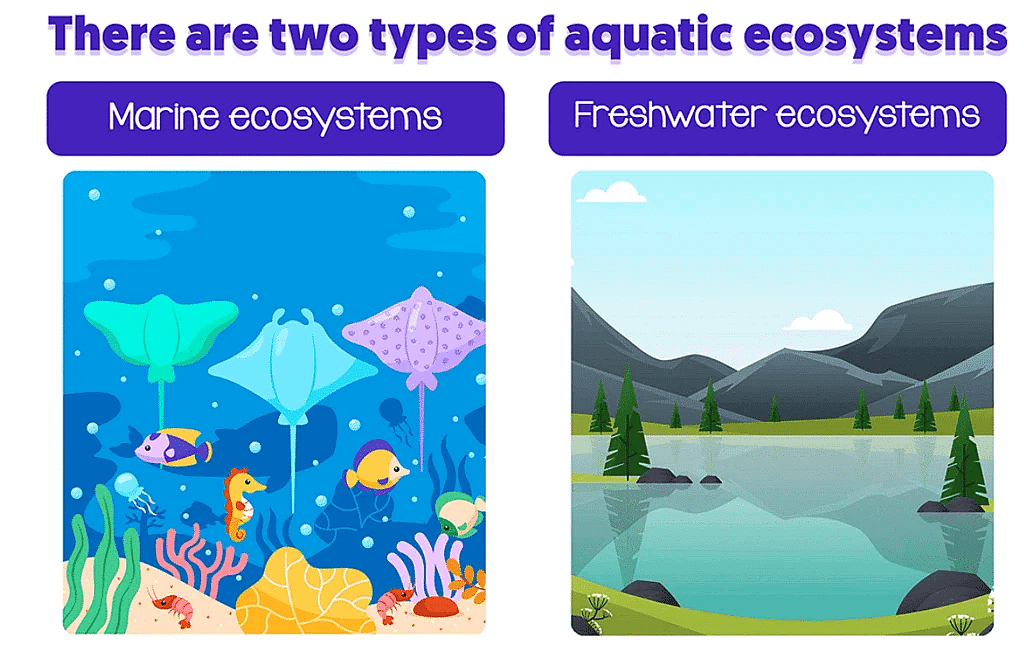
(a) The Marine Ecosystem: It is the biggest ecosystem that covers around 71% of the surface of earth. Water in marine ecosystem is salty and has high amount of minerals. Several divisions of marine ecosystem are coral reefs, oceanic, salt marshes, estuaries and hydrothermal vents.
(b) The Freshwater ecosystem: In contrast with the marine ecosystem, the freshwater ecosystem is just 0.8% of the earth surface. Three basic kinds of freshwater ecosystem are wetlands, lentic and lotic. This ecosystem comprises of amphibians, reptiles and 41% of the fish species of the world.
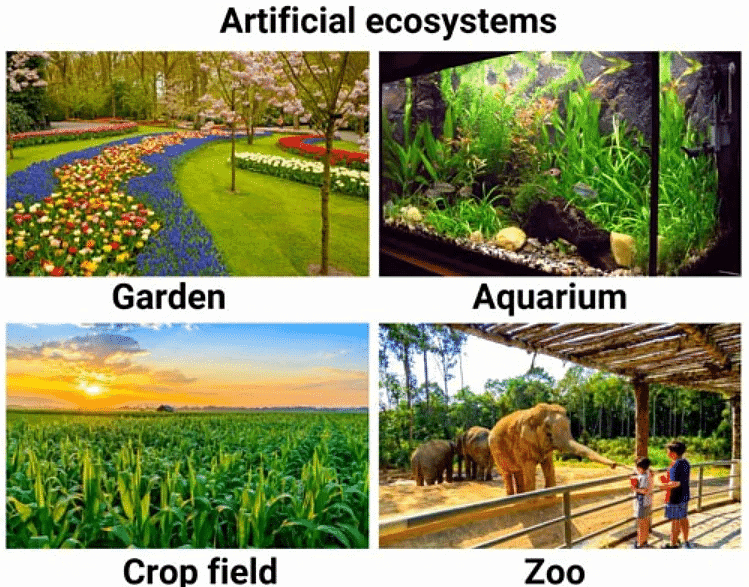
Artificial Ecosystem
In addition to natural ecosystems, man-made ecosystems also exist. For example, crop fields created for agricultural purposes can be considered man-made ecosystems. They are designed and managed to support the growth of specific crops. Similarly, an aquarium with its carefully balanced water chemistry and chosen fish species can also be seen as a man-made ecosystem.
By understanding the different types of ecosystems, their components, and the interactions between organisms and their environment, ecologists gain valuable insights into the intricate workings of nature. The study of ecosystems helps us appreciate the interdependence of living organisms and their role in maintaining the balance and sustainability of our planet.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Ecosystem: Introduction & Types - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the main types of natural ecosystems? |  |
| 2. How do terrestrial ecosystems differ from aquatic ecosystems? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of artificial ecosystems? |  |
| 4. Why are ecosystems important for the environment? |  |
| 5. What roles do producers, consumers, and decomposers play in an ecosystem? |  |





















