Facts that Matter: Criminal Law | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
1. Overview of New Criminal Laws
Fact 1: On which date did the new criminal laws—Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, and Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam—come into effect?
Ans: July 1, 2024
Fact 2: Which colonial-era law did the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023 replace to define offenses and punishments?
Ans: Indian Penal Code, 1860
Fact 3: What does the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023 govern, replacing the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973?
Ans: Investigation, trial, and procedural aspects
Fact 4: Which law did the Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA), 2023 replace to outline rules for evidence admissibility?
Ans: Indian Evidence Act, 1872
Fact 5: How many sections does the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023 have, compared to the 511 sections of the Indian Penal Code, 1860?
Ans: 358 sections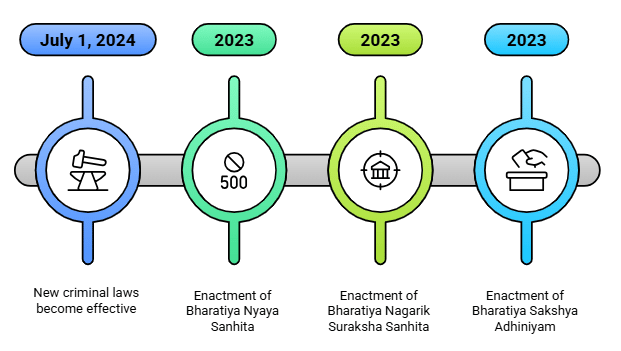
2. Key Principles of Criminal Law (BNS)
Fact 1: What are the two essential elements retained in the BNS for most offenses, ensuring both a guilty act and guilty mind are present?
Ans: Actus Reus and Mens Rea
Fact 2: Under the BNS, what principle ensures that an accused person is not considered guilty unless proven so beyond reasonable doubt?
Ans: Presumption of Innocence
Fact 3: Who bears the burden of proof in most cases under the BNS, except in defenses like insanity under Section 22?
Ans: The prosecution
Fact 4: Which principle under the BNS ensures that no one can be punished for an act that was not a crime when committed?
Ans: Nullum Crimen Sine Lege
Fact 5: What does the BNS stipulate regarding strict liability offenses, differing from the requirement of Mens Rea?
Ans: Mens Rea is not required; only Actus Reus needs to be proven

3. General Defenses under BNS
Fact 1: Which section of the BNS provides a defense for an honest and reasonable belief in a fact that negates criminal liability?
Ans: Mistake of Fact under Section 20
Fact 2: Under which section of the BNS can an act done accidentally, without intent and with due care, be used as a defense?
Ans: Accident under Section 21
Fact 3: Which BNS section allows the defense of committing a lesser harm to prevent a greater one, such as saving a life?
Ans: Necessity under Section 23
Fact 4: Which defense under Section 22 of the BNS applies if the accused was mentally unsound and incapable of understanding the wrongfulness of their act?
Ans: Insanity
Fact 5: Which sections of the BNS allow the right to defend oneself or property, provided the response is necessary and proportionate?
Ans: Private Defense under Sections 34-40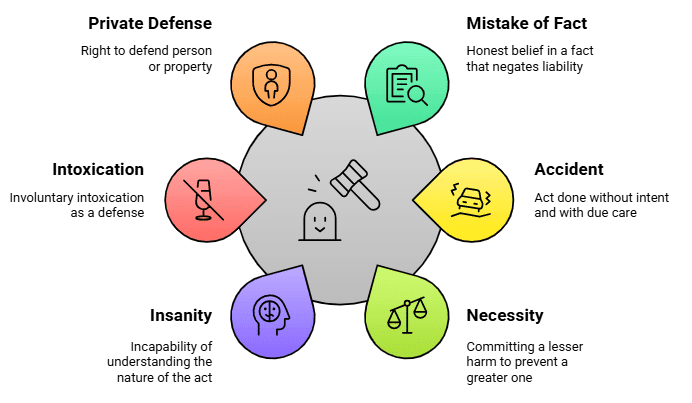
4. Key Offenses under Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023
Fact 1: Which section of the BNS defines murder as intentional killing, punishable by death or life imprisonment?
Ans: Section 103
Fact 2: Under which section does the BNS address sexual intercourse without consent, raising the gangrape victim age threshold to 18 from 16?
Ans: Rape under Section 63
Fact 3: Which new offense under Section 111 of the BNS covers organized crime, including kidnapping, extortion, and cybercrime by syndicates?
Ans: Organized Crime
Fact 4: Which section of the BNS replaces IPC Section 124A (sedition) with acts endangering India’s sovereignty, unity, or integrity?
Ans: Acts Endangering Sovereignty under Section 152
Fact 5: What offense was removed from the BNS following its decriminalization in the 2018 Joseph Shine v. Union of India case?
Ans: Adultery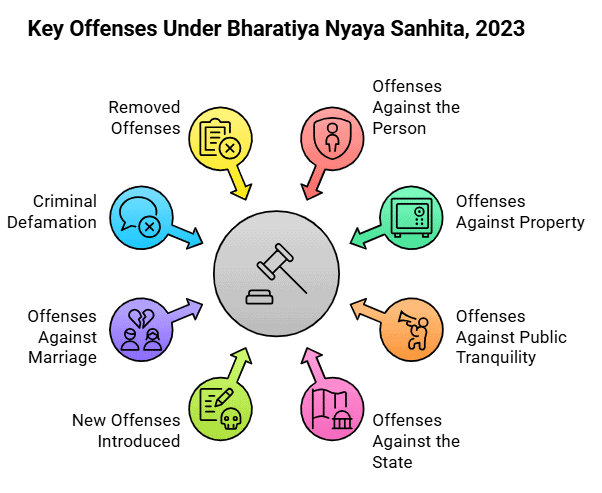
5. Punishments under BNS
Fact 1: Under which section of the BNS are the types of punishments, such as death penalty and life imprisonment, outlined?
Ans: Section 4
Fact 2: What new type of punishment was introduced in the BNS for minor offenses like defamation or public nuisance?
Ans: Community Service
Fact 3: Which sentencing principle under the BNS ensures that the punishment matches the severity of the offense?
Ans: Proportionality
Fact 4: Besides deterrence and retribution, what other objective does the BNS aim to achieve through its sentencing principles?
Ans: Reformation
Fact 5: What type of punishment under the BNS involves the seizure of an offender’s assets as a penalty?
Ans: Forfeiture of property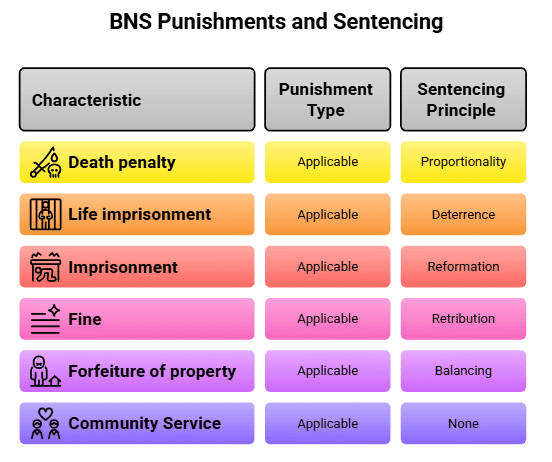
6. Procedural Changes under Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023
Fact 1: Under which section of the BNSS is forensic investigation mandatory for offenses punishable with 7 or more years?
Ans: Section 176
Fact 2: What does the BNSS require to be electronically recorded to ensure transparency during investigations?
Ans: Searches and seizures
Fact 3: Under the BNSS, where are terrorism cases now tried, unlike UAPA cases which go to Special Courts?
Ans: Sessions Courts
Fact 4: What is the time limit set by the BNSS for filing charge sheets in certain cases, such as those involving women and children?
Ans: 45 days
Fact 5: Which BNSS provision allows an FIR to be filed at any police station, regardless of jurisdiction, to enable faster action?
Ans: Zero FIR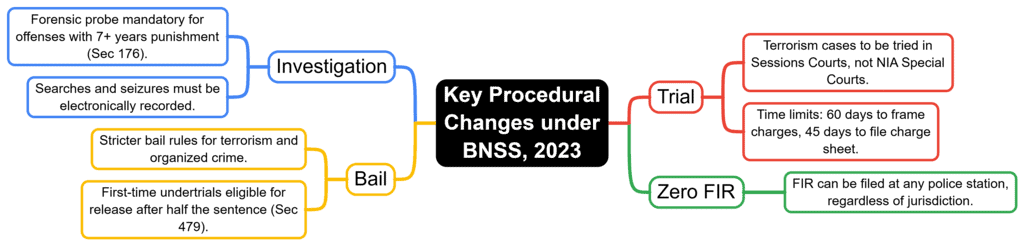
7. Evidence Rules under Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam, 2023
Fact 1: What types of digital records does the BSA, 2023 expand provisions for in terms of admissibility as evidence?
Ans: Digital records, emails, and electronic communications
Fact 2: Under which section of the BSA do police confessions remain inadmissible unless recorded before a Magistrate?
Ans: Section 23
Fact 3: Who bears the burden of proof under the BSA, 2023, except in specified defenses, aligning with the BNS?
Ans: The prosecution
Fact 4: What modern method does the BSA, 2023 include to facilitate the submission of evidence during trials?
Ans: Electronic submission of evidence
Fact 5: What technology does the BSA, 2023 provision for to modernize court proceedings, such as remote hearings?
Ans: Video conferencing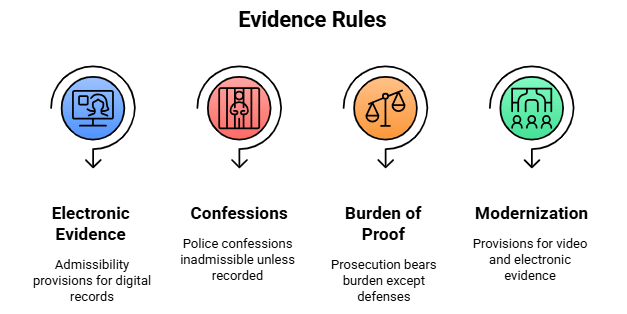
8. Key Legal Maxims
Fact 1: What does the legal maxim "Actus Non Facit Reum Nisi Mens Sit Rea" mean in the context of criminal law?
Ans: A guilty act requires a guilty mind
Fact 2: Which legal maxim states that not knowing the law cannot be used as a defense against liability?
Ans: Ignorantia Juris Non Excusat
Fact 3: What does the maxim "In Dubio Pro Reo" direct courts to do when there is doubt in a criminal case?
Ans: Favor the accused
Fact 4: Which legal maxim emphasizes that the prosecution must prove guilt beyond a reasonable doubt to secure a conviction?
Ans: Ei Incumbit Probatio Qui Dicit
Fact 5: What does the maxim "Audi Alteram Partem" ensure in legal proceedings to uphold natural justice?
Ans: The right to a fair hearing for both parties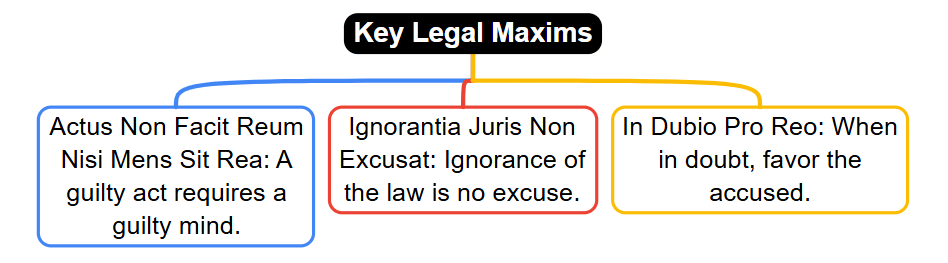
9. Landmark Case Laws (Relevant to BNS Context)
Fact 1: Which 2018 case struck down adultery under IPC Section 497, leading to its removal from the BNS?
Ans: Joseph Shine v. Union of India
Fact 2: Which case decriminalized consensual homosexual acts under IPC Section 377, with BNS retaining only non-consensual acts?
Ans: Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India (2018)
Fact 3: Which 1962 case is significant for understanding the defense of provocation, now under Section 105 of the BNS?
Ans: K.M. Nanavati v. State of Maharashtra
Fact 4: Which 2021 case challenged the sedition law, influencing BNS Section 152 to have a narrower scope?
Ans: SG Vombatkere v. Union of India
Fact 5: Which case emphasized the right to privacy as a Fundamental Right, impacting BNS provisions on sexual offenses and evidence?
Ans: Justice K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India (2017)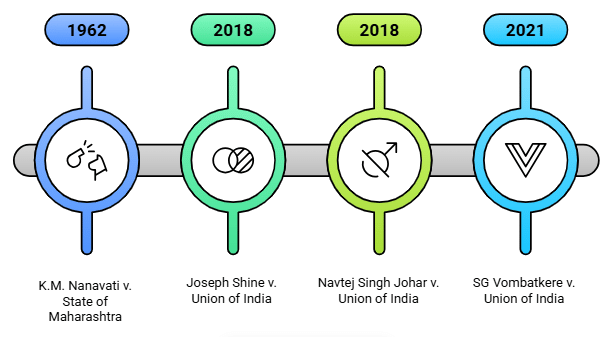
10. Key Changes from IPC, CrPC, and Indian Evidence Act
Fact 1: What new offenses were added to the BNS, 2023, to address contemporary issues like group violence and national security?
Ans: Terrorism, organized crime, and mob lynching
Fact 2: Which offenses were removed from the BNS, 2023, reflecting judicial rulings and societal changes?
Ans: Sedition and adultery
Fact 3: What new punishment type did the BNS, 2023 introduce for minor offenses to promote rehabilitation?
Ans: Community service
Fact 4: How did the BNSS, 2023 improve the criminal justice process for serious crimes with a punishment of 7+ years?
Ans: Mandates forensic evidence
Fact 5: Under the new section mapping, which BNS section corresponds to the offense of rape, previously under IPC Section 375?
Ans: BNS Section 63
|
63 videos|172 docs|37 tests
|





















