Geography: November 2024 UPSC Current Affairs | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Dinosaurs and UNESCO Global Geoparks
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Geological Survey of India is advocating for the Dinosaur Fossil Park and Museum located in Raiyoli village, Gujarat, to receive a UNESCO Global Geoparks designation.
Key Takeaways
- The site is recognized for its geological significance, having been the location where large dinosaur bones and fossilized eggs were discovered in the early 1980s.
- It is one of the largest dinosaur egg hatcheries globally, ranking third after Aix-en-Provence in France and the Mongolian Gobi Desert.
- The park attracted international attention in the 1990s when a team of 50 palaeontologists studied its dinosaur eggs.
Additional Details
- Geological Importance: Dinosaur bones belonging to the carnivorous species Rajasaurus Narmadensis and Rahiolisaurus Gujaratensis from the Late Cretaceous period (approximately 67 million years ago) were discovered here.
- Historical Context: The first dinosaur bones in Asia were found in India in 1828 by Captain William Henry Sleeman, later named Titanosaurus indicus in 1877, a large herbivore from the Late Cretaceous period.
- Fossil Distribution: Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat are key regions for dinosaur fossils, yielding significant discoveries such as Barapasaurus (herbivorous) and Indosuchus (carnivorous).
- Hatcheries: India is considered one of the largest dinosaur hatcheries globally, with nesting sites identified in Jabalpur (MP), Balasinor (GJ), and Dhar District (MP).
- UNESCO Global Geoparks: These are designated areas with significant geological sites, aimed at protection, education, and sustainable development. Currently, there are 213 Global Geoparks across 48 countries, but India lacks any such designation.
Gujarat's Dinosaur Fossil Park is a site of global significance, showcasing vital dinosaur fossils and eggs, and emphasizing India's rich paleontological heritage. With growing international interest, it has the potential to achieve UNESCO Global Geopark status, which could enhance geo-tourism and contribute to local development while preserving the geological and cultural history of the region.
Mains Question
Q: Evaluate the geological and paleontological importance of the dinosaur fossils found in India and their potential impact on geo-tourism.
Mangroves in Coastal Resilience
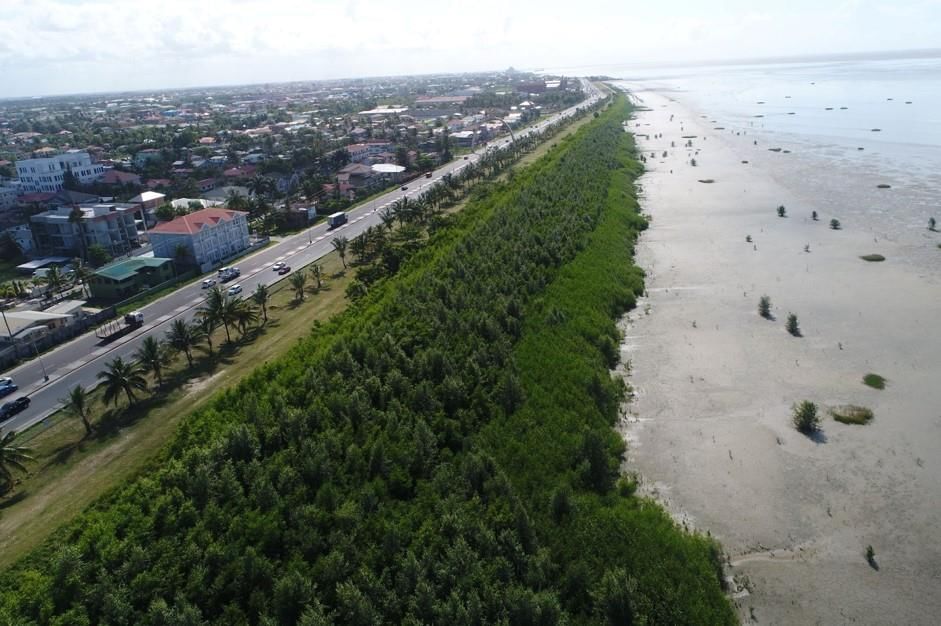

Why in News?
Recently, Cyclone Dana made landfall near Bhitarkanika National Park and Dhamra Port in Odisha, highlighting the crucial role of mangrove forests in mitigating cyclone impacts. The cyclone caused less damage than expected due to the extensive mangrove cover in Bhitarkanika, which has historically withstood the effects of several cyclones, including the Super Cyclone of October 1999.
Key Takeaways
- Mangroves serve as natural barriers that protect coastal areas from storm surges and erosion.
- India's mangrove cover is approximately 4,992 sq. km, constituting 0.15% of the country's total geographical area.
- Bhitarkanika National Park is one of the most significant mangrove ecosystems in India, second only to the Sundarbans.
Additional Details
- Mangroves: These are salt-tolerant trees and shrubs that thrive in estuarine and intertidal regions where freshwater meets saltwater. Their adaptations, such as aerial roots and waxy leaves, enable survival in saline environments.
- Role in Cyclone Mitigation: Mangroves stabilize shorelines, reduce erosion, and protect communities from cyclone-driven storm surges.
- Conservation Initiatives: Notable initiatives include the MISHTI initiative for mangrove plantations and the Blue Carbon Initiative aimed at restoring coastal ecosystems.
- Strengthening mangrove conservation is essential for enhancing India's resilience to cyclones and safeguarding coastal communities. Integrating ecological approaches with infrastructure development is vital for achieving sustainable disaster risk reduction.
WMO’s Greenhouse Gas Bulletin 2023
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) published its annual Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Bulletin for 2023. This bulletin offers the latest analysis from the WMO Global Atmosphere Watch (GAW) regarding atmospheric concentrations of GHGs.
Key Takeaways
- Since 1990, the warming effect from GHGs has increased by 51.5%, with CO2 being responsible for approximately 81% of this effect.
- In 2023, GHG levels reached record highs, with CO2 rising by 2.3 ppm from 2022 to reach 420 ppm.
- 2023 has been recorded as the warmest year, surpassing the previous record set in 2016, with global temperatures being 1.48°C above the pre-industrial average.
- The current CO2 concentration is comparable to levels seen 3-5 million years ago, when global temperatures were 2-3°C higher.
Additional Details
- Causes of Increased CO₂ Levels: The rise in CO2 levels is largely attributed to human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and industrial processes.
- El Niño Impact: The El Niño phenomenon has led to warmer weather and drier conditions, especially in South Asia, resulting in increased forest fires and GHG emissions.
- Vicious Cycle Warning: Rising CO2 levels may turn natural ecosystems into sources of GHGs, as warming could lead to more carbon release from wildfires and reduced absorption by oceans.
- Methane Surge: Methane levels have surged, with the largest increase occurring from 2020 to 2022, particularly from natural wetlands due to warmer La Niña conditions.
- Policy Responses: According to the UNFCCC 2023 assessment, current Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) could reduce global emissions by 2.6% from 2019 to 2030, which falls short of the 43% reduction needed to limit warming to 1.5°C as per the Paris Agreement.
- The UNFCCC has urged countries to submit stronger NDCs by February 2024, emphasizing the need for enhanced global emission reduction efforts.
- The WMO's 2023 Greenhouse Gas Bulletin highlights alarming increases in GHG levels and underscores the urgent need for stronger policy responses. As climate change continues to escalate, collaboration among nations and enhanced national contributions are crucial for mitigating environmental impacts and ensuring global sustainability.
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
















