Environment and Ecology: September 2024 UPSC Current Affairs | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
India as the World Largest Plastic Polluter
Why in news?
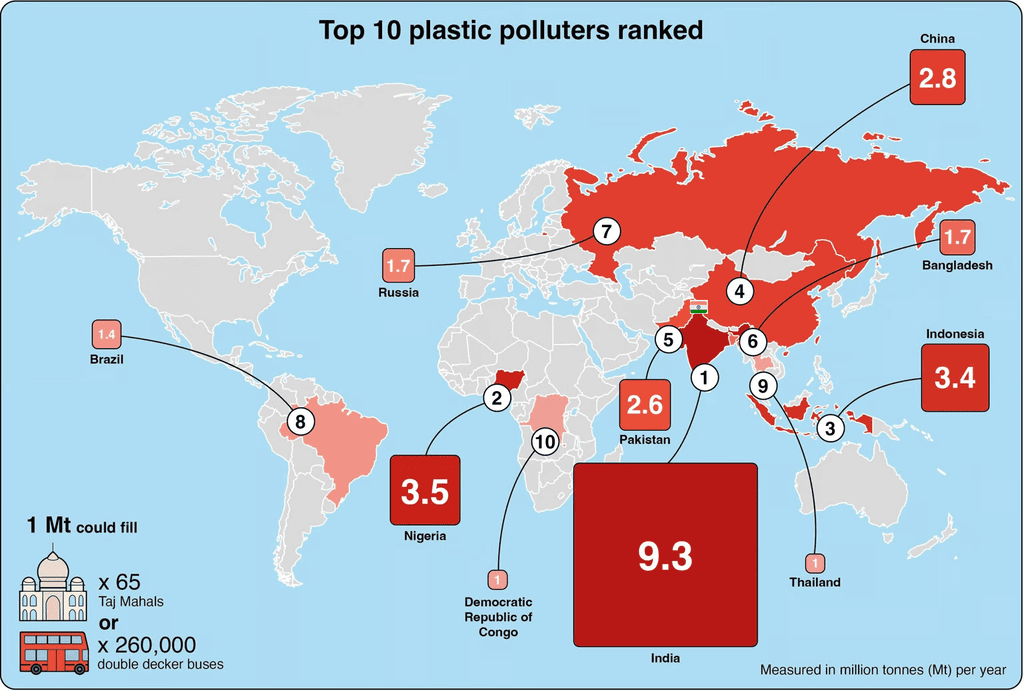
A recent study published in the journal Nature has revealed that India is the highest contributor to global plastic pollution. India accounts for approximately one-fifth of the total plastic waste generated worldwide.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- India generates approximately 9.3 million tonnes of plastic pollution annually. Out of this, 5.8 million tonnes (mt) are incinerated, while 3.5 million tonnes are released into the environment as debris.
- This figure is significantly higher than Nigeria (3.5 mt), Indonesia (3.4 mt), and China (2.8 mt). India’s waste generation rate is approximately 0.12 kilograms per capita per day.
- Plastic waste emissions are highest across countries in Southern Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and South-eastern Asia, revealing a clear divide in plastic pollution sources.
- Global South countries, such as India, often rely on open burning for waste management, while the Global North uses controlled systems, leading to less unmanaged waste.
- Globally, 69% or 35.7 Mt per year of plastic waste emissions come from 20 countries. In the Global South, plastic pollution mainly comes from open burning due to poor waste management, while in the Global North, it's mostly from uncontrolled debris.
- High-income countries have higher plastic waste generation rates but are not among the top 90 polluters due to 100% collection coverage and controlled disposal.
- The study has faced criticism for its narrow focus on waste management, neglecting the need to reduce plastic production, potentially diverting attention from upstream solutions like phasing out single-use plastics.
- The endorsement by plastics industry groups raises concerns about aligning with industry interests rather than broader environmental goals, and the focus on waste management might undermine comprehensive solutions to production and recycling issues.
What are the Reasons for High Plastic Pollution in India?
- Rapid Population Growth and Urbanization: India’s increasing population and affluence lead to higher consumption and waste generation. Urbanization intensifies the demand for plastic products and packaging.
- Inadequate Waste Management Infrastructure: The existing waste management infrastructure is insufficient to manage the large volumes of waste, resulting in more uncontrolled dumping sites than sanitary landfills.
- Discrepancies in Waste Collection Data: The official waste collection rate in India is overstated at 95%, while research suggests the actual rate is around 81%, indicating a significant gap in efficiency.
- Open Burning of Waste: Approximately 5.8 million tons of plastic waste are burned each year, releasing toxic pollutants that pose health and environmental risks.
- Informal Sector Recycling: The unregulated informal recycling sector handles much plastic waste that is not captured in official statistics, complicating the understanding of pollution levels.
What are the Issues Associated With Mismanaged Plastic Waste in India?
- Environmental Degradation: Plastic waste clogs waterways, leading to flooding and marine pollution. It harms marine life through ingestion, and burning it releases toxic pollutants, worsening air quality.
- Public Health Concerns: Microplastics in water and food can pose long-term health risks. Plastic waste also creates breeding grounds for disease vectors, increasing the spread of diseases like dengue and malaria.
- Economic Challenges: A FICCI report estimates that India could lose over USD 133 billion in material value from plastic packaging by 2030, with uncollected plastic packaging waste accounting for USD 68 billion of this loss.
- E-commerce and Packaging Waste: The growth of e-commerce has led to increased plastic packaging waste, much of which is difficult to recycle and ends up as litter or in landfills.
- Regulatory and Enforcement Challenges: Inconsistent enforcement of plastic waste regulations and issues with the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) system hinder effective waste management.
- Microplastic Pollution in Agriculture: Plastic use in agriculture and inadequate wastewater treatment lead to microplastics accumulating in soil, impacting soil health and food safety.
- Technological and Infrastructure Gaps: Limitations in waste segregation and processing facilities, along with a lack of advanced recycling technology, complicate effective plastic waste management.
What are the Regulations Related to Plastic Waste Management in India?
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2018: Phases out multi-layered plastic (MLP) that is non-recyclable, non-energy recoverable, or has no alternate use. Establishes a central registration system by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) for producers, importers, and brand owners.
- Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021: Prohibits specific single-use plastic items by 2022 due to low utility and high littering potential. Enforces collection and environmental management of plastic packaging waste through EPR. Increases plastic carry bag thickness from 50 microns to 75 microns by September 2021 and to 120 microns by December 2022.
- Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022
- Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2024
Other Initiatives:
- Swachh Bharat Mission
- India Plastics Pact
- Project REPLAN
- Un-Plastic Collective
- GoLitter Partnerships Project
Way Forward
- Circular Economy: Promote RRR i.e. reduce, reuse, and recyclability in design, establish recovery facilities, incentivize recycled plastics, and mandate recycled content in products.
- Smart Waste Management: Integrate smart technology in waste management, such as IoT-enabled bins, AI for sorting, and mobile apps for reporting illegal dumping and locating recycling centers.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Strengthen EPR by introducing graded fees for difficult-to-recycle plastics, a plastic credit trading system, and extending EPR to the informal sector for better conditions for waste pickers.
- Awareness Campaigns: Launch national campaigns in multiple languages, integrate plastic waste education in schools, conduct community workshops, and use influencers to promote plastic-free lifestyles. Establish a national innovation challenge for youth involvement.
- Waste-to-Energy: Invest in advanced waste-to-energy technologies like pyrolysis and gasification for non-recyclable plastics, ensuring strict emissions controls and using generated energy to power waste management facilities.
- Green Procurement: Apply plastic waste reduction criteria in government procurement and use government buildings as models.
Adverse Effects of Lithium Mining

Why in News?
According to a new study, land subsidence is occurring in Chile's Atacama salt flat due to lithium mining. What are the Key Revelations of the Study?
Findings:
- Rate of Sinking: The Atacama salt flat in Chile is subsiding at a rate of 1 to 2 centimeters annually due to lithium brine extraction.
- Extraction Process: Lithium brine extraction involves pumping salt-rich water to the surface, which is then placed in evaporation ponds to obtain lithium. This process accelerates subsidence as it draws out lithium-rich brine faster than natural aquifer recharge can occur.
Lithium Mining Impact on the Environment:
- Water Usage: The extraction process demands substantial amounts of fresh water, requiring approximately 2,000 tons of water to produce a single ton of lithium.
- Water Scarcity: This extensive water usage intensifies water scarcity in the Atacama Desert, adversely affecting local communities and the surrounding ecosystems.
- Chemical Contamination: Chemicals like sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide, utilized in lithium extraction, pollute soil and water, posing risks to ecosystems and endangered species.
- Impact on Wildlife: A 2022 study noted a decline in flamingo populations in the Atacama region due to lowered water levels, which negatively impacts their breeding success.
Potential Impact of Lithium Mining in Reasi (J&K):
- Water Crisis: Many villages in Reasi are facing water shortages following the drying up of perennial streams after the construction of the Chenab Rail Bridge. Water-intensive lithium mining could exacerbate this issue.
- Threat to Biodiversity: The Himalayan region of J&K is recognized as a biodiversity hotspot. Mining activities could significantly threaten local biodiversity, disrupting habitats for migratory birds such as the Common Teal and Northern Pintail that depend on the wetlands of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Food Insecurity: The processes involved in lithium mining and processing could further undermine food security due to their significant carbon emissions and extensive water and land usage.
- Pollution: Mining in the Himalayas poses a risk of contaminating the vast riparian ecosystems that serve as sources for numerous rivers.
What are the Key Facts about Lithium?
- About: Lithium is a soft, silvery metal recognized for having the lowest density among all metals, as well as high reactivity and excellent electrochemical properties. Its primary ores include Petalite, Lepidolite, and Spodumene. It is often referred to as "white gold."
- Applications:
- Batteries: Lithium is predominantly used in rechargeable batteries for devices such as mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras, and electric vehicles. It is also found in some non-rechargeable batteries, including those in heart pacemakers, toys, and clocks.
- Alloys: A magnesium-lithium alloy is utilized for armor plating.
- Air Conditioning: Lithium chloride and lithium bromide are used in air conditioning and industrial drying systems due to their hygroscopic properties.
- Lubricants: Lithium stearate is employed as a versatile and high-temperature lubricant.
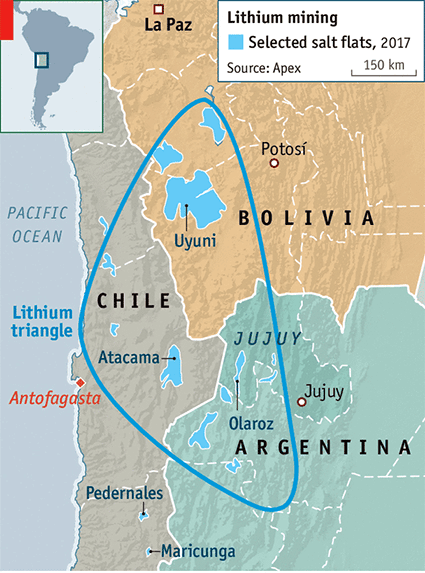
- Reserves: Chile holds the largest lithium reserves worldwide, accounting for 36% of the total, and is the second-largest producer, contributing 32% to global supply. Chile is part of the "lithium triangle" along with Argentina and Bolivia, while Australia and China rank as the first and third largest producers of lithium globally.
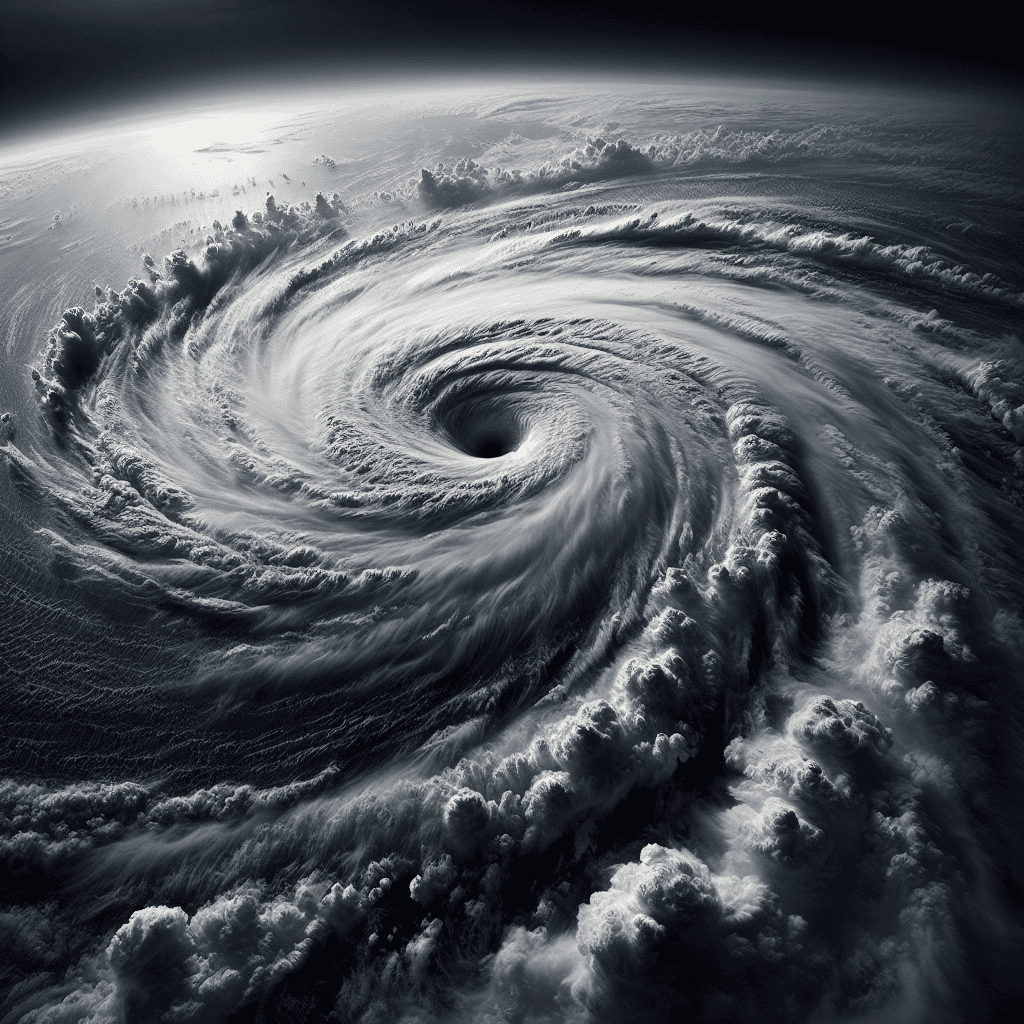
Typhoon Yagi

Why in news?
Recently, Typhoon Yagi has wreaked havoc across Southeast Asia, impacting countries such as the Philippines, China, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and significantly Vietnam. It is noted as the strongest tropical cyclone recorded until September 2024, being the second most powerful globally after Hurricane Beryl in the Atlantic Ocean.
- Initially forming as a tropical storm with wind speeds of up to 63 km/h in the western Philippine Sea, it escalated into a Category 5 typhoon with winds reaching 260 km/h. According to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, tropical cyclones are classified into categories ranging from Category 1 (119-153 km/h) to Category 5 (252 km/h or higher).
- Storms classified as Category 3 or above are deemed major tropical cyclones due to their significant potential for destruction.Storm systems characterized by wind speeds of 119 km/h and higher are identified as hurricanes, typhoons, or tropical cyclones.
- In response to the devastation, India has initiated Operation “Sadbhav” to deliver aid and essential supplies to Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar. This operation is part of India’s overarching strategy to contribute to Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) within the ASEAN region, aligning with its long-standing 'Act East Policy.'
Reasons for More Intense Typhoons:
- Global mean sea surface temperatures have risen by approximately 0.9°C since 1850, with around 0.6°C of this increase occurring in the last four decades.
- Elevated sea surface temperatures contribute to marine heat waves and heightened evaporation rates, which in turn lead to the development of more intense typhoons.
- These intensified storms tend to form closer to coastlines and can escalate rapidly in strength, causing greater destruction.
Teal Carbon Study at Keoladeo National Park

Why in News?
The study depicted the potential of teal carbon as a tool to mitigate climate change, if the anthropogenic pollution in the wetlands can be controlled.Study also reveals elevated methane emissions can be reduced by use of a specialized type of biochar, which is a form of charcoal.
About Teal Carbon
- Teal carbon refers to the carbon that is stored in non-tidal freshwater wetlands.
- This includes carbon that is found in plants, microbial life, and both dissolved and solid organic matter.
- The term "teal carbon" is based on color and describes how organic carbon is classified by its function and location instead of its physical features.
- In comparison, black and brown carbon are the results of not fully burning organic materials and contribute to global warming.
- Importance:Teal carbon helps to:
- Increase the level of groundwater
- Reduce flooding risks
- Lower the effects of heat islands
- Support a sustainable approach to urban adaptation
About Keoladeo National Park (Bharatpur, Rajasthan)
- Established as a national park in 1982.
- Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985.
- Home to over 370 species of birds and various animals, including pythons and Siberian cranes.
- Listed on the Montreux Record (under the Ramsar Convention) in 1990 due to concerns about water shortage and an unbalanced grazing system.
Hottest August Recorded: Climate Records Continue to Break

Why in News?
The Earth has been experiencing record-breaking heat more frequently, with August 2024 becoming the hottest August ever recorded in 175 years. This pattern of extreme temperatures is a clear sign of how climate change is affecting the planet.
Global Temperature Averages
- According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the average temperature of land and ocean surfaces globally for August 2024 was 2.29°F (1.27°C) above the average from the 20th century.
- The 20th-century average temperature is 60.1°F (15.6°C).
- This means that August 2024 is officially the warmest August ever recorded in history.
Regional Temperature Records
- Europe and Oceania: Both regions had their hottest Augusts ever recorded.
- Asia: Experienced its second-warmest August.
- Africa and North America: Saw their third-warmest Augusts.
- Northern Hemisphere: The summer of 2024 was the hottest on record.
- Southern Hemisphere: Winter was the warmest ever, with temperatures 0.96°C higher than average.
Decline in Sea Ice
- In addition to high temperatures, sea ice levels are also decreasing.
- The total area of sea ice around the world is now 8.32 million square miles, which is the second smallest amount ever recorded. This is 1.05 million square miles less than the average from 1991 to 2020.
- Arctic sea ice has reached a level that is much lower than normal, being the fourth lowest on record.
- Antarctic sea ice is also below average, marking the second lowest level ever noted.
- The ongoing breaking of heat records and the reduction of sea ice show the serious and continuing impacts of climate change.
- These patterns serve as a warning that immediate action is necessary to avoid more severe impacts in the future.
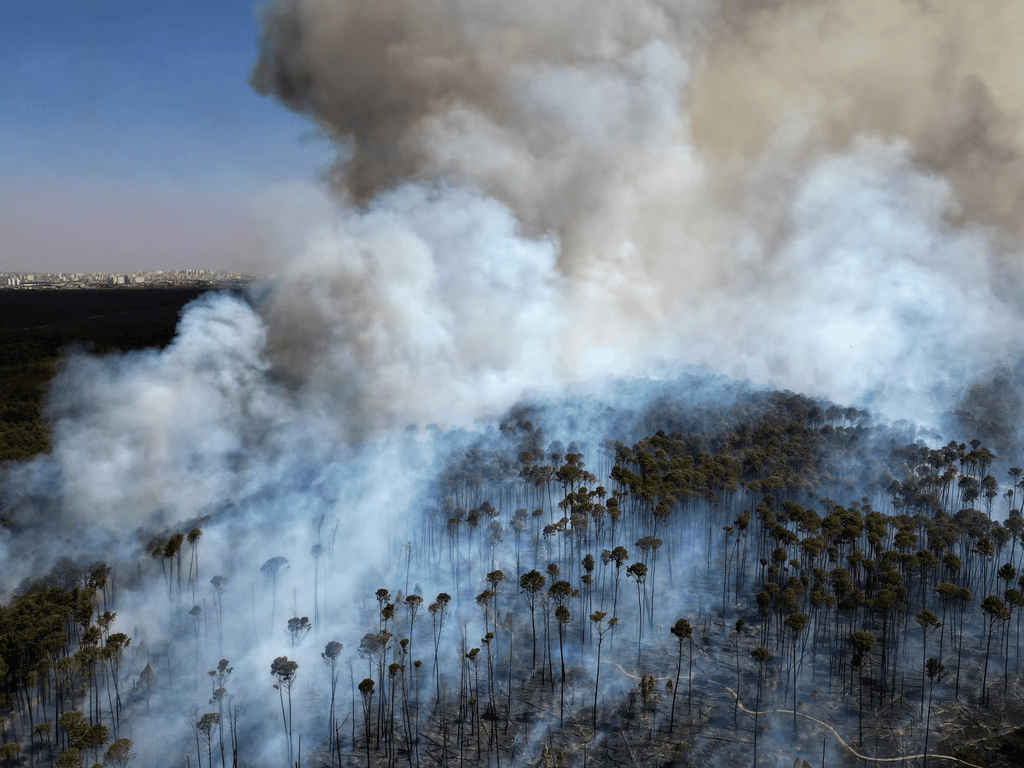
Amazon Faces Severe Drought and Record Wildfires in 2024

Why in News?
In 2023, the Amazon region faced one of its worst droughts ever, leading to a significant drop in water levels in major rivers like the Solimoes. By September 2024, the water level in the Madeira River in Porto Velho dropped to just 48 cm, compared to the normal level of 332 cm. This drastic change caused the Brazilian government to declare state of emergency in six cities.
How the Drought Affected Biodiversity and Communities
- The drought has greatly affected both the wildlife and the people living in the Amazon.
- Many communities rely on rivers for transportation, particularly the Indigenous and river-dwelling populations.
- As the rivers dry up, it has become challenging to travel, which isolates people from essential supplies such as food, fuel, and medicine.
- The Amazon region is home to about 47 million people, who depend heavily on its rivers for their daily needs.
- This situation is particularly tough for those who live in this area.
Record-Breaking Wildfires
- The drought led to an increase in wildfires.
- In July 2023, there were around 11,500 fires.
- This number rose dramatically to 38,000 fires in August 2023.
- This was the highest number of fires in twenty years.
- These wildfires released a significant amount of carbon into the air.
- The levels of carbon emissions reached the highest point since 2005.
- This situation has made the environmental crisis even worse.
What Caused the Drought?
- The main reason for the drought is climate change and the El Niño weather pattern, which leads to less rainfall.
- Another important factor is the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ), which influences rain in the area.
- Warmer ocean temperatures in the tropical Atlantic Ocean have caused the ITCZ to move further north, leading to even less rainfall in the Amazon.
- Over the years, the Amazon has faced more frequent and intense droughts.
- Major drought years include 2005, 2010, and 2015-2016.
- In the last 25 years, there have been four significant droughts, indicating a worrying trend of more frequent dry periods.
Long-Term Effects of the Drought
- The ongoing drought could lead to serious effects in the long run.
- Drier weather can cause more trees to die.
- When trees die, it reduces the forest's ability to take in carbon.
- This situation also raises the chance of wildfires.
- Although we don’t fully understand all the effects of the drought yet,
- it is likely to have a lasting impact on the environment.
- People who rely on the Amazon for their livelihoods may also be affected.
Nagar Van Yojana Surpasses Target with 111 Urban Forests

Why in News?
The Nagar Van Yojana (NVY) was launched by the Government of India in 2020 to increase the amount of greenery in cities. Within the first 100 days of this new initiative, the government aimed to create 100 urban forests, called Nagar Vans. This target was exceeded, with 111 Nagar Vans approved across 6 states and 1 union territory.
Purpose of Nagar Van Yojana
- The main goal of NVY is to enhance the quality of life in cities by creating more green spaces.
- These urban forests will offer places for relaxation, education, and provide environmental benefits.
- They also aim to combat climate change by improving air quality and lessening the impact of rising temperatures in city areas.
Financial Support and Size
- The government is offering Rs. 4 lakh for each hectare to support the establishment and upkeep of Nagar Vans.
- Each forest area will range from 10 to 50 hectares, depending on how big the city is.
- This initiative is aimed at cities that have Municipal Corporations, Municipalities, and Urban Local Bodies.
Focus on Biodiversity
- NVY aims to enhance biodiversity by planting various types of trees.
- The trees include fruit-bearing, medicinal, and native species.
- This planting strategy will help attract wildlife and create a more balanced environment in urban areas.
- These urban forests will serve as not only green spaces but also as sanctuaries for different types of life.
Community Participation
- The community's involvement is a crucial part of the Nagar Van Yojana.
- People are encouraged to take part in tree-planting events and educational programs.
- Each urban forest should have at least two-thirds of its area filled with trees.
- By getting the public involved, the initiative aims to create a strong connection between people and their local environment.
Components of Nagar Vans
- Biodiversity Parks to safeguard different types of plants and animals.
- Smriti Vans, where trees are planted in honor of those we have lost.
- Butterfly Conservatories designed to attract and protect butterflies.
- Herbal Gardens for growing plants that have medicinal properties.
- Matri Vans, which are planted as part of the “Ek Ped Ma Ke Naam” (A Tree in Mother’s Name) initiative.
Future Goals
- By 2027, the government intends to set up 1,000 Nagar Vans across India.
- This initiative is backed by the National Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA).
- The main goal is to safeguard urban forests.
- This project aims to address serious environmental problemssuch as:
- Air pollution
- Loss of natural habitats in cities
Ecological Degradation in Veli-Akkulam Lake

What in News?
A recent study presented by researchers from the University of Kerala at the ECSA 60 conference in Hangzhou has uncovered a significant ecological decline in Veli-Akkulam Lake. Over the past 30 years, the lake’s ecosystem has been deeply affected by the invasion of non-native species, which has changed its trophic status (how nutrients move through the food chain) and disrupted the natural food web.
Study Overview
- The researchers utilized the Ecopath Model to examine how well the lake's ecosystem operates.
- They mapped out the structure of the lake's food web.
- The study revealed a significant drop in native species that originally lived in the lake.
- In contrast, there has been a large increase in invasive species, which are species that are not originally from the lake.
Historical Background
- In the 1990s, a scientist named C.M. Aravindan was the first to explore the Veli-Akkulam ecosystem.
- At that time, the lake supported a wide range of native species, including prawns, cichlids, barbs, and catfish.
- These species played a crucial role in keeping the ecosystem healthy.
- However, recent research indicates that many of these native species have greatly decreased in number.
Species Decline
- Prawns: The quantity of prawns has significantly decreased. In the past, there were about 57.60 tonnes of prawns for every square kilometer. Now, this figure has fallen to just 0.110 tonnes per square kilometer.
- Indigenous Cichlids: Similarly, the number of indigenous cichlids has also dropped. Their population used to be around 41.6 tonnes per square kilometer, but it has now reduced to 0.350 tonnes per square kilometer.
Rise of Invasive Species
- By the 2000s, many local species were overtaken by invasive species, which are plants or animals brought in from different areas that compete with the native wildlife.
- Some of the main invasive species found in the lake include:
- Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
- Mozambique Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus)
- Other invasive species are the Amazon African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) and the Amazon sailfin catfish (Pterygoplichthys pardalis).
- These species have multiplied quickly, dominating the lake and disrupting the natural balance.
Invasion Meltdown
- Professor Biju Kumar called this situation an “invasion meltdown.” This term describes the negative effects that occur when many non-native species invade an ecosystem, causing more harm to the local environment.
- The changes in the lake's ecosystem have greatly affected the people who rely on it for their livelihood.
- In the 1990s, more than 100 local fishers depended on the lake for their income.
- Now, fewer than 20 fishers are left, as the decline of native fish populations has made it hard for them to continue fishing.
About Veli-Akkulam Lake
- Veli-Akkulam Lake is a stunning freshwater lake located in Kerala, India.
- The lake spans approximately 20 acres and is nourished by the Veli River.
- It is famous for its beautiful scenery and serves as a popular location for boating and kayaking.
- The lake attracts both tourists and local residents who enjoy its peaceful environment.
- There is a narrow channel connecting the lake to the Arabian Sea.
- Veli-Akkulam Lake is home to various species, including migratory birds.
Ozone Pollution Hurts Tropical Forest Growth, Study Finds

Why in News?
A recent study published in Nature Geoscience has revealed that ozone pollution is harming the growth of tropical forests, causing them to lose nearly 300 million tonnes of carbon every year. This is a big concern because tropical forests play a key role in fighting climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the air. The study highlights the urgent need to tackle air pollution to protect these important ecosystems.
Tropical Forests and Climate Change
- Tropical forests play a crucial role in helping to combat climate change because they function like a large sponge that soaks up carbon dioxide, which is a significant greenhouse gas.
- When tropical forests are in good health, they effectively lower the amount of carbon present in the atmosphere, benefiting the planet.
- However, if their growth is hindered or harmed, their ability to absorb carbon diminishes, making it more difficult to address climate change.
Impact of Ground-Level Ozone
- Ground-level ozone is a dangerous pollutant.
- It forms when gases from human activities, such as driving cars and operating factories, mix with sunlight.
- This type of ozone is different from the ozone layer in the sky, which protects us from harmful rays of the sun.
- While the ozone layer is beneficial, ground-level ozone is harmful to both plants and people.
- Ground-level ozone makes it hard for plants, including tropical trees, to absorb carbon dioxide effectively.
- A recent study found that this pollution has caused a 5.1% decrease in the annual growth of tropical forests.
Research Findings
- Scientists studied various kinds of tropical trees to understand how they react to ozone pollution.
- They used a computer model to forecast how plants might respond to increasing ozone levels.
- The research revealed that ozone pollution is worsening due to factors like urbanization, industrialization, and the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas.
- This rise in ozone levels poses a significant threat to tropical forests.
Worsening Conditions
- If ozone pollution keeps increasing, the harm to tropical forests will become worse.
- This is very worrying for places where people are trying to restore forests to help fight climate change.
- High levels of ozone in these areas could make it more difficult for restoration projects to be successful.
- The study recommends taking stronger actions to lower ground-level ozone.
- Improving air quality will not only help tropical forests grow better but also allow them to take in more carbon.
- This will contribute to the global efforts to tackle climate change.
What is Ozone Pollution?
- Ozone pollution mainly comes from vehicle emissions and industrial activities.
- It forms near the ground, where it can harm both plants and people.
- Unlike the ozone layer high in the atmosphere, which protects us from the sun's rays, ground-level ozone can cause breathing problems, especially for vulnerable groups like children and the elderly.
- Ozone levels are highest in the summer when there is more sunlight to help it form.
- Cities generally have higher levels of ozone compared to rural areas.
- Ozone pollution can also affect crop yields, leading to a decrease in food production.
- Efforts like the Clean Air Act in the U.S. aim to control ozone levels.
- There are also ongoing global efforts to reduce the harmful effects of ozone pollution.
Researchers Discover Endangered Myristica Swamp Forest in Maharashtra

Why in News?
Researchers near the Goa-Maharashtra border have recently discovered a sacred Myristica swamp forest in Kumbral, Maharashtra. This finding highlights the importance of local communities in preserving rare ecosystems. Sacred groves like this are often protected due to cultural beliefs, in this case, tied to the reverence of Lord Shiva, locally known as Bhalandeshwar.
What Is Myristica magnifica?
- Myristica magnifica is a plant that is in danger of extinction.
- This species is mostly found in the states of Karnataka and Kerala.
- It has an important role in the ecosystem, serving as a food source for wildlife.
- One of the key species that rely on it for food is the hornbill bird, which is also threatened.
- This tree belongs to the nutmeg family and can reach heights of up to 50 meters.
- Its seeds look like nutmeg seeds, but they are not as valuable for commercial use.
- The wood of this tree is used by local communities.
- Additionally, the tree produces essential oil, which has potential uses in aromatherapy.
Significance of Discovery
This discovery makes Kumbral the second village in Maharashtra, following Hewale-Bambarde in Sindhudurg, to have a Myristica swamp forest. The local community has always regarded this area as sacred, linking it to Lord Shiva, who is referred to as Bhalandeshwar in the region. Their dedication has played a significant role in protecting this endangered ecosystem.
The grove in Kumbral spans 8,200 square meters and is home to 39 different plant species. Within this grove, there is a specific section of 770 square meters dedicated to the swamp forest, which includes 70 Myristica magnifica trees. This forest offers important benefits to the environment, such as:
- Groundwater recharge: This process helps store water underground.
- Carbon sequestration: The forest absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Flood mitigation: It helps reduce the impact of flooding.
Research and Documentation
- The research was conducted by Pravin Desai, along with Vishal Sadekar and Shital Desai.
- Their findings were published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa.
- The study highlights that this freshwater ecosystem is vital for many species.
- Among these species is the vulnerable Asian short-clawed otter.
- The ecosystem also supports a diverse array of wildlife.
Conservation Importance
- Preserving the Myristica swamp forest is essential for keeping the ecological balance in the Western Ghats, which is a place rich in biodiversity.
- Conservationists are pushing for stronger protection measures due to the forest's irreplaceable benefits for the environment.
- The Myristica swamp forest plays a crucial role in supporting local wildlife.
World Experiences Hottest Northern Hemisphere Summer
Why in News?
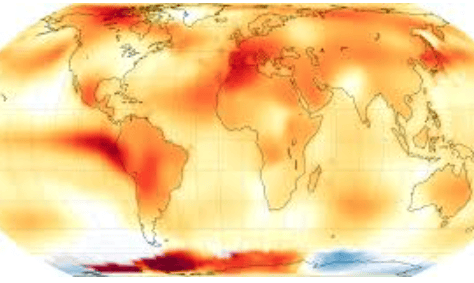
The Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) has announced that the summer of 2024 was the hottest ever recorded in the northern hemisphere, from June to August. This surpassed the previous record set last year. The rising temperatures are a result of ongoing global warming trends, driven by human activities.
Key Findings
- The summer of 2023 has been recorded as the hottest summer in history across the globe.
- Experts are warning that 2024 might be even hotter than 2023.
- During the past three months, several temperature records were set, including the hottest single day ever and the hottest summer in the northern hemisphere.
Causes of Climate Change
- The main reason for climate change is human actions, especially the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas.
- This process releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap heat and lead to rising temperatures.
- Another factor is the El Niño phenomenon, which is a natural climate pattern that has also played a role in increasing temperatures.
- However, there are indications that the climate may shift towards La Niña, a pattern that generally results in cooler weather.
Impact on Weather Patterns
- Extreme weather events, like floods and droughts, are happening more often and are getting worse due to climate change.
- Sudan is facing serious flooding issues.
- Italy is experiencing lengthy periods of drought.
- Typhoon Gaemi was made worse by climate factors, causing many casualties in the Philippines, Taiwan, and China.
Global Temperature Trends
- According to data from C3S, which has been tracking climate patterns since 1940, the summer of 2024 was the hottest recorded since the pre-industrial era began in 1850.
- Although La Niña might cause some short-term cooling, the temperatures of the ocean's surface are still unusually high, especially in August.
- Experts are calling for immediate action to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- If emissions keep rising at their current level, we will see more frequent and severe extreme weather events.
- These weather events pose serious risks to ecosystems, human communities, and our planet as a whole.
About Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S)
- C3S is a part of the European Union's Copernicus Programme, which began in 2015.
- This program provides valuable information about climate change by using data from satellite observations.
- C3S serves over 7,000 users around the world.
- It aids policymakers in making well-informed decisions to deal with climate change.
- C3S collaborates with top research institutions in Europe.
- Each year, it releases a report known as the European State of the Climate.
Ancient Ice Core Reveals Genomes of 1,700 Viruses

Why in News?
Scientists from the United States have made a remarkable discovery of over 1,700 ancient viruses in ice core samples taken from the Guliya Glacier on the Tibetan Plateau. Some of these viruses are over 40,000 years old. The study, led by Zhi-Ping Zhong of Ohio State University, offers valuable insights into how viruses have evolved and survived in response to changing climates.
Ice Core Sampling
- Ice cores are cylindrical samples taken from glaciers.
- These cores enable scientists to examine layers of ice that have accumulated over many thousands of years.
- Each layer contains vital environmental details, which include preserved microorganisms such as viruses.
- The ice core from the Guliya Glacier measures 310 meters in length and offers samples from various climatic periods.
- This makes the Guliya ice core an essential resource for studying both ancient climates and the history of viruses.
Genomic Analysis
- The research team utilized advanced methods to extract DNA and sequence the genomes of viruses discovered in the ice.
- They found a total of 1,705 different virus species.
- Each virus showed notable genetic differences that varied according to the climate conditions during their period of activity.
Viral Communities and Adaptation
- The research found that certain viral communities were special to the area.
- These viral groups were especially active around 11,000 years ago during times of climate change.
- These viruses displayed impressive adaptations, such as taking in genetic material from the bacteria they attacked, like Flavobacterium.
- This genetic exchange helped the viruses to better their survival and metabolic functions.
Evolutionary Insights
- Analysis revealed a significant link between viral activity and climate change.
- This indicates that as the climate changes, new viruses can arise, which puts pressure on existing strains to adapt.
- This type of evolutionary interaction may have been important in shaping the populations of viruses over time.
- With global warming leading to the melting of glaciers and permafrost, there is increasing worry that ancient viruses, which have been trapped in ice for a long time, might be released into today’s environments.
- This situation presents potential health risks, as these ancient viruses could interact with current ecosystems in ways that are hard to predict.
- More research is necessary to understand how these ancient viruses behave and how they might adapt to modern conditions.
Importance of the Research
- This study emphasizes the significance of gathering and examining ice core samples from various locations worldwide.
- As glaciers continue to melt, these ice cores hold vital information regarding past interactions between viruses and climate.
- If not studied soon, this important data could be lost forever.
- Learning about these ancient viruses is crucial for predicting how they may react to current and future climate changes.
- This is particularly important in the Anthropocene era, which is the current time when human activities significantly impact the climate and the environment.
|
95 videos|234 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Environment and Ecology: September 2024 UPSC Current Affairs - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main reasons for India being labeled as the world's largest plastic polluter? |  |
| 2. What are the environmental impacts of lithium mining? |  |
| 3. How does Typhoon Yagi relate to environmental changes and climate patterns? |  |
| 4. What steps is India taking to combat plastic pollution? |  |
| 5. How can lithium mining practices be made more sustainable? |  |





















