Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
UPSC Exam > Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) > Flashcards: Atomic Structure
|
1189 videos|2215 docs|849 tests
|
FAQs on Flashcards: Atomic Structure Flashcard - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the main components of an atom? |  |
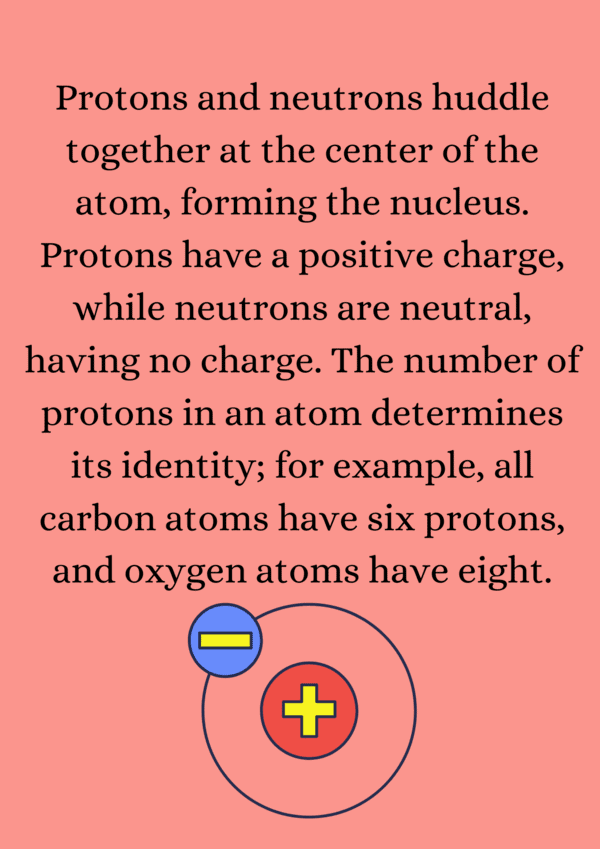
Ans. The main components of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus, neutrons are neutral particles also located in the nucleus, and electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus in electron shells.
| 2. How do protons and neutrons differ from electrons in terms of mass and charge? |  |
Ans. Protons and neutrons, which are located in the nucleus of an atom, have a significantly greater mass than electrons. A proton has a positive charge (+1), a neutron has no charge (0), and an electron has a negative charge (-1). The mass of a proton is approximately 1836 times that of an electron, while a neutron's mass is similar to that of a proton.
| 3. What is the atomic number, and how does it relate to the identity of an element? |  |
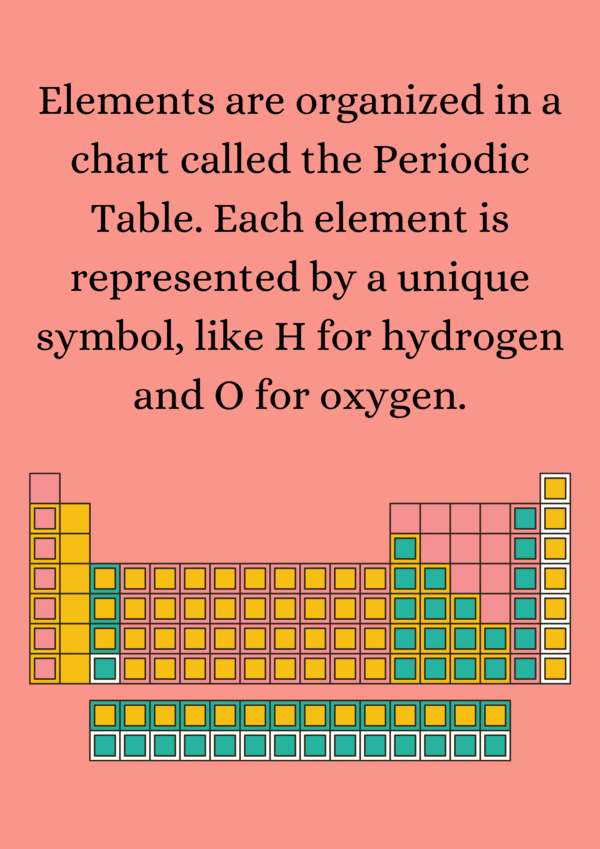
Ans. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and uniquely identifies an element. For example, an element with an atomic number of 6 is carbon because it has six protons. The atomic number also determines the element's position on the periodic table.
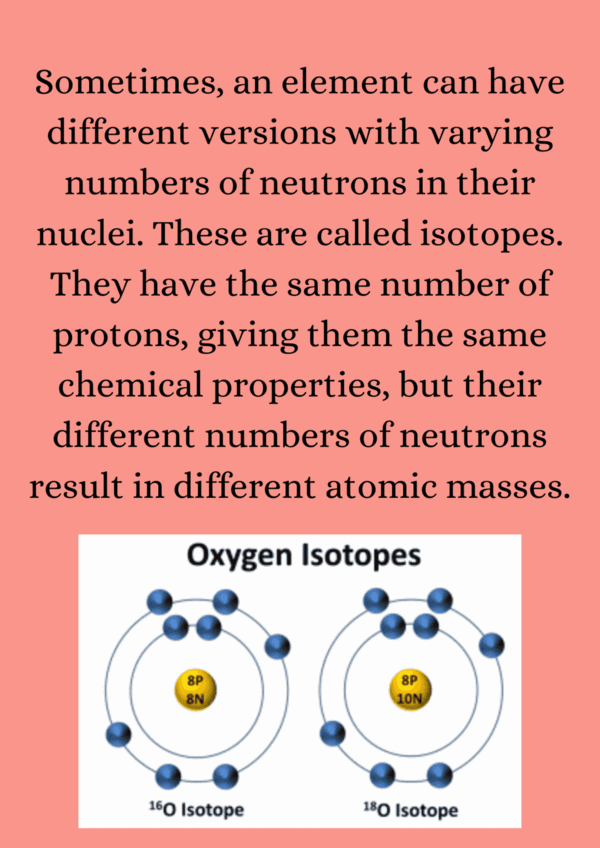
| 4. What are isotopes, and how do they differ from each other? |  |
Ans. Isotopes are variants of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This means they have the same atomic number but different atomic masses. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon, with 6 protons and 6 or 8 neutrons, respectively.
| 5. How does the arrangement of electrons affect the chemical properties of an atom? |  |
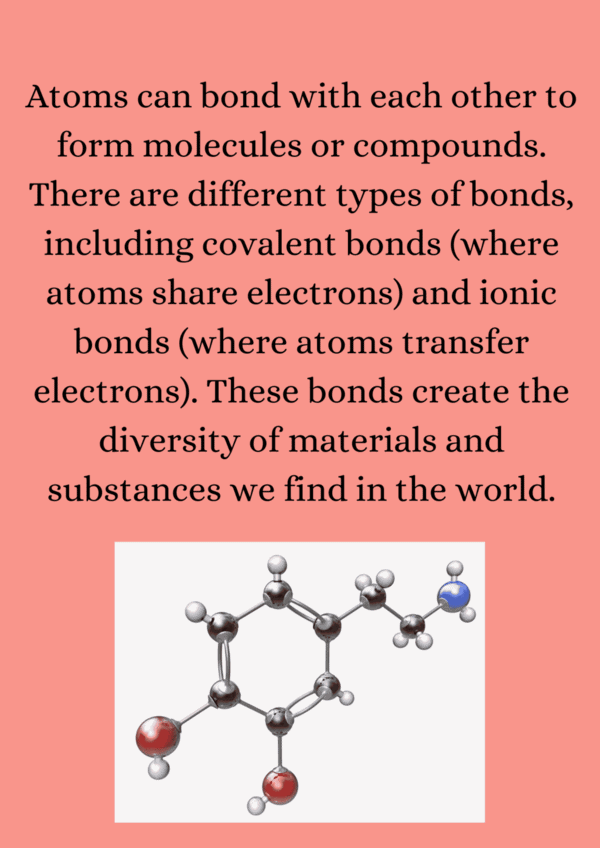
Ans. The arrangement of electrons, particularly in the outermost shell or valence shell, determines an atom's chemical properties and reactivity. Atoms with a full valence shell are generally more stable and less reactive, while those with incomplete valence shells tend to form bonds to achieve stability, influencing how they interact with other elements.
Related Searches