UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Science & Technology for UPSC CSE > Fundamentals of Medicine, Causes of Disease
Fundamentals of Medicine, Causes of Disease | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
- Etiology: Etiology is the study of the causation of disease. It may be intrinsic (within the body) or extrinsic (outside the body).

- Pathology: Pathology deals with the study of diseases and their causes.
- Homeostasis: The mechanism by which the body is kept in equilibrium is known as Homeostasis.
- Predisposing Causes: These are those that make the person susceptible to the disease and are also known as remote, distant or preparatory causes.
- Pathogenesis: The mechanism by which the causes produce disease.
- Symptoms or Signs is the outward manifestations of the patient suffering from disease while alive.
- The lesion is the alteration in the structure, detectable macroscopically by the naked eye or microscopically.
- The incubation period is the time that elapses between the action of a cause and the manifestation of disease.
- Prognosis is the estimation of the probable severity and outcome of the disease.
- Morbidity is the percentage of deaths among the population affected by a disease.
- An autopsy is seeing with one's own eyes. Also known as necropsy.
- A biopsy is an examination of tissues received from the living body.
Causes of Disease
Etiological Factors
The disease-causing agents can be classified as follows:
I. Genetic or Inherited Causes: These causes are transmitted to the offspring through the germplasm.
- Lethal factors: Some factors cause death in utero or after birth death
- Sublethal factors: Those factors which are inherited and interfere with the function of the body but do not cause death.
- Defects that are inherited errors in structure or function
Cryptorchidism: The condition in which one or both testicles do not descend to the scrotal sac and remain in the abdominal cavity. The testicle is complete or partial non-functional in this condition.
Webbed digits: Web-like structures are present in between the digits.
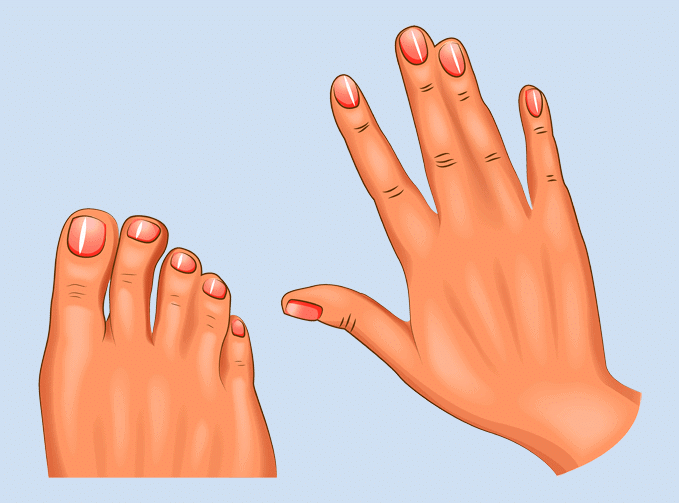 Webbed Digits
Webbed Digits
II. Non-genetic or Non-inherited Defects: These causes do not transmit through the germplasm.
Anomalies: Developmental defect affecting an organ or part of the body.
1. Disturbances in the development
2. Arrest of development
- Agenesia or aphasia: Complete absence of a body part. Agenesia renale—when there is no Kidney in the body.
- Hypoplasia: Reduction in size of a body part.
- Atresia: Closer of the lumen of a hollow organ or duct - Atresia ani (closure of ana opening)
- Fissure: Inability to fuse the part on the median line.
- Fusion of paired organs: Horseshoe kidney.
3. Excessive Development
- Congenital hypertrophy: Increase in the size of the organ. Example: Ventricular hypertrophy is the hypertrophy of the myocardium of the ventricle.
- Increase in number - Example: Polydactyla is the presence of supernumerary digits on the hands or feet.
The document Fundamentals of Medicine, Causes of Disease | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Science & Technology for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Fundamentals of Medicine, Causes of Disease - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main causes of diseases? |  |
Ans. The main causes of diseases can vary depending on the specific illness, but some common causes include infections (such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi), genetic factors, environmental factors (such as exposure to toxins or pollutants), lifestyle choices (such as poor nutrition or lack of exercise), and underlying medical conditions.
| 2. How do infections cause diseases? |  |
Ans. Infections can cause diseases by invading the body and disrupting its normal functioning. When a pathogen, such as a bacteria or virus, enters the body, it can multiply and produce toxins that harm cells and tissues. This can lead to a range of symptoms and can potentially cause severe illness or even death if left untreated.
| 3. Can genetic factors alone cause diseases? |  |
Ans. Genetic factors alone can contribute to the development of certain diseases. Some conditions, known as genetic disorders, are caused by mutations or changes in specific genes. These genetic abnormalities can result in various health problems, including inherited conditions like cystic fibrosis or certain types of cancer. However, it is important to note that genetic factors often interact with other environmental or lifestyle factors to increase the risk of disease.
| 4. How do environmental factors contribute to disease development? |  |
Ans. Environmental factors play a significant role in the development of diseases. Exposure to harmful substances such as pollutants, toxins, or radiation can damage cells and tissues, leading to various health problems. Additionally, environmental factors can also impact lifestyle choices, such as access to healthy food or safe living conditions, which can further contribute to disease development.
| 5. Can lifestyle choices be a major cause of diseases? |  |
Ans. Yes, lifestyle choices can be a major cause of diseases. Poor nutrition, lack of exercise, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and stress are examples of lifestyle factors that can significantly increase the risk of developing various illnesses, including heart disease, diabetes, certain types of cancer, and mental health disorders. Making healthier lifestyle choices can help prevent or manage these diseases.
Related Searches

















