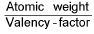Important Physical Chemistry Formulas for JEE and NEET
Atomic Structure
Estimation of closest distance of approach (derivation) of α-particle : 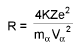
The radius of a nucleus : R = R0 (A)1/3 cm
Planck's Quantum Theory : Energy of one photon = hv = (hc/λ)
Photoelectric Effect: 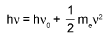
Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen like atoms :
- mvr = n(h/2π) (Quantization of angular momentum)
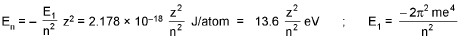
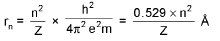
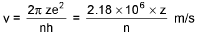
De-Broglie wavelength :
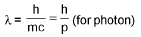
Wavelength of emitted photon :
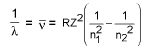
No. of photons emitted by a sample of H atom :
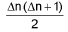
Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle:
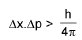
Or
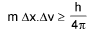
Or
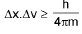
Quantum Numbers:
- Principal quantum number (n) = 1,2, 3, 4 .... to∞.
- Orbital angular momentum of electron in any orbit = nh/2π.
- Azimuthal quantum number (l) = 0 , 1 .... to (n - 1).
- Number of orbitals in a subshell = 2l + 1
- Maximum number of electrons in particular subshell = 2x (2l+ 1)
- Orbital angular momentum L =
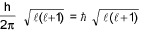
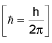
Stoichiometry
- Relative atomic mass (R.A.M)=
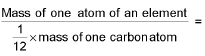 Total Number of nucleons
Total Number of nucleons - Y-map
Density:
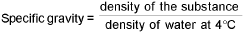
For gases:
Absolute density (mass/volume) = 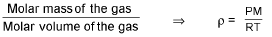
Vapour density 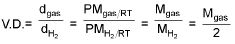
Mgas = 2 V.D.
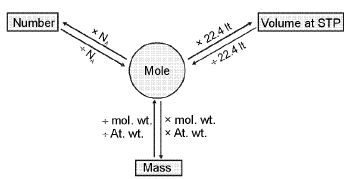
Mole-mole analysis:
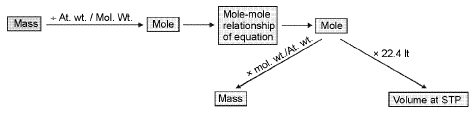
Concentration terms:
Molarity (M):
∴ 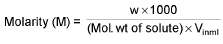
Molality (m):
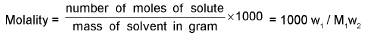
Mole fraction (x):
∴ Mole fraction of solution (x1) =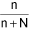 ∴ Mole fraction of solvent (x2) =
∴ Mole fraction of solvent (x2) =
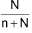
% Calculation:
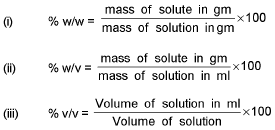
Derive the following conversion:
- Mole fraction of solute into molarity of solution M =
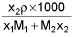
- Molarity into mole fraction x2 =
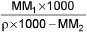
- Mole fraction into molality m =
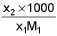
- Molality into mole fraction x2 =
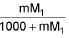
- Molality into molarity M =
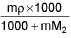
- Molarity into Molality m =
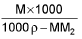
M1 and M2 are molar masses of solvent and solute, ρ is density of solution (gm/mL)
M = Molarity (mole/lit.), m = Molality (mole/kg), x1 = Mole fraction of solvent, x2 = Mole fraction of solute
Average/Mean atomic mass:
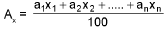
Mean molar mass or molecular mass:
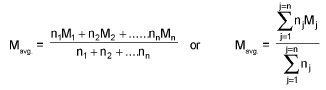
Calculation of individual oxidation number :
Oxidation Number = number of electrons in the valence shell - number of electrons left after bonding
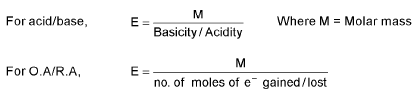
Concept of Equivalent weight/Mass:
For elements, equivalent weight (E) =
Equivalent weight (E) = 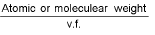 (v.f. = valency factor)
(v.f. = valency factor)
Concept of number of equivalents:
No. of equivalents of solute = 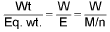
No. of equivalents of solute = No. of moles of solute x v.f.
Normality (N):
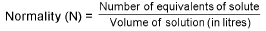
Normality = Molarity x v.f.
Calculation of valency Factor:
n-factor of acid = basicity = no. of H+ ion(s) furnished per molecule of the acid,
n-factor of base = acidity = no. of OH- ion(s) furnised by the base per molecule.
At equivalence point:
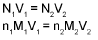
Volume strength of H2O2:
20V H2O2 means one litre of this sample of H2O2 on decomposition gives 20 It. of O2 gas at S.T.P.
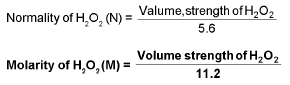
Measurement of Hardness:
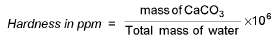
Calculation of available chlorine from a sample of bleaching powder :
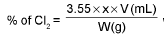 where x = molarity of hypo solution and v = mL. of hypo solution used in titration.
where x = molarity of hypo solution and v = mL. of hypo solution used in titration.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|