Geography of Africa | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
INTRODUCTION
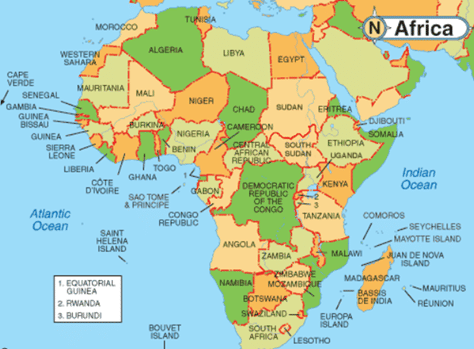
- Africa is the second largest continent in the area (30,330,000 sq Km) which covers 6% of Earth’s total surface area and 20.4 % of its total land area.
- Algeria is Africa’s largest country by area, and Nigeria by population.
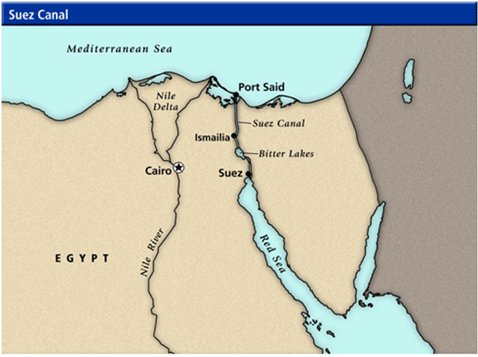
Separated from Europe by the Mediterranean Sea, it is joined with Asia at its northeast extreme end by the Isthmus of Suez 163 Km wide. - It is bounded by the Red Sea along the Sinai Peninsula to the northeast, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
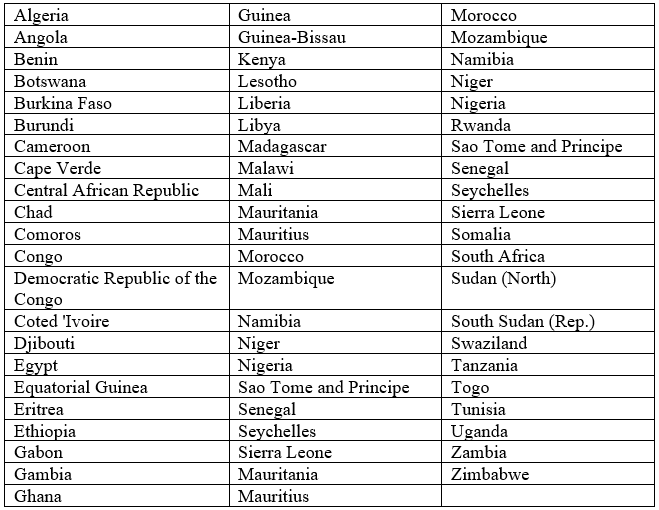
- It has fully recognized 54 sovereign states.
Alphabetical list of countries in Africa –
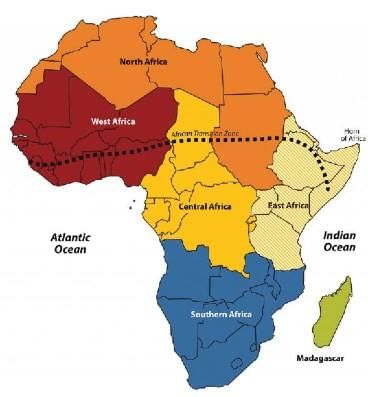
REGIONAL DIVISIONS OF AFRICA
The physiographic divisions of Africa are into the following six regions:
- Northern Africa
- Northeast Africa
- Eastern Africa
- Central Africa
- Southern Africa
- Western Africa
➢ Northern Africa
It extends from Algeria in the north, through, the Canary Islands, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Ceuta, Egypt, Libya, Madeira, Melilla, Morocco, Sudan and Tunisia, It reaches up to Western Sahara.
➢ Northeast Africa
It is also called the horn of Africa which extends several hundred kilometers into the Arabian Sea and lies along the southern side of the Gulf of Aden. It contains countries such as Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
➢ Eastern Africa
The extensive area stretches from the Red Sea and the Horn of Africa to Mozambique including Burundi, Comoros, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mayotte, Mozambique, Réunion, Rwanda, Seychelles, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe.
➢ Central Africa
It is the large landmass situated exactly in the middle of the continent covering Angola, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, São Tomé and Príncipe.
➢ Southern Africa
It is the southern most part of the continent and covers the countries such as Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, and Swaziland.
➢ Western Africa
It is situated roughly at 26°W to 16° E longitude covering countries like Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Saint Helena, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo.
MAJOR PHYSICAL DIVISIONS OF AFRICA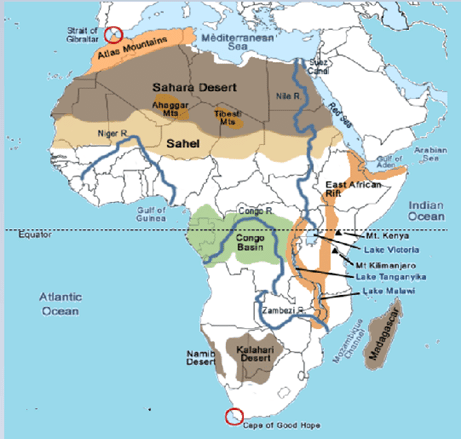
The major physical divisions of African continent are:
- The Plateau
- The Fold Mountains
- Deserts
- Rivers
- Islands
➢ The Plateaus
The vast African continents are famous for its saucer-shaped and steep edged plateaus that are facing towards the coast and extending from Guinea coast to Somali Land and north Sahara to the Cape Province.
These are divided into three groups:
(i) South African plateau – The South African plateau as far as about 12°S, bounded east, west and south by bands of high ground which fall steeply to the coasts. The South African plateau is connected towards the north-east with the East African plateau.
(ii) East African plateau – The East African plateau, with probably a slightly greater average elevation, and marked by some distinct features. It is formed by a widening out of the eastern axis of high ground, which becomes subdivided into a number of zones running north and south and consisting in turn of ranges, tablelands and depressions.
(iii) Ethiopian Highlands – The third division of the higher region of Africa is formed by the Ethiopian Highlands, a rugged mass of mountains forming the largest continuous area of its altitude in the whole continent.
Plateaus –
(i) Katanga Plateau Farming, ranching, resource-rich – copper and Uranium deposits
(ii) Ethiopian Plateau Lake Tana (Source of Blue Nile), cooler despite close to the equator
(iii) Great Karoo Semi-desert region
(iv) Bie Plateau Important for copper, Agriculture and cattle rearing
(v) Adamawa Plateau Savannah vegetation, Bauxite deposits
➢ Mountains
- Africa is famous for its newly formed folded mountains.
- Prominent mountain ranges with some of the very high raised mountain peaks are the specialty of African Continents.
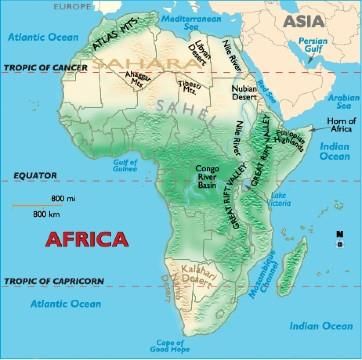
Some of the well known mountain ranges are:
Atlas Mountains –
- It is situated on the northwestern part of the continent stretching over an area of 2400 km towards the southwest direction across Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
- The range is again subdivided into high, medium, and Anti – Atlas group. The Jebel Toubkal is among such highlands or mountain whose height is 4165 m from sea level.
- It is a physical separator between the extensive coasts of the Mediterranean and the Atlantic Sea and the Sahara Desert.
Ruwenzori Mountains –
- Stretching over an area of 240 sq. miles the range borders Uganda and Congo (Kinshasa) and thought to be the “Mountains of the Moon.
- Mount Stanley at Margherita Peak (5,119 m is the highest pick of this mountain system.
- It is a gigantic horst of six separate glaciated masses which falls steeply westward to the Western Rift Valley.
Mount Elgon –
- It is an extinct volcanic mountain situated in the northeast part of lake Victoria on the Uganda – Kenya border.
- The height is about 4,321 km from the mean sea level.
- As a volcanic mountain it has a crater which is 610 m deep and 8 km across.
Tibesti Mountains –
- These are mostly situated in the northern part of Chad and spread west into northern Niger and the Southern border area of Libya.
- They have a volcanic origin.
- The highest peak is 3,415 m. from mean sea level.
Ahaggar Mountains –
- The Ahaggar Mountains, also known as the Hoggar, is a highland region in central Sahara, or southern Algeria near the Tropic of Cancer. They are located about 1,500 km south of the capital, Algiers. Mount Tahat is the highest peak (2, 918 m).
- It has a volcanic formation.
The Drakensberg –
- These mountains are the highest in Southern Africa rising up at Thabana Ntlenyana at 3,482 m (11,422 ft) in height. They are located in the eastern part of South Africa, running from some 1,000 km. The highest peak is Thabana Ntlenyana at 3,482 m (11,422 ft). It is also the highest peak of Lesotho.
Mount Kenya –
- Mount Kenya is the highest mountain in Kenya, and the second-highest in Africa (after Mount Kilimanjaro). The highest peaks of the mountain are Batian (5,199m – 17,058 ft), Nelion (5, 188m – 17,022 ft) and Lenana (4,958 – 16,355 ft). Mount Kenya is located in central Kenya, just south of the equator, around 150 km (95 miles) north-northeast of Nairobi.
Kilimanjaro –
- Kilimanjaro with its three volcanic cones, Kibo, Mawensi, and Shira, is an inactive stratovolcano in north-eastern Tanzania.
- Kilimanjaro is the tallest free-standing mountain rise in the world rising 4,600 m (15,100 ft) from its base and includes the highest peak in Africa at 5,895 meters (19,340 ft).
➢ The Deserts
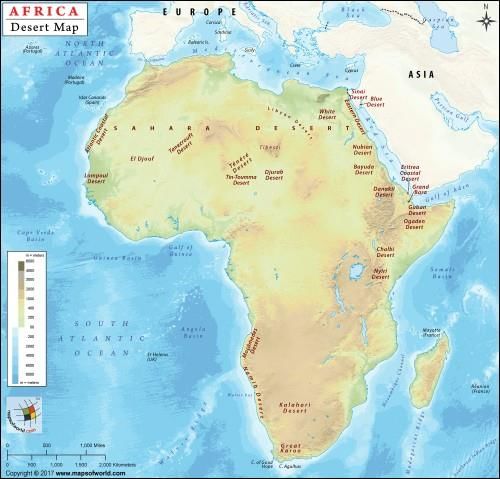
- The Sahara, the largest hot desert in the world, stretches across the entire width of North Africa. It covers an area of approx. 3,320,000 sq. miles.
- The major countries contributing their land to Sahara deserts are Libya, Algeria, Egypt, Tunisia, Chad, Morocco, Eritrea, Niger, Mauritania, Mali, and Sudan.
- The Nubian Desert is the eastern region of the Sahara desert, between the Nile and the Red Sea. There is virtually no rainfall here, and there are no oases. It is in Egypt. It covers an area of 1,54,000 sq. miles approx.
- The Kalahari Desert lies in the south and the Namib Desert is along the south-west shore of Africa. It covers an area of 3,50,000 sq. miles and encroaching parts of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, Angola, and Zimbabwe.
(i) Sahara desert – Largest hot desert – subtropical HP zone, Tuareg tribes
(ii) Namib desert - Off-shore trade wind + cold Benguella current, sandy desert, Hottentots tribes
(iii) Kalahari desert - Rain-shadow effect, stony-rocky desert. Bushmen tribe (the oldest surviving tribal group of Africa)
(iv) Nubian desert - Separated by Libyan desert by Nile river rocky desert
➢ The Islands
There are very few islands near Africa.
- Madagascar (Malagasy) in the Indian Ocean is the largest island in Africa.
- To the north-west, in the Atlantic Ocean are the Canary Islands.
- West of Africa in the South Atlantic Ocean is the island of Saint Helena where Napoleon died in exile.
- Zanzibar belongs to Tanzania and is closer to the Indian Ocean.
- Madeira – Portugal
- Canary – Spain
- Cape Verde
- Mauritius
- Reunion – France
- Comoros – France
- Seychelles
Islands between Africa and Latin America –
- All of them –British overseas territories
- Ascension Islands– UK military base
- St. Helena Islands – the exile of Napoleon
- Tristan De Cunha Island – the most remote island of the world
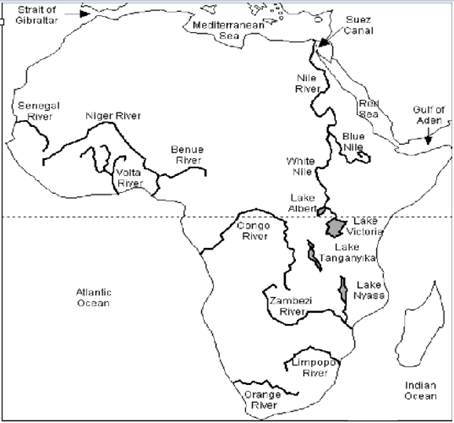
➢ The Rivers Of Africa
The most important ones are the Nile, the Congo, the Niger, and the Zambezi.
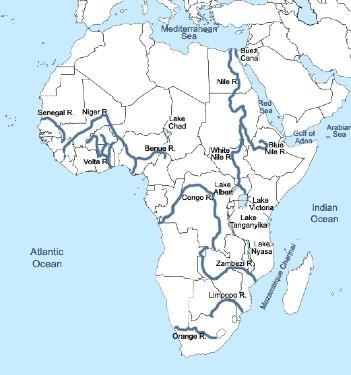
River Nile –
- This is the longest river in the world.
- It starts from many streams in the equatorial rainforest of the Lake Victoria and Ruwenzori Mountain (the mountains of the moon) region.
- From Lake Albert, it flows as the White Nile.
- At Khartoum, it is joined by the Blue Nile which starts from Lake Tana on the Ethiopian Highlands.
- The Nile flows from 3,000 kilometers through the dry Sahara Desert of Egypt and enters the Mediterranean Sea.
- Egypt is called the gift of the Nile because without the river it would have been a desert.
- Cotton cultivation,
- Petroleum at mouth, navigable, irrigation
- Aswan dam, lake Naseer
- Port Said and Alexandria at the mouth
- Cairo, Giza, Khartoum cities are on River Nile
River Congo or Zaire –
- The Congo is the second-longest river in Africa.
- It starts from the south-west of Lake Tanganyika and flows into the Atlantic Ocean.
- The Zaire basin is one of the wettest regions of the Earth and is covered with dense impenetrable jungle.
- The river and its network of tributaries are not navigable because of rapids and waterfalls caused by the descent from the plateau to the coast.
- Origin : Katanga Plateau
- Boyoma waterfall
- Pigmy tribes
- Petroleum reserve at the mouth
- Crosses equator twice
River Niger –
- This river is the chief river of West Africa. It rises from the Fout Djllon Mountain quite close to the sea but flows north and then turns south again to form a wide arc.
- Finally, it joins the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean.
River Zambezi –
- River Zambezi flows into the Indian Ocean.
- The famous Victoria Falls at the head of a long gorge is on this river.
River Limpopo –
- River Limpopo also flows into the Indian Oceans, which crosses the Tropic of Capricorn twice.
River Orange –
- This flows from the Drakensberg Mountains into the Atlantic Ocean.
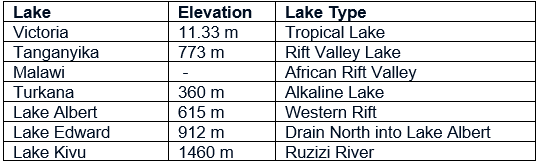
Lakes Of Africa
- Lake Victoria is the second-largest freshwater lake in the world. It is the largest lake in Africa. It is situated on the block mountain between the two branches of the Great Rift Valley. The Equator passes through it. It is the source of the white Nile.
- The lakes of the rift valley. There is a string of lakes in the rift valley. Lake Tanganyika and Lake Nyasa (Malawi) are the larger ones.
- Lake Tana is on the Ethiopian Plateau. It is the source of the Blue Nile.
- Lake Chad at the southern edge in the Sahara Desert is in a region of inland drainage. Streams start from the surrounding hills and flow into this lake instead of the sea. River Charl is the largest river in this area.
- Lake Nasser is on the river Nile. It is a man-made lake located between Egypt and Sudan.
- Lake Kariba is situated in the southernmost part of Africa a Zambezi river. It is one of the biggest looks man-made like and it is the largest producer of hydroelectricity in Africa.
- Lake Assal is situated in Djibouti and the lowest point in Africa.
Famous Lakes of Africa –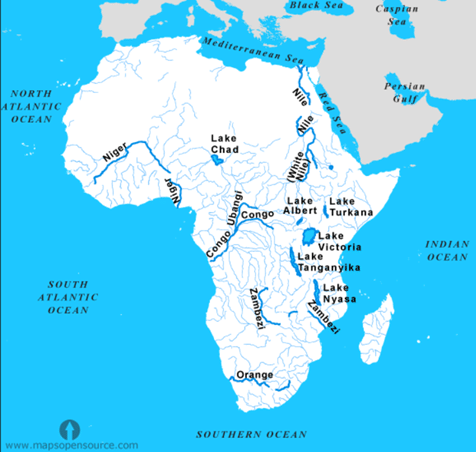
Africa lakes and rivers
Important Dams And Waterfalls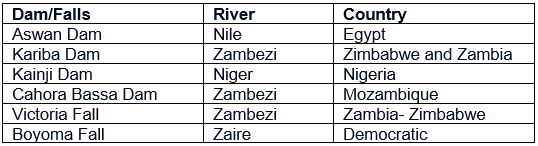
CLIMATE
It is quite obvious that as a large continent Africa experiences a highly variable climate.
Keeping in view the prevailing weather conditions such as temperature, rainfall, humidity etc the climatic zones of Africa are:
- Equatorial rainforest climate
- Temperate grasslands
- Mediterranean Hot Summer
- Hot Desert Climate
- Tropical Wet/Dry (Savanna) Climate
Natural Vegetation
There are extensive areas in Africa where few people live and where natural vegetation and wild animals have not been disrupted by such activities as farming or the raising of livestock. In some parts of the continent, large forest reserves have been established.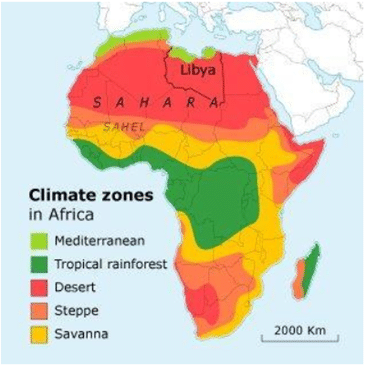
Tropical Rain Forests
- The large area of Africa is covered by tropical rain forests or selvas type of vegetation covering less than a tenth of the continent with heavy rain throughout the year. These forests contain several layers of vegetation.
- The top layer consists of the crowns of trees rising 125 to 250 feet (38 to 76 m) in height; the lower layers are arranged according to their height like shorter trees, shrubs, and vines respectively.
- They yield pulp, timber, and such cabinet woods as mahogany, ebony, and teak. Oil palms, rubber-producing trees and vines, orchids, and lilies are among the numerous kinds of plants found in these forests.
Tropical Savannas
- Savannas, covering perhaps one-third of the continent, consist of areas mainly growing grass.
- There are spots of woodlands, scattered trees, or shrubs, depending on the length of the dry season. Coarse grasses up to 12 feet (3.7 m) high and large woodlands of deciduous trees are found near the border of Tropical forest. They even include many evergreens found in tropical rain forests, such as oil palms, rubber trees, and African ebony trees.
- Away from the Equator to the north and south, rainfall decreases and there is a zone where there is a definite dry season unlike the equatorial region where it rains always.
- This is the Sudan type of climate and has tropical Grassland or Savanna vegetation.
- This region continues over the Eastern Highlands and forms a wide area around the equatorial forests.
- The grass is thick and coarse. In some places, there is the tall elephant grass.
Tropical Steppes And Deserts
- Increased aridity and longer dry seasons are the main features of tropical steppes.
- These are regions that grow short grasses only.
- Thorny acacias, dwarf palms, and jujube trees are found here. Steppes bordering on deserts no trees are spotted, rather widely scattered bunches of grasses grow.
- Vegetation at oases includes date palms, fig-trees, willows, poplars, and tamarisks.
Mediterranean Forests
- Mediterranean type of vegetation in Africa is found along the northern and southern coast.
- Different variety of shrubs and small trees, both deciduous and evergreen are grown.
- The plants are able to withstand long, dry summers with waxy, leathery leaves and long taproots develop here.
- The northern region raises cork oak, olive trees, cedars, and pines; in the south, laurels, cedars, and ironwood.
- Grasses and low flowering plants grow only during the rainy months.
Montane Forests
- The Montane vegetation of highlands, particularly in Ethiopia and the mountains of the Great Rift Valley are such examples.
- Depending on elevation, latitude, and direction of the winds vegetation grows.
- The region under Montane forests yields valuable timber and cabinet woods along with bamboo and wild varieties of coffee and banana. The slopes of the mountain are covered with thick evergreen forests.
- The High Veld of southern Africa is temperate grassland between 3,500 and 11,000 feet (1,070 and 3,350 m) above sea level.
Mangrove Forests
- Mostly found along the African coast, but are most extensive along the Gulf of Guinea.
- A variety of other trees tailored to life in muddy estuaries and tidal flats are found other than Mangrove.
- Swamp and marsh also occur along the larger rivers and lakes of western and central Africa. Papyrus, tall grasses and lotus are the most common plants.
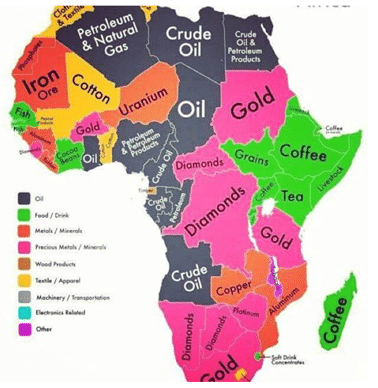
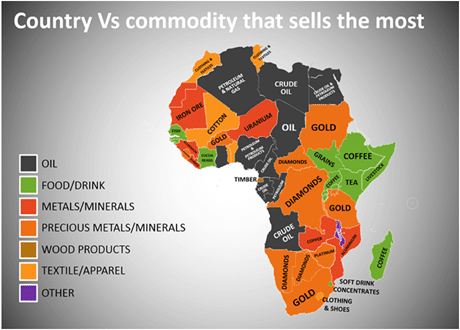
MINERAL RESERVE OF AFRICA
- Petroleum
- Coal Iron
- Diamonds
- Gold
- Uranium, Platinum
AGRICULTURE
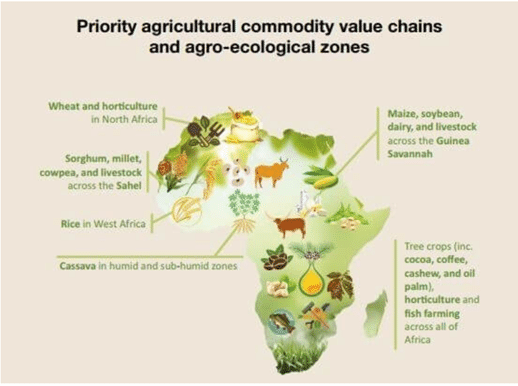
|
269 videos|870 docs|231 tests
|
FAQs on Geography of Africa - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major geographical features of Africa? |  |
| 2. How does Africa's geography influence its climate? |  |
| 3. How does Africa's geography impact its wildlife? |  |
| 4. How does Africa's geography affect its economy? |  |
| 5. How does Africa's geography impact its cultural diversity? |  |

















