First World War | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
World War First the Background 1914-1918
- World War I transpired between the Central Powers and the Allied Powers, sparked by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the prominent heir to the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
- According to reports, the conflict claimed the lives of around nine million military personnel and thirteen million civilians. This monumental war in geopolitical history marked the downfall of four major imperialist powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Turkey, and Russia, subsequently contributing to the emergence of the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia.
World War I: Participants
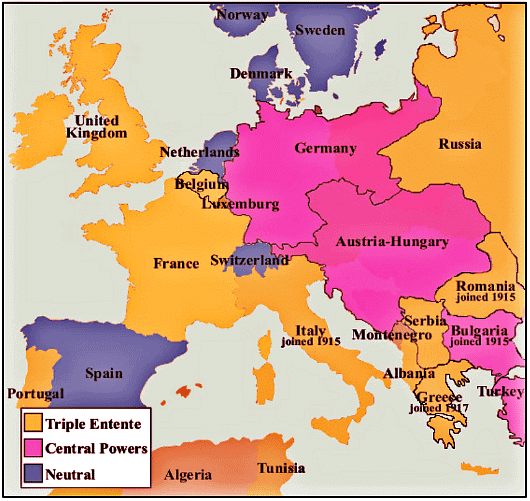
The war was fought between Allied Powers and Central Powers
- Allied Powers-France, Russia, Italy, Japan, and Britain. The United States joined after 1917.
- Central Powers-Germany, Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria
India made a huge contribution to Britain’s cause of the war. Almost 1.5 million Indians from parts such as Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Maharashtra volunteered for the war.
Causes of First World War
There is a chain of events that led to devastating World war I the root cause of which is deeply integrated. We will try to understand the root causes under several heads and what factors were responsible for the First World War.
Mutual Defence Alliance
Before World War I many countries went under a treaty wherein when one of the countries was attacked the other was bound to defend the. The following Alliances existed before the War
- Russia and Serbia
- Germany and Austria-Hungary
- France and Russia
- Britain and France and Belgium
- Japan and Britain
The Alliance of Austria- Hungary was attacked by Serbia since Russia was in an alliance with Serbia it came to defend Serbia. Germany being in alliance with Austria – Hungary attacked Russia. France attacked Germany, Austria – Hungary.
Germany Attacked Belgium and France which brought Britain into the war. Japan came to defend Britain. Lastly, Italy and the United States Joined.
Imperialism
The policy of extending one’s own territorial boundary using power is known as imperialism. Africa and Asia were a point of conflict and attracted many European Countries. The desire for power and increased competition was a major force in imitation of World War I
Militarism
By the beginning of the 20th century, countries were in a sort of arms race and there was a great display of military powers. Germany was winning the race followed by Russia and France. The increase in military powers was also one of the causes that pushed the world into this disastrous war.
Nationalism
This can be considered one of the most important causes of triggering war. The people of Bosnia and Herzegovina no longer wanted to be part of Austria-Hungary but to be associated with Serbia. Each country in Europe contributed to extending the war by proving their nationalism and trying to dominate others.
Immediate Cause: Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Franz Ferdinand was a member of the royal Habsburg dynasty, which ruled the Austro-Hungarian Empire. After a first failed attempt to assassinate Ferdinand by a Serbian-nationalist terrorist group called the Black Hand, Ferdinand and his were assassinated in 1914 by a Serbian nationalist named Gavrilo Princip while they were in Sarajevo, Bosnia which was part of Austria- Hungary. This led to Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia while other countries were also mobilized to prove their alliances.
The course of World War I
Start of War
After the assassination, the following series of events took place:
- July 28 – Austria declared war on Serbia.
- August 1 –Germany – Austria’s ally declares war on Russia- an ally of Serbia
- August 3 – Germany declares war on France
- August 4 – Great Britain, an ally of France, declares war against Germany
President Wilson of The United States declared that they will remain neutral
Western and Eastern Fronts
- In West – Germany attacked Belgium and France
- In East – Russia attacked both Germany and both Austria-Hungary
Battle of Marne fought between 5th -9th Sept 1914 Central France became the center of the eastern front and also the gateway for the rest of the war.
Ottoman Empire
During the 1915s allied powers rose against the Ottomans in the Mediterranean as Germany tricked Russia and they thought Russia was attacked by Turkey. A Series of campaigns by the British was launched at Dandrelles, Gallipoli Peninsula, and Mesopotamia. The British had some success in their campaign except at Dandrelles where they were defeated.
Trench Warfare
Fight was fought in a series of trenches dug from the North Sea through Belgium and France. Soldiers from dug-in positions gave them a slight advantage. The land between two enemy French lines was covered with land mines and barbed fences and is termed as No Man’s Land
United States Entrance and Russia’s Exit
- In 1917 this war took a major turn when the United States, angered by an attack on its ship in the Atlantic Ocean declared War on Germany.
- Another was the withdrawal of Russia from the war due to the Bolshevik Revolution.
End of War and Armistice
Such a long war extending for a span of 4 years takes a toll both emotionally and physically on the troops fighting and is enough to demoralize them from moving forward. Along with the soldiers being demoralized, there was a deadly spread of influenza which took the lives of soldiers on both sides, and eventually, both the parties Germany and Austria Hungary signed an Armistice where Germany agreed to surrender and give up their occupied territories.
Timeline of First World War
Let us look into the detailed timeline of WWI

World War I: List of Important Battles
- First Battle of Ypres 1914- Between allied powers and Germany, Marked the beginning of the Trench Warfare system
- Battle of Mons 1914 – Germans against British
- First Battle of Marne 1914 – French against Germany
- Battle of Dogger Bank 1915- British against Germany
- Battle of Verdun 1916 – French checked German
- Sussex Incident 1916- Sinking of French passenger steamer Sussex led to Germany’s unrestricted submarine warfare
- Second Battle of Somme 1916-British and French against Germany
- First Battle of Somme 1916- British and French against Germany
- Battle of Passchendaele or Third battle of Ypres 1917- Between allied powers and Germany
- Battle of Jutland 1916 – British and German Battle fleets
- Gallipoli Campaign 1916 – Anglo French Operation
- June Offensive 1917- Launched by Russia
- Battle of Isonzo 1917- 11 battles between Austria and Italy
- First Battle of Cambrai 1917- first use of tanks in warfare by British offensive
- Battle of Mons 1918- Canadian forces against Germans
- Battles of the Meuse-Argonne 1918- Allied army against Germany
- Second Battle of Marne 1918- Last major German offensive
- Second Battle of Cambrai 1918- Hundred days battle by Canadian troops
- Battle of Amiens 1918- Collapse of Germany army and end of war
Consequences of World War I
Consequences or Aftermath of the war can be read under Political, Social, Territorial and Military causes.
- Political Consequences
- Rule of the king ended in Germany and it became a Republic in Nov 1918.
- The fall of the Russian revolution led to the formation of the USSR IN 1922
- the United States emerged as a superpower
- European Supremacy began to end and Japan emerged as powerful in Asia
- Emergence of Independent countries like Poland, Yugoslavia, and Czechoslovakia
- Baltic countries – Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania – became independent.
- Austria Hungary break into several states
- Leftover Ottoman Empire became Turkey
- Germany, Austria, Hungary, Turkey and Russia moved towards monarchy
- Treaties after World War I
- Three treaties were signed during the course of the Paris Peace Conference between Allied and Central powers.
- The first and most important is the Treaty of Versailles, a peace document signed between allied and central powers on 28 June 1919. This treaty included a contract of the League of Nations under which members guaranteed each other’s independence and territorial integrity.
- The treaty of Saint – Germain 10 Sept 1919, dissolved the Austria-Hungary Empire, and independence was given to the new Republic of Austria
- Treaty of Sevres- Signed between 1920between allied and Ottoman Empire
- Social Consequences
- Around 1 crore people were killed
- Birth rate declined due to decrease in no of males due to death and exodus in large numbers
- Due to fewer males available women were employed in major works such as factories and offices and were given more rights, their position changed and were uplifted.
- Territorial Cause
- Alsace and Lorraine went back to France
- Belgium regained Eupen and Malmedy
- Poland annexed Eastern territories and thus East Russia became territorially isolated.
- Former Baltic German cities Danzig and Memel were declared free
- Northern Schleswig-Holstein was annexed by Denmark
- Germany Lost all Colonies
- Military Consequences
- Decline in the numbers of the German navy.
- Dramatic reduction of the Army to 100,000
- Rhineland region was demilitarised
India and World War I
- Although India had a neutral stance towards war and didn’t want to participate, being a British colony at that time Indian nationalists mostly moderates believed India’s effort in Britain’s cause of war will have a beneficial impact on Britain and it could help Indians to attain the goal of Self rule earlier.
- India being a Britain colony made huge efforts to the cause of World War I. Indian men from all over the region were seen fighting at the western front during the war.
- Indians were employed in France first as Britain’s force was not optimum in France.
- Indian men served in various places such as France and Belgium, Mesopotamia, Egypt, Gallipoli, Palestine, and Sinai
- Britain raised both men and money from India from the harsh taxation rules imposed. In return, a promise of self-rule was given which was never fulfilled.
- Indian men were paid 11 rupees a month which motivated Indians to fight for someone else’s cause thousands of miles away.
Concluding Remarks
- The First World War or World War I is momentous in history for all negative reasons. It will be buried in history with the large-scale blood bath, destruction, and casualties it caused.
- The Impact of the First World War destroyed empires, created numerous new nation-states, encouraged independence movements in Europe’s colonies, forced the United States to become a world power, and led directly to Soviet communism and the rise of Hitler.
|
1243 videos|2222 docs|849 tests
|
















