Facts that Matter : Law of Torts | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to Torts and Basic Principles |

|
| Negligence |

|
| Nuisance |

|
| Trespass |

|
| Defamation |

|
| Strict and Absolute Liability |

|
| Vicarious Liability |

|
| Defenses and Remedies |

|
Introduction to Torts and Basic Principles
Fact 1: What is the primary objective of the Law of Torts in India?
Ans: To compensate victims for civil wrongs causing harm or loss, distinct from contractual or criminal liabilities.
Fact 2: What does the tort law maxim Damnum sine injuria signify?
Ans: Damage suffered without the violation of a legal right, which does not entitle the plaintiff to compensation.
Fact 3: What are the essential elements required to establish liability under tort law?
Ans: Existence of a legal duty, breach of that duty, causation, and actual or potential harm.
Fact 4: How is a tort distinguished from a breach of contract in legal terms?
Ans: A tort arises from a breach of a duty imposed by law, not by an agreement between parties.
Fact 5: What does the maxim Injuria sine damno imply in the context of tort law?
Ans: A violation of a legal right without actual damage, which is actionable under tort law.
Negligence
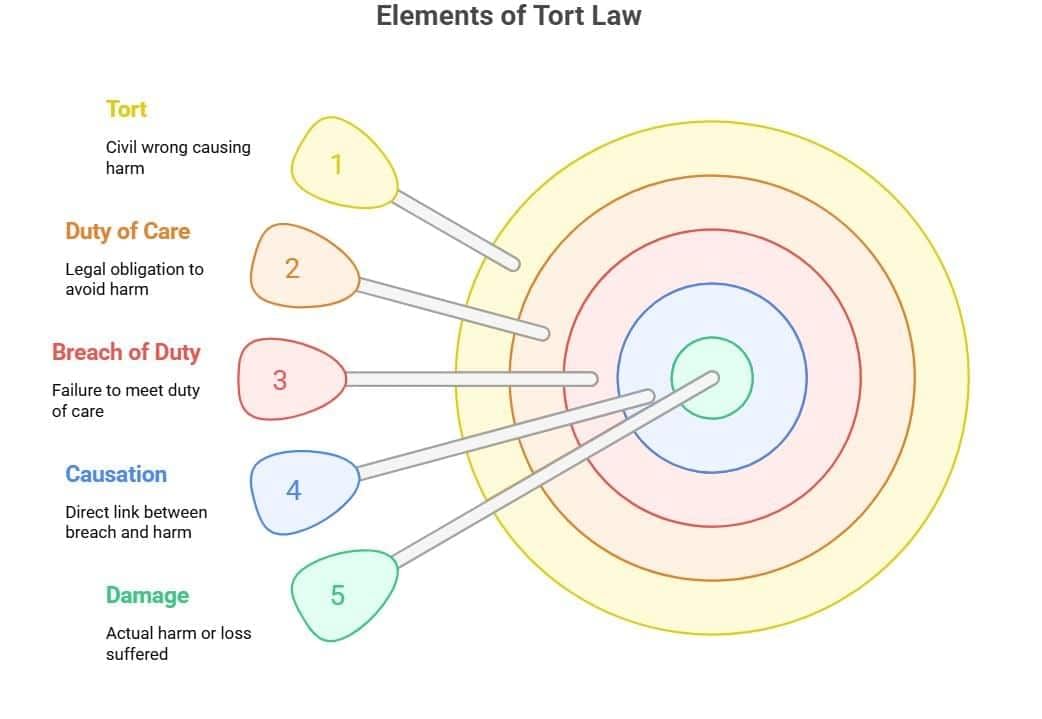
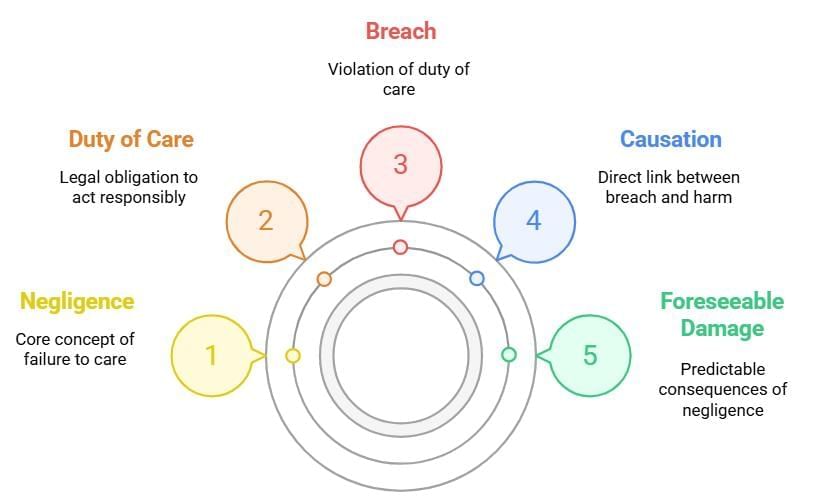
Fact 1: What is the definition of negligence under the Law of Torts?
Ans: Negligence is the failure to exercise reasonable care, resulting in harm or loss to another person.
Fact 2: What are the essential elements required to prove negligence in a tort case?
Ans: Duty of care, breach of that duty, causation, and foreseeable harm.
Fact 3: Which landmark case established the modern principle of duty of care in negligence?
Ans: Donoghue v. Stevenson (1932).
Fact 4: What does the principle of res ipsa loquitur mean in the context of negligence?
Ans: The thing speaks for itself, implying that the negligence is evident from the incident itself.
Fact 5: What is a common defense used to counter a claim of negligence?
Ans: Contributory negligence, where the plaintiff’s own actions contributed to the harm suffered.
Nuisance
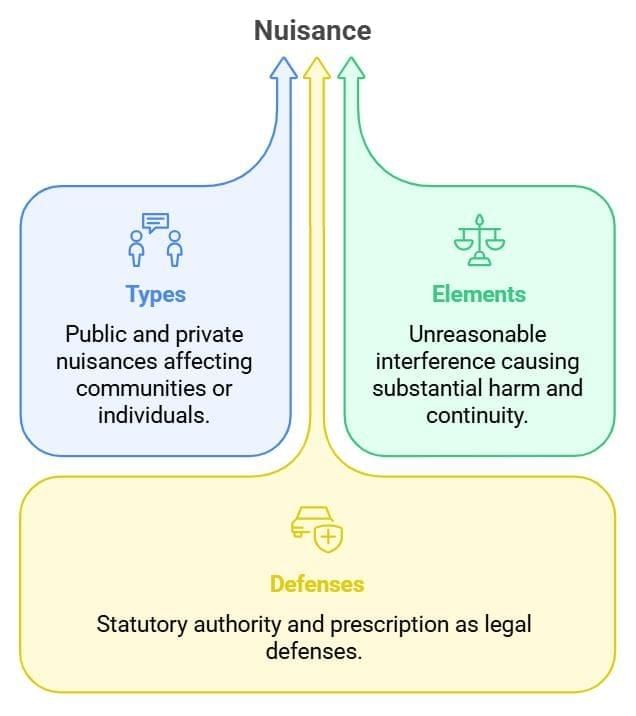
Fact 1: Under which section of the Indian Penal Code, 1860, is public nuisance defined?
Ans: Section 268
Fact 2: What type of nuisance involves interference with the rights of the public at large?
Ans: Public nuisance
Fact 3: What type of nuisance involves unreasonable interference with an individual's use or enjoyment of land?
Ans: Private nuisance
Fact 4: What defense can be claimed in a private nuisance case if the activity has been ongoing for a specific period in India?
Ans: Prescription (after 20 years)
Fact 5: What are the primary remedies available for private nuisance under tort law?
Ans: Damages and injunction
Trespass
Fact 1: Under which section of the Indian Penal Code, 1860, is criminal trespass defined?
Ans: Section 441
Fact 2: What type of trespass involves unlawful interference with a person’s body or liberty?
Ans: Trespass to person
Fact 3: What type of trespass involves unauthorized entry onto another’s land or property?
Ans: Trespass to land
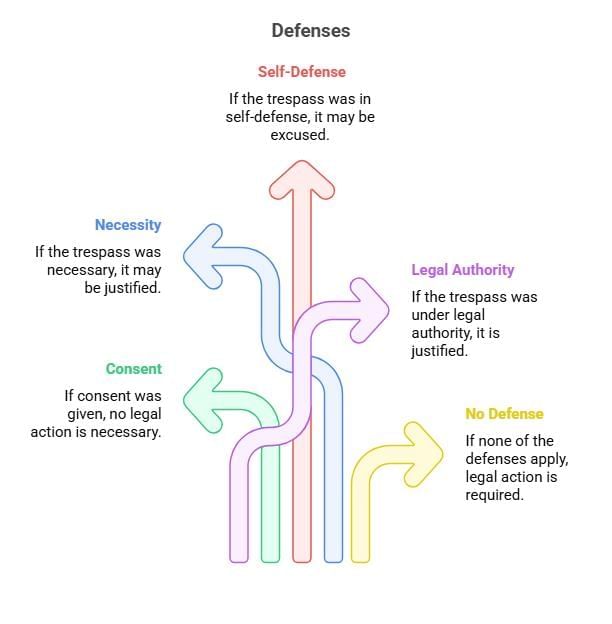
Fact 4: What defense can be claimed if the trespasser entered the property with the owner’s permission?
Ans: Consent or license
Fact 5: What are the primary remedies available for trespass to land under tort law?
Ans: Damages and injunction
Defamation
Fact 1: Under which section of the Indian Penal Code, 1860, is defamation defined as a criminal offense?
Ans: Section 499
Fact 2: What type of defamation involves a statement made in a permanent form, such as writing or printing?
Ans: Libel
Fact 3: What type of defamation involves a statement made in a transient form, such as spoken words?
Ans: Slander
Fact 4: What defense can be claimed in a defamation case if the statement is true and made for public good?
Ans: Justification or truth
Fact 5: What are the primary remedies available for defamation under tort law?
Ans: Damages and injunction
Strict and Absolute Liability
Fact 1: Which rule, established in the case of Rylands v. Fletcher, forms the basis for strict liability in tort law?
Ans: Rule in Rylands v. Fletcher
Fact 2: What type of liability holds a person responsible for harm caused by hazardous activities, even without negligence, subject to certain exceptions?
Ans: Strict liability
Fact 3: What type of liability imposes responsibility for harm without any exceptions or defenses, often applied in cases involving ultrahazardous activities?
Ans: Absolute liability
Fact 4: Which landmark Indian case replaced strict liability with absolute liability for industries engaged in hazardous activities ?Ans: M.C. Mehta v. Union of India (Oleum Gas Leak Case)
Fact 5: What defense is NOT available under absolute liability in India for harm caused by inherently dangerous activities?
Ans: Act of God or consent of the plaintiff
Vicarious Liability
Fact 1: Under what principle is a master held liable for the wrongful acts of their servant committed in the course of employment ?Ans: Respondeat Superior
Fact 2: What type of relationship is essential to establish vicarious liability between an employer and an employee?
Ans: Master-servant relationship
Fact 3: In which scenario can a principal be held vicariously liable for the acts of their agent under tort law?
Ans: When the agent acts within the scope of their authority
Fact 4: What defense can an employer use to avoid vicarious liability if the employee’s act was entirely outside the scope of employment?
Ans: Frolic of their own
Fact 5: Which landmark Indian case established that the state can be vicariously liable for the torts committed by its employees?
Ans: State of Rajasthan v. Vidyawati
Defenses and Remedies
Fact 1: What defense in tort law excuses a defendant’s liability if the plaintiff voluntarily agreed to the risk of harm?
Ans: Volenti non fit injuria (Consent)
Fact 2: What remedy in tort law involves a court order to stop or prevent a wrongful act, such as nuisance or trespass?
Ans: Injunction
Fact 3: Which defense can a defendant use if the plaintiff’s own negligence contributed to the harm suffered?
Ans: Contributory negligence
Fact 4: What primary remedy in tort law compensates the plaintiff for the harm or loss suffered due to the defendant’s wrongful act?
Ans: Damages
Fact 5: Which defense protects a defendant if the tortious act was committed to prevent a greater harm, such as saving a life or property?
Ans: Necessity
|
65 videos|181 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Facts that Matter : Law of Torts - Legal Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What is the Law of Torts and its significance in legal studies? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of torts recognized in the legal system? |  |
| 3. How does the concept of negligence apply in tort law? |  |
| 4. What are some defenses available in tort cases? |  |
| 5. How does tort law differ from criminal law? |  |














