Ethers: Preparation, Properties & Reactions | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Ether |

|
| Structure of Ether |

|
| IUPAC Nomenclature of ether "Alkoxy Alkane" |

|
| Methods of Preparation of Ethers: |

|
| Physical Properties Of Ethers |

|
| Reactions of ethers |

|
Ether
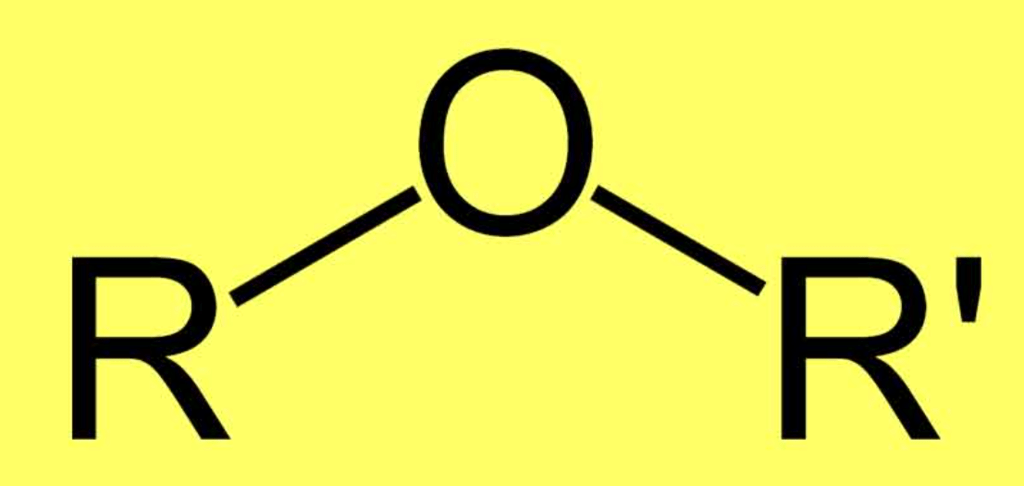
Structure of Ether
Classification of Acyclic ethers:
IUPAC Nomenclature of ether "Alkoxy Alkane"
| S.NO. | Compound | IUPAC Name |
| 1 | 2-Methoxy propane | |
| 2 | Chloromethoxy methane | |
| 3 | Methoxy benzene (Anisole) | |
| 4 | 3-Ethoxy-1, 1-dimethyl cyclohexane | |
| 5 | trans-1-Chloro-2-methoxy cyclobutane | |
| 6 | 2-Ethoxy ethan-1-ol |
Methods of Preparation of Ethers:
(1) Williamson synthesis-
General reaction:RX + R - OR'
e.g. (i) n-PrOH
(ii) MeOH Me
(iii) t-BuOH t-Bu
t-Butyl ethyl ether
(This reaction produces a poor yield of ether because of the bulkiness of t-BuO-)
(2) Williamson's Continuous Etherification process or by Dehydration of Alcohols-
(i) ROH + RO +
ROR + H3O+
(ii) ....
e.g.
Mechanism
Step-1:
This is an acid-base reaction in which the alcohol accepts a proton from the sulfuric acid.
Step-2 :
Another molecule of the alcohol acts as a nucleophile and attacks the protonated alcohol in an reaction.
Step-3 :
Another acid-base reaction converts the protonated ether to an ether by transferring a proton to a molecule of water (or to another molecule of the alcohol).
Only one combination of alkylhalide and alkoxide is appropriate for the preparation of each of the following ethers by Willianson ether synthesis. What is the correct combination in each case ?
(3) From alkenes
(a) By the addition of alcohols in alkenes:
When alcohol is added to alkenes in presence of an acid, we get ethers.
General reaction:
(I) carbocation
(II) Carbocation alcohol
e.g. (I) = CH2 +
(H2SO4)
Me3
(II) Me3 + EtOH
Me3COEt
(b) Alkoxymercuration - demercuration:
e.g.
(i) RCH=CH2 +R'OH RCH(OR')CH3
(ii) CH2=CHCH3 +CH3CH(OH)CH 3
(iii) CH3CH=CHCH3 +CH3CH(OH)CH 2CH3
Physical Properties Of Ethers
Dimethyl ether and ethyl methyl ether are both gases at room temperature. Other lower homologues are colourless, pleasant smelling, volatile liquids with a typical ether smell.
- Dipole moment: C-O-C bond angle is not 180°, dipole moments of the two C-O bonds do not cancel each other and thus ethers possess a small net dipole moment.
- Boiling point: Boiling points of ether molecules are comparable to that of alkanes but they are very low compared to that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass. This is because of the presence of hydrogen bonding in alcohol.
- Solubility: The solubility of ethers with water resembles those of alcohols of comparable molecular mass. Ether molecules are soluble in water. This is because of the fact that like alcohol, oxygen atoms of ether can also form hydrogen bonds with a water molecule. Also, solubility decreases with an increase in carbon atoms. This is because the relative increase in hydrocarbon content of the molecule decreases the tendency of H-bond formation.
- Polarity: Ether is less polar than esters, alcohols or amines because oxygen atom unable to participate in hydrogen bonding due to the presence of bulky alkyl group on both side of the oxygen atom. but ether is more polar than alkenes.
- Hybridization: In Ether oxygen atom is sp3 hybridized with a bond angle of 109.50,
Reactions of ethers
1. With HX-
General reaction:
X-R X-R'
e.g. (i) CH3CH2CH2CH3 2CH3-CH2Br
2. Reaction with sulphuric acid-
Ethers dissolve in concentrated solutions of strong inorganic acids to from oxonium salts, i.e. ether behave as Bronsted Lowry bases.
R2O H2SO4 R-OH
When heated with dilute H2SO4
R2O H2SO4 2ROH
e.g. C2H5OC2H5 +H2SO4 C2H5OH +C2H5OHSO4
C2H5OH+ H2SO4
3. Autoxidation of ethers :
When ethers are stored in the presence of atmospheric oxygen, they slowly oxidize to produce hydroperoxides and dialkyl peroxides, both of which are explosive. Such a spontaneous oxidation by atmospheric oxygen is called an autoxidation.
General reaction:
+
Ex.
(i) +
(ii)
4. Reaction with acid chlorides and anhydrides:
Reagent : ZnCl2, AlCl3 etc.
General reaction: (i) R-O-R +R-CO-Cl R-Cl +RCOOR
Mech.
RCOCl +AlCl3 RCO + AlCl4-
RCO
RCOOR' +
R"Cl + AlCl3
e.g.
C2H5OC2H5 + CH3COCl C2H5Cl + CH3COOC2H5
(ii) R2O + 2CH3COOR
e.g. C2H5OC2H5 + (CH3CO)2O 2CH3COOC2H5
5. Reaction with carbon monoxide :
Ether react with CO at 125-180oC and at a pressure of 500 atm, in the presence of BF3 plus a little water.
R2O + CO RCOOR
6. Reaction with halogens :
When treated with chlorine or Br, ether undergoes substitution, the extent of which depends on the conditions.
CH3CH2OCH2CH3 CH3CHClOCH2CH3
CH3CHClOCHClCH3
In presence of light,
(C2H5)2O
Mech.
The reaction proceeds by a free-radical mechanism, and α-substitution occurs readily because of resonance stabilization of the intermediate radical.
, etc.
|
75 videos|339 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Ethers: Preparation, Properties & Reactions - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the IUPAC nomenclature for ethers? |  |
| 2. How are ethers prepared? |  |
| 3. What are the physical properties of ethers? |  |
| 4. What are some common reactions of ethers? |  |
| 5. Are ethers commonly used in any industries or applications? |  |




















