GC Leong: Summary of Landforms Made By Running Water | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
- Denudation is general lowering of earth’s surface by agents of erosion such as Wind, Water, Ice, Waves etc.
- Unlike glaciers & snow, which are confined to cold & temperate latitudes; waves, which acts only on coastlines; winds, are only efficient in deserts; the effect of running water is felt all over the world, thus, making it the most important agent of denudation.
- The source of river is generally found in an upland region with a slope down for the ran offs.
- Hence, the uplands form the catchment areas of the rivers & the crest of mountains become the divide or watershed from which the streams flows down the slope.
- The initial stream that exists as a consequence of the slope is called the consequent stream.
- As the consequent stream wears down the surface, it is joined by several tributaries from either side.
Processes of River Action
- When a river flows it carries with it eroded materials which can be divided into 3 distinct types
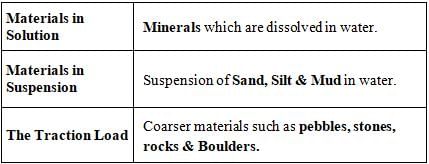
- The ability of river to move the various grades of materials depends greatly on the volume of the water, velocity of the flow & size, shape and weight of the load.
- It is said that by doubling the velocity of a river, its transporting power is increased by more than 10 times.
River Erosion and Transportation Processes
1. Corrasion / Abrasion
- Mechanical grinding of river’s traction load against the banks & bed of the river.
- The rock fragments hurdle against the sides as well as bottom of the river leading to lateral & vertical corrosion.
- Lateral corrasion is sideways erosion which widens the V shaped valley.
- Vertical corrasion is the downward action which deepens the river channel.
2. Corrosion / Solution
- Chemical action of water on soluble or partly soluble rocks with which river come into contact. For Example: in case of Calcium carbonate.
3. Hydraulic Action
- Mechanical loosening & sweeping away of materials by river water.
- Mainly by surging into the crevices & cracks of rocks & disintegrating them.
4. Attrition
- Wear & tear of transported material among them when they roll and collide into one another.
Upper Mountain Course (Youth Stage)
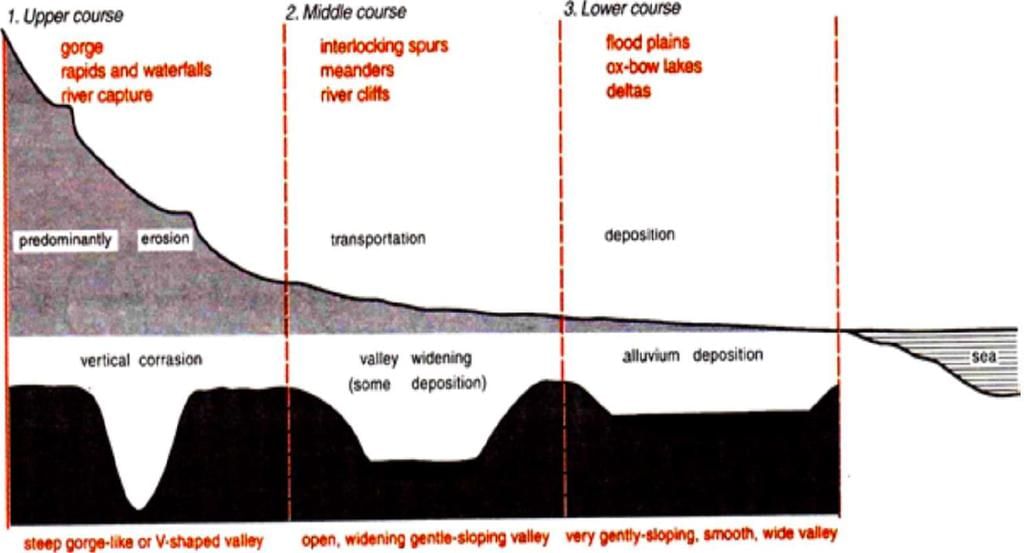 The graded long profile and typical cross section of a river from source to mouth
The graded long profile and typical cross section of a river from source to mouth
- Begins at the source of the river near the watershed, generally at the crest or mountain range.
- Flow is very swift as it descends the steep slopes & predominant action of the river is vertical erosion.
- Valley developed is thus deep, narrow & distinctively V shaped which sometimes results in formation of gorges & canyons.
Some of the features associated with the upper course of the river
1. River Capture
- Also known as river piracy or river beheading.
- Its development depends upon different rate of back cutting (headward erosion) into a divide mainly due to difference in precipitation received by streams.
- If one side of the divide cut more rapidly than the other then its greater erosive power will succeed in enlarging its basin at the expense of weaker stream.
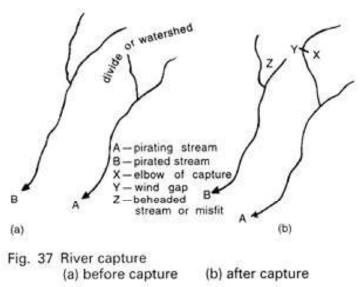
- For example in given figure, Stream A may eventually break through the divide & capture & pirate stream B.
- The bend at which the piracy occurs is termed as Elbow of the capture & the beheaded stream is called as misfit.
- The valley below the elbow is wind gap which may be useful for road & rail route.
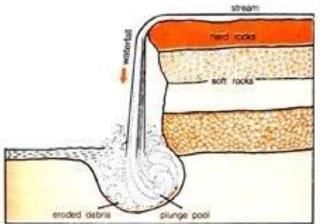
2. Rapids, Cataracts & Waterfalls
- Liable to occur in any part of river course but most numerous in mountains course where changes in gradient are more abrupt & frequent.
- Due to unequal resistance of hard & soft rocks transverse by a river, the outcrop of hard rock may cause a river to jump & fall, known as Rapids.
- Similar falls of greater dimensions are referred as Cataracts.
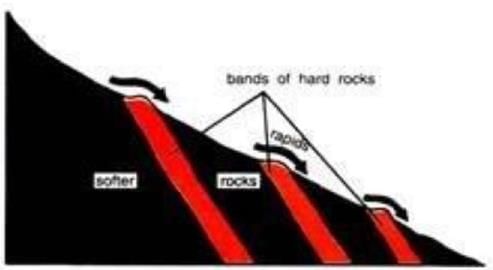
- When river plunges down in a sudden fall via. some height, they are called Waterfalls.
- Their greater force usually wears out a plunge pool beneath.
Middle or Valley Course (Maturity Stage)
- In the middle course, lateral corrasion tends to replace vertical corrasion; active corrasion of the bank thus widens V shaped valleys.
- Volume of water increases with the confluence of many tributaries which increases river’s load.
- The work of the river is predominantly transportation with some deposition in clearer manner, although velocity does not decrease.
Some of the features associated with the Middle course of the river
1. Interlocking spurs
- Downstream, interlocking spurs that project from both side of the valley are cut back into a line of bluffs.
- Rainwash, soil creeps, landslides & gullying gradually widens the valley, cutting back the sides.
- As the stream flows on, the meanders migrate progressively outward with the interlocking spurs alternating with the undercut slopes.
- Meanders in the middle course are only the beginning of the downward swing as bends are restricted by the interlocking spurs.
- In the lower course, the loops are enlarged across the level plain & meanders are fully developed.
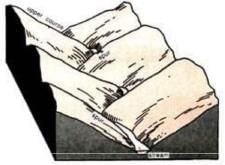 Interlocking spurs
Interlocking spurs
2. River cliffs & Slip off slopes
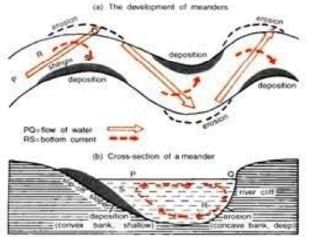 Meanders
Meanders
- When the flow of water PQ enters the bend of the river, it dashes straight into Q, eroding the outer bank into a steep river cliff at Q.
- The water piles up on the outside of the bend due to centrifugal force.
- A bottom current RS is setup in a cork screw motion & is hurled back into midstream & inner bank. Shingle is thus deposited here at S, where the slip off is gentle.
- The outer bank is therefore the bank of continuous erosion & the inner bank is the bank of continuous deposition.
3. Meanders
- As water flowing under gravity seldom flows straight for long distance, a winding course soon develops.
- The irregularities of the ground forces the river to swing in loops forming Meanders.
Lower or Plain Course (Old Stage)
- The river moving downstream across a broad, level plain is heavy with debris brought down from the upper course.
- Vertical corrasion has almost ceased though lateral corrasion still goes on to erode its banks further.
- Volume of water is greatly swelled with work of the river is mainly depositional, building up its bed & forming flood plains.
Some of the features associated with the plain course of the river
1. Flood Plain
- During sporadic floods, large quantity of sediments are spread over the low lying adjacent areas by the rivers, thus gradually building up a fertile flood plain.
- When the river flows normally its bed is raised through accumulation of deposits.
- Material is also deposited on the sides forming raised banks called Levees.
- In an attempt to minimize the risk of the floods, artificial embankments are erected on the natural levees.
- Nowadays, huge dredgers are also brought up in use to deepen the channels to avoid excessive sedimentation.
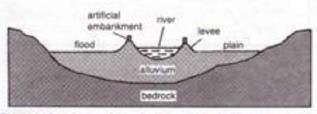 Section of a flood plain (with levee and artificial embankment)
Section of a flood plain (with levee and artificial embankment)
2. Ox-Bow Lakes (Dead Lake)
- In the lower course of the river, a meander becomes very much pronounced.
- The outside bank is so rapidly eroded that the river becomes almost a complete circle.
- There comes a time, when the river cuts through the narrow neck of the loop, abandoning an Ox-bow lake & then flows straight.
- The ox-bow lake will later degenerate into a swamp through subsequent floods that may silt up the lake, thus becoming marshy & eventually dries up.
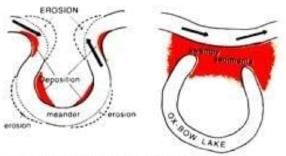 The formation of an ox bow lake
The formation of an ox bow lake
Delta
- When the river reaches the sea, the tine materials it has not dropped yet are deposited at its mouth, forming a fan shaped alluvial area called a delta.
- The alluvial tract is in fact the seaward extension of the flood plains.
- Due to obstruction caused by the deposited alluvium, the river may discharge its water through several channels called distributaries.
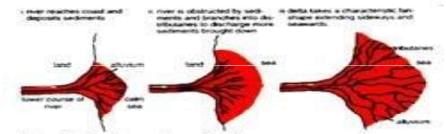 The formation of deltas
The formation of deltas
(a) Stages in the formation of a delta
 (b) Section through the lower course of a river, showing flood plain and delta
(b) Section through the lower course of a river, showing flood plain and delta
Favourable conditions for delta are
- Active vertical & lateral erosion in upper course of the river to provide extensive sediments.
- Coast should be sheltered preferably tideless & no strong current at right angle to the mouth of the river washing away the sediments.
- Sea adjoining the delta should be shallow or else the load will disappear in deep waters.
- No large lakes in the river course to filter off sediments.
River Rejuvenation
- When in the course, if the river parts are uplifted or depressed, they rejuvenate the river & make it young again.
- Rejuvenation mainly occurs when there is either a fall in sea level relative to the level of the land or a rise of the land relative to the sea known as negative movements leading to fall in river’s base level.
- This steepens the slope so that river’s eroding power or down cutting is renewed.
- River with its renewed vigour cuts into the former plain, leaving behind traces on both sides of the river.
- Point where the old & rejuvenated profile meet is called Knick point, which can be seen as waterfalls and rapids.
- If rejuvenation occurs in upper course, the river valleys are deepened & steep sided gorges are formed.
- In middle & lower course vertical corrasion replaces lateral corrasion & thus the existing meanders are vertically eroded by the rejuvenated stream.
- A distinct new trench is cut in old valley & the river develops a deep valley with incised meanders; which are of 2 types’ entrenched meanders & ingrown meanders.

- A rejuvenating river can erode vertically into the former flood plain to produce features called river terraces.
- If vertical erosion is rapid then paired terraces are formed either side of the channel.
- If vertical erosion is slower though, unpaired terraces form as the river is given opportunity to meander.
- River terraces are particularly useful for settlements as they provide flat areas above the present floodplain.
- Oxford, Cambridge and London all are developed on the river terraces of the Isis, Cam and Thames respectively.
- A positive movement occurs when there is either a rise in sea level relative to the level of the land or a fall of the land relative to the sea level.
- This will submerge the land along the coast, drown the valleys & weaken the erosive power of the river.
- The lower course of the river may be partly in the sea & features of deposition are shifted in the middle course; with the upper course affected only a little.
- Rise in the sea level mainly occurs due to release of the water locked up in the ice masses during the Quaternary ice ages.
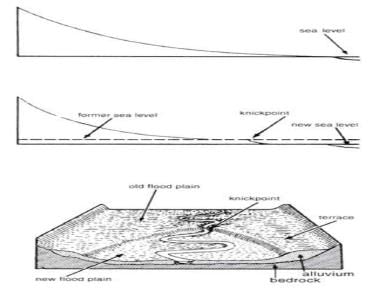 River terraces and knickpoint due to rejuvenation
River terraces and knickpoint due to rejuvenation
The rejuvenated river outs down into previously deposited sediments to form a new valley leaving terraces at either side- At the head of rejuvenation the river falls to its new valley at a knickpoint
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|

















