Environment and Ecology - 1 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
Rhisotope Project?
Why in News?
Recently, scientists in South Africa have initiated the Rhisotope Project, which involves injecting radioactive material into rhinoceros horns as a measure to combat poaching.
Key Takeaways
- The Rhisotope Project was launched in 2021 in South Africa.
- The primary goal is to make rhino horns easily detectable at border posts and to render them ineffective for human use.
Additional Details
- Radioactive Chips: The project includes the insertion of two tiny radioactive chips into the horns of 20 rhinos. This low-dose radioactive material is designed to be detected by radiation sensors at international borders without causing harm to the animals or the environment.
- The radioactive material is expected to last for five years on the horn, offering a cost-effective alternative to dehorning, which typically occurs every 18 months.
- In addition, the project team has sprayed 11,000 microdots on each treated horn for enhanced identification.
- Follow-up blood samples will be collected to ensure the protection of the rhinoceroses.
- South Africa, which is home to the majority of the world's rhinos, is facing a poaching crisis driven by high demand in Asia, where rhino horns are utilized in traditional medicine.
The Rhisotope Project represents a significant step in wildlife conservation efforts aimed at reducing poaching and preserving rhinoceros populations.
What is Radioactivity?
Radioactivity is the physical phenomenon where certain elements, such as uranium, emit energy in the form of radiation due to the decay of an unstable nucleus.
Great Nicobar Project
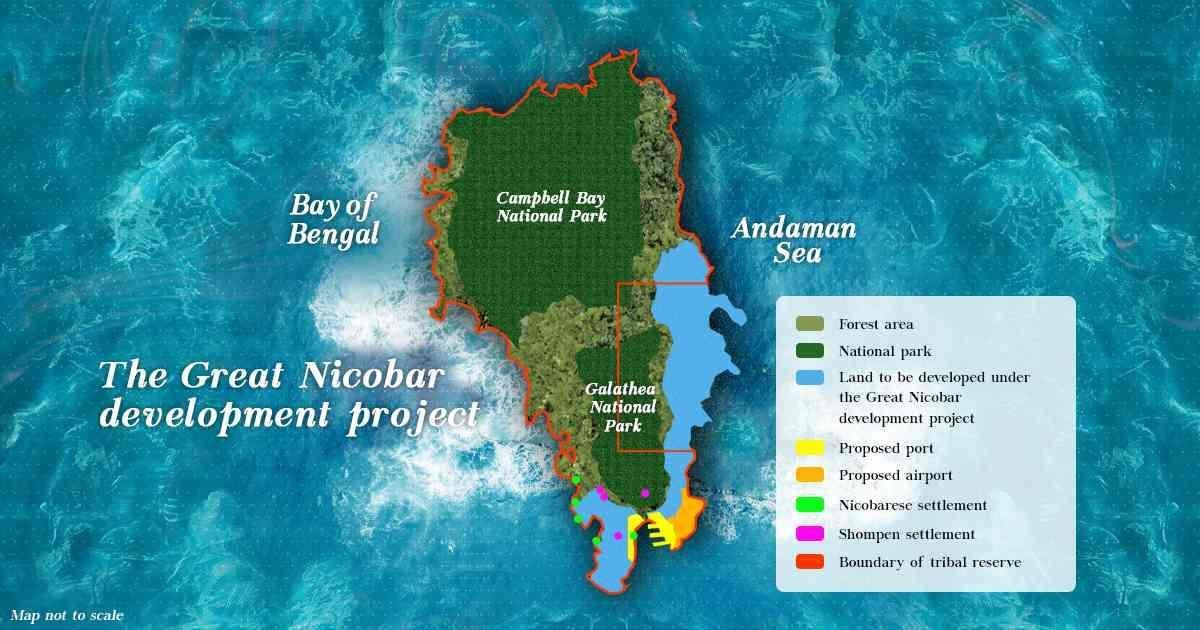 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Great Nicobar Project has recently gained attention as the Ministry of Environment confirmed that the initiative will not displace or disturb indigenous tribes, following consultations with tribal councils.
Key Takeaways
- The project aims for holistic development of Great Nicobar Island, enhancing India's strategic presence in the region.
- It focuses on countering expansionist activities by neighboring countries, particularly China, while safeguarding India's maritime interests.
Additional Details
- Strategic Importance: The project is intended to curb illegal activities, such as poaching by Myanmarese fishers, and is a response to regional security concerns.
- Infrastructure Development: Valued at ₹72,000 crore, the project includes the construction of an international container trans-shipment terminal, a greenfield international airport with dual military-civilian functions, township development, and a 450 MVA power plant combining gas and solar energy.
- Geographical Context: Great Nicobar Island, located at the southernmost tip of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, features tropical wet evergreen forests and is home to significant biodiversity, including endangered species like the leatherback sea turtle.
- Impact on Indigenous Tribes: The island is inhabited by the Shompen and Nicobarese tribes, with approximately 237 Shompen and 1,094 Nicobarese living in a reserve that may see 84 sq km denotified for the project.
- Environmental Considerations: The project will involve the diversion of about 13,075 hectares of forest land and is located in a seismically active region, adhering to the National Building Code for constructing earthquake-resistant structures.
The Great Nicobar Project represents a significant effort towards development while aiming to balance ecological preservation and indigenous rights. Its success will depend on effective implementation and ongoing dialogue with local communities.
E-flow Monitoring System
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Jal Shakti Ministry has launched an innovative Environmental Flows (E-flows) system to enable real-time monitoring of river water quality. This initiative aims to assist in the planning and oversight of projects related to river ecosystems, enhancing the management of water resources and environmental flows in major Indian rivers, particularly the Ganga and Yamuna.
Key Takeaways
- The E-flow Monitoring System was developed by the National Mission for Clean Ganga, under the Jal Shakti Ministry.
- This system responds to a 2018 mandate to maintain minimum e-flows in various stretches of the Ganga throughout the year.
- It addresses concerns from environmental groups regarding the adverse effects of dams on river ecology and flow.
Additional Details
- Real-Time Monitoring: The system facilitates continuous analysis of water quality in the Ganga, Yamuna, and their tributaries.
- Centralised Oversight: It enables monitoring of activities under the Namami Gange programme, focusing on the effectiveness of Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs).
- Comprehensive Data Analysis: Utilizes quarterly reports from the Central Water Commission to track inflow, outflow, and mandated E-flows across 11 projects along the Ganga Mainstream.
What is the Namami Gange Programme?
The Namami Gange Programme is an Integrated Conservation Mission, recognized as a 'Flagship Programme' by the Union Government in June 2014 aimed at effectively abating pollution and conserving the National River Ganga.
- Main Pillars:
- Sewerage Treatment Infrastructure
- River-Front Development
- River-Surface Cleaning
- Biodiversity Conservation
- Afforestation
- Industrial Effluent Monitoring
- Ganga Gram
- Public Awareness
- Despite its ambitious goals and significant funding, the Namami Gange Programme is falling short of its targets.
Challenges Faced by the Namami Gange Programme
- Delays in Project Execution: Many sewage treatment projects are delayed due to land acquisition issues and the need for revisions in Detailed Project Reports (DPRs).
- Funding and Budget Allocation: Although projects worth Rs 37,396 crore have been approved, only Rs 14,745 crore has been released, affecting timely project completion.
- Insufficient Sewage Treatment Capacity: The programme has installed treatment plants that can treat only about 20% of sewage generated in the five major states along the Ganga.
- Persistence of Industrial Pollution: Many industries continue to discharge untreated effluents into the Ganga, contributing to its pollution.
Measures to Enhance Conservation and Rejuvenation of Ganga River
- Leverage Technology for Monitoring: Employ advanced technologies such as remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for effective monitoring and data management.
- Adopt-a-Ghat Initiative: Partner with NGOs and local communities to foster responsibility for specific ghats, enhancing community involvement in river conservation.
- Riverine Economy Incentives: Create a certification for businesses promoting sustainable practices to minimize pollution and encourage responsible water usage.
- Floodplain Restoration: Identify and implement floodplain restoration projects to improve water filtration and provide habitat for aquatic life.
- Waste-to-Wealth Handicrafts: Support local self-help groups in creating eco-friendly handicrafts from waste, promoting sustainable practices and generating income.
In conclusion, maintaining environmental flows is crucial for the health of river ecosystems. The E-flow monitoring system plays a vital role in rejuvenating and conserving the Ganga River by providing essential data and oversight necessary for effective management and conservation efforts.
Environmental Performance Index Ranking 2024
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, Oman achieved a remarkable milestone by ranking second in the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) 2024 among GCC nations and within the Middle East. This ranking underscores Oman's commitment to enhancing its environmental standards.
Key Takeaways
- Oman secured a score of 51.9 out of 100, placing it 50th globally, a significant improvement from its 149th rank in 2022.
- The establishment of new natural reserves has increased Oman's biodiversity sites to over 25, boosting its environmental performance.
Additional Details
- What is the Environmental Performance Index (EPI)?: The EPI is a global ranking system assessing the environmental health of countries. It was introduced by the World Economic Forum in 2002 and is updated biennially.
- Published by: The EPI is prepared by the Yale Center for Environmental Law and Policy in collaboration with the Columbia University Center for International Earth Science Information Network.
- Significance: The EPI helps identify key drivers of environmental performance, such as financial resources, governance, and regulatory quality, promoting sustainable development.
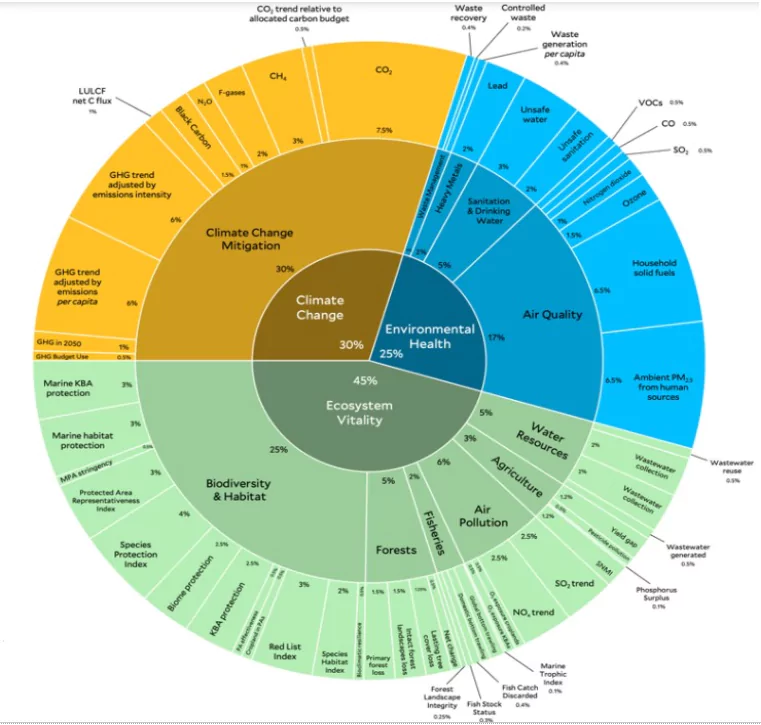
- Framework: The EPI framework organizes 58 indicators into 11 issue categories and three policy objectives, with weights indicating their contribution to the total score.
- New Metrics: The 2024 EPI introduces metrics for assessing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and habitat protection, aligning with global biodiversity goals.
Oman's impressive performance in the Environmental Performance Index illustrates its dedication to environmental sustainability. By continuing to establish protected areas and enhance biodiversity, Oman is setting a strong example for environmental stewardship.
Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) 2024
 Why in News?
Why in News?
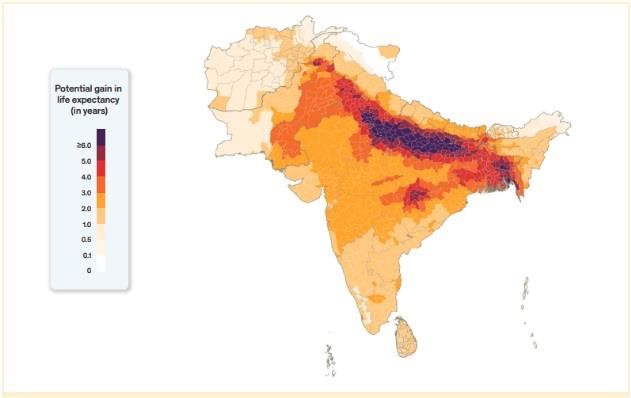
Recently, the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago (EPIC) released the Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) 2024, highlighting significant concerns regarding air quality and its impact on life expectancy, particularly in India where over 40% of the population breathes air exceeding the annual PM2.5 standard of 40 µg/m³.
Key Takeaways
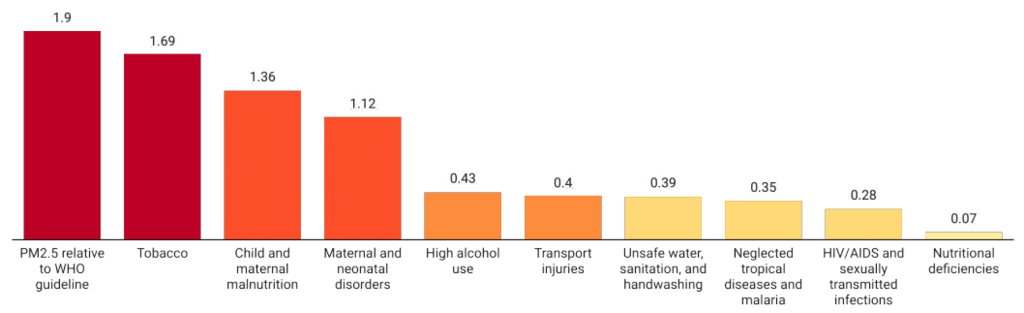
- The AQLI report indicates that reducing PM2.5 pollution to meet the World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines could extend average life expectancy by 1.9 years, adding a total of 14.9 billion life years globally.
- Air pollution's impact on health is more severe than that of chronic diseases such as smoking and heavy drinking.
- Pollution is distributed unevenly, with those in the most polluted areas experiencing air quality six times worse than those in cleaner regions, leading to a life expectancy reduction of 2.7 years.
- Compliance with air quality standards is a challenge, with 94 countries having established PM2.5 standards, yet 37 do not meet them.
- If all countries meet WHO pollution standards, an average person could gain 1.2 years of life expectancy.
Additional Details
- Impact of Air Pollution: The report asserts that reducing PM2.5 levels to the WHO's recommended maximum of 5 µg/m³ could significantly improve life expectancy.
- Global Scenario: Countries like the United States, China, and those in Europe have implemented policies that led to considerable pollution reductions, translating into extended life spans for their populations.
- Regional Challenges: South and Southeast Asia, despite improvements, still suffer from high pollution levels, contributing to 45% of global life years lost due to pollution.
- Specific Findings for India: In Delhi, cleaner air could increase life expectancy by 7.8 years if PM2.5 levels are reduced to 5 µg/m³.
In conclusion, air pollution remains a critical public health challenge in India, demanding stronger policies and enforcement to ensure cleaner air. Meeting WHO guidelines could lead to significant enhancements in life expectancy and overall public health.
Drishti Mains Question:
Air pollution is a significant public health challenge in India, impacting life expectancy and quality of life. Suggest additional strategies to achieve sustainable air quality improvement.
Horseshoe Crabs
 Why in News?
Why in News?
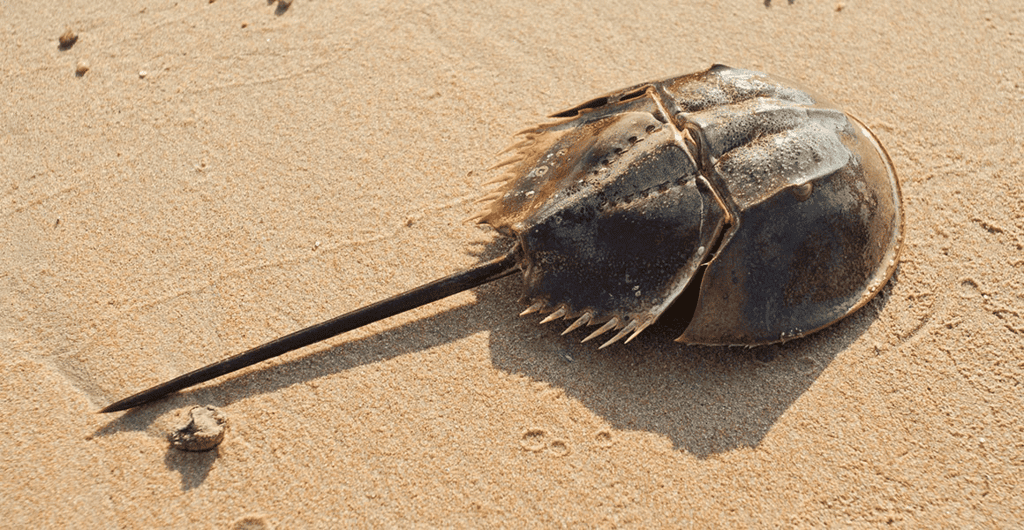
Recently, the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) and the Odisha Forest Department have initiated efforts to tag and conserve the ancient species of horseshoe crabs. The ZSI plans to tag hundreds of these crabs to assess their population patterns and identify the threats they face.

Key Takeaways
- Horseshoe crabs are ancient marine and brackish water arthropods.
- They are often referred to as 'living fossils' due to their long evolutionary history.
Additional Details
- About Horseshoe Crabs: These creatures belong to the family Limulidae and are the only living members of the order Xiphosura. They have been around for approximately 250 million years.
- Species and Location:There are four existing species of horseshoe crabs. India is home to two species:
- Tachypleus gigas: Found in Odisha and West Bengal.
- Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda: Located in the Sundarbans mangroves of West Bengal.
- Threats: Horseshoe crabs face dangers from destructive fishing practices and illegal smuggling.
- Conservation Status: Under the Wildlife Protection Act (WPA) of 1972, Indian species are protected under Schedule II. The IUCN categorizes the American horseshoe crab as Vulnerable and the Tri-spine horseshoe crab as Endangered, while the other two species are not currently listed.
- Medicinal Uses: The carapace of horseshoe crabs is used for treating scars. Their blue blood contains immune cells that are highly sensitive to toxic bacteria, which have led to the development of the Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) test for ensuring the safety of vaccines.
- International Horseshoe Crab Day: Celebrated on June 20 each year, this day highlights global conservation efforts for horseshoe crabs.
The conservation efforts for horseshoe crabs are crucial not only for maintaining biodiversity but also for their significant role in medical science and ecological systems.
Registration of Exotic Animals - PARIVESH 2.0 Portal
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has mandated the registration of exotic pets listed under Schedule IV of the Wildlife Act with state wildlife departments via the PARIVESH 2.0 portal within a timeframe of 6 months.
Key Takeaways
- The registration requirement applies to exotic species as defined under the Wildlife Act.
- Delhi's forest and wildlife department has registered eight exotic species so far.
- The registration is part of the Living Animal Species (Reporting and Registration) Rules, 2024.
Additional Details
- Exotic Species: These refer to animals or plants that are moved from their natural habitat to a new location, often due to human activities.
- Status of Registration:The registered species include:
- Ball Python
- Iguana
- Cockatiel
- Red-eared Slider Turtle
- African Grey Parrot
- Amazonian Parrot
- Blue-headed Parrot
- Conure
- Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act, 2022: Introduces Section 49 M, mandating the registration of the possession, transfer, birth, and death of species listed in the Appendices and Schedule IV of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Concerns with Exotic Species:
- Non-regulation: Many exotic species are imported and bred in India without proper registration, posing risks, including zoonotic diseases.
- Pandemic Risk: The recent pandemic highlighted the dangers associated with the unregulated trade and ownership of exotic animals.
- Smuggling Concerns: Activists have raised alarms over the increasing smuggling of endangered exotic animals into India, especially from Southeast Asia. Significant seizures have been reported in Assam and Mizoram, involving animals like Kangaroos, Koalas, and Lemurs.
- PARIVESH 2.0 Portal: A web-based workflow application developed by MoEFCC for the online submission and monitoring of proposals related to environmental, forest, wildlife, and coastal regulation zone clearances.
In summary, the PARIVESH 2.0 portal is a crucial step towards regulating the possession of exotic species in India, ensuring better management and compliance with wildlife protection laws.
Critical Threats Facing the Aravallis

Why in News?
A recent scientific study on land use dynamics in the Aravallis has brought to light the severe challenges that the region faces, including significant biodiversity loss, soil degradation, and a reduction in vegetation cover.
Key Takeaways
- Loss of Hills: From 1975 to 2019, nearly 8% (5,772.7 sq km) of the Aravali hills have disappeared, with 5% (3,676 sq km) converted into barren land and 1% (776.8 sq km) into settlements.
- Increase in Mining Area: Mining activity has risen from 1.8% in 1975 to 2.2% in 2019, contributing to air pollution and environmental degradation.
- Increase in Human Settlements: The area occupied by human settlements increased from 4.5% in 1975 to 13.3% in 2019.
- Decline in Forest Cover: Forest cover in the central range decreased by 32% between 1975 and 2019, with an average annual deforestation rate of 0.57%.
- Impact on Water Bodies: Water bodies have declined since 1989, with illegal mining damaging aquifers and disrupting natural water flow.
Additional Details
- Impact of Protected Areas: Wildlife sanctuaries like Todgarh-Raoli and Kumbhalgarh have positively influenced the eco-sensitive zone, helping to minimize forest depletion.
- Future Projections: By 2059, projections indicate a total loss of 22% (16,360 sq km) of the Aravali area, with 3.5% (2,628.6 sq km) expected to be used for mining.
- Flora and Fauna Decline: Significant declines in species such as leopards and striped hyenas have been reported, alongside the extinction of rivers originating in the Aravallis.
In summary, the Aravalli Range is facing critical threats due to illegal mining, urbanization, and environmental degradation. Immediate and effective actions are required to prevent further loss and restore the ecological balance. Enforcing existing legal measures and implementing large-scale restoration projects can help mitigate these challenges and protect this vital ecological region.
|
38 videos|5264 docs|1112 tests
|
















