Government Schemes | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
Introduction
The Union Budget for 2025-26, presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on February 1, 2025, builds on the vision of transforming India into a developed nation by 2047 under the Viksit Bharat initiative. It introduces new schemes and updates existing ones to promote economic growth, social inclusion, sustainability, and technological advancement. This document outlines the Government Schemes for 2025, including updates from central and state levels, reflecting the government's commitment to inclusive development and resilience against future challenges.

Government Schemes List 2025
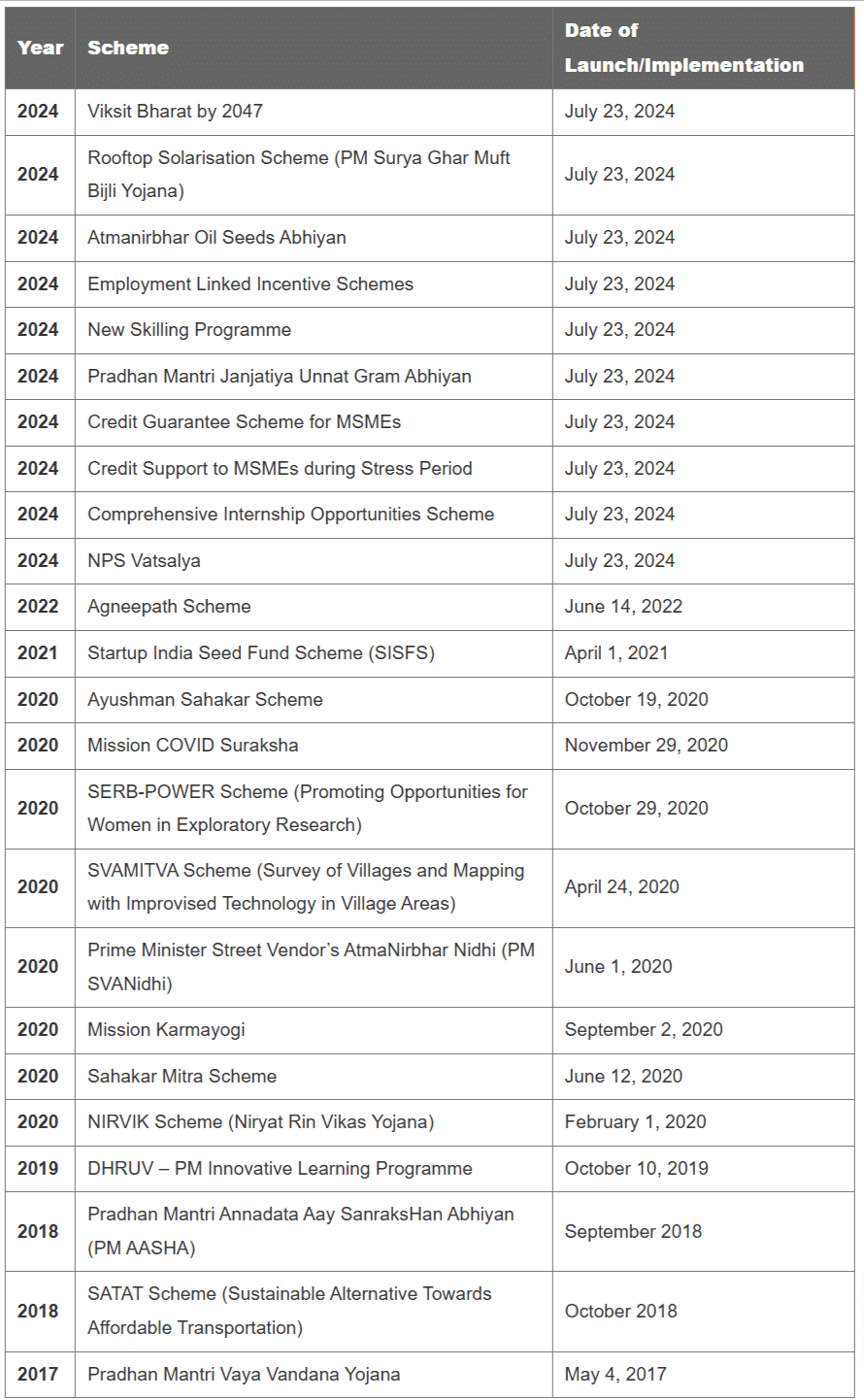
The Union Budget for 2025-26 introduces innovative schemes and enhances existing ones, focusing on digital transformation, green energy, youth empowerment, and rural development. Below is a list of key schemes, including new initiatives launched in 2025
1. Viksit Bharat by 2047
Objective: Transform India into a developed nation by 2047.
Purvodaya Plan:
- Regions Covered: Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, West Bengal, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Focus: Infrastructure development, human resource improvement, and economic growth opportunities.
- Goal: Establish the eastern region as a growth engine.
- Introduction
- Introduction of the Purvodaya Digital Corridor to establish high-speed internet and AI-based skill training centers in the eastern region.
Nuclear Energy Development:
- Initiatives: Collaboration with the private sector for Bharat Small Reactors, Bharat Small Modular Reactors, and advancement of new nuclear technologies.
- Launch of Bharat Clean Energy Fund to support nuclear and renewable energy integration.
2. Rooftop Solarisation Scheme
- Scheme Name: PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
- Objective: Provide 300 units of free electricity per month to 1.5 crore households via rooftop solar installations.
- Benefits:Annual savings of Rs. 15,000 – Rs. 18,000 per household. Facilitates EV charging and creates entrepreneurial and employment opportunities in the solar sector.
- Expanded to include community solar grids in rural areas, targeting 50,000 villages.
3. Atmanirbhar Oil Seeds Abhiyan
- Objective: Achieve self-sufficiency in oil seeds.
- Coverage: Groundnut, mustard, soybean, sesame, and sunflower.
- Focus Areas:Modern farming practices, high-yield varieties, value addition, procurement, market linkages, and crop insurance.
- Introduction of AI-based crop monitoring systems to enhance yield prediction and pest control.
4. Employment Linked Incentive Schemes
Scheme A: First Timers
- Target: New workforce entrants in the formal sector.
- Benefit:One-month wage up to Rs. 15,000 in three installments.
- Eligibility: Salary up to Rs. 125 lakh per month.
- Impact: Benefits 250 lakh youth.
Scheme B: Job Creation in Manufacturing
- Focus: Employment linked to first-time workers in manufacturing.
- Incentive:EPFO contribution support for the first four years.
- Impact: Benefits 30 lakh youth and their employers.
- Extended to green manufacturing sectors like EV and solar panel production.
Scheme C: Support to Employers
- Coverage: Additional employment across all sectors with salaries under Rs. 1.25 lakh per month.
- Incentive: Reimbursement of up to Rs. 3,000 per month for EPFO contribution for two years.
- Impact: Encourages employment of 60 lakh people.
5. New Skilling Programme
- Objective: Skill 20 lakh youth over the next five years.
- Initiative: Upgrade 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes with industry collaboration.
- Focus: Align courses with industry needs and introduce new courses in emerging sectors.
6. Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan
- Objective: Enhance socio-economic conditions of tribal communities.
- Coverage:63,000 villages in aspirational districts and tribal-majority areas and also Integration with fintech platforms for faster loan disbursal.
- Beneficiaries:5 crore tribal people.
- Launch of Tribal Digital Literacy Mission to provide internet access and digital skills training.
7. Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs
- Objective: Facilitate term loans to MSMEs without the need for collateral.
- Mechanism: Pooling credit risks and creating a self-financing guarantee fund.
- Guarantee Cover: Up to Rs. 100 crore per applicant.
8. Credit Support to MSMEs during Stress Period
- Objective: Ensure credit continuity for MSMEs during stressful periods to prevent NPAs.
- Support: Government-backed fund guarantees to ensure credit availability.
9. Comprehensive Internship Opportunities Scheme
- Objective: Provide internships to 1 crore youth within five years.
- Details:
- 12-month internships at the top 500 companies.
- Benefits: Rs. 5,000 monthly allowance and Rs. 6,000 one-time assistance.
- CSR Contribution: Companies bear training cost and 10% of internship cost.
- Inclusion of startups and green tech firms in the internship ecosystem.
10. NPS Vatsalya
- Objective: Allow parents and guardians to contribute to NPS for minors.
- Feature: Seamless conversion of minor's NPS to a regular account upon reaching the age of majority.
- Introduction of a mobile app for real-time tracking of NPS contributions.
11. Bharat Digital Education Mission
Objective: Provide free digital education resources to 2 crore students in rural and semi-urban areas.
Focus: AI-driven personalized learning platforms and tablet distribution.
Impact: Bridge the digital education gap by 2030.
12. Green Mobility Yojana
Objective: Promote electric vehicle adoption in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Details: Subsidies for EV purchases and establishment of 5,000 charging stations.
Impact: Reduce carbon emissions and create 10 lakh jobs in the EV sector.
Changes in Existing Schemes
PM Awas Yojana
- New Target: 4 crore additional houses by 2027 in rural and urban areas.
- Introduction of eco-friendly construction materials for sustainable housing.
- Urban 2.0 Initiative:
- Focus on providing housing for 1 crore urban middle-class and poor families.
- Investment: Rs. 12 lakh crore.
Skill Loan Scheme
- Revised Loan Limit: Loans up to Rs. 10 lakh with a government-backed fund guarantee.
- Impact: Assists 30,000 students annually.
Mudra Yojana
- Enhanced Loan Limit: Loans up to Rs. 25 lakh under the ‘Tarun’ category.
- Focus: Targeting entrepreneurs with a successful loan repayment track record.
- Digital loan application portal for faster processing.
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
- Phase IV: Provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations with larger populations.
- Integration of solar-powered streetlights along rural roads.
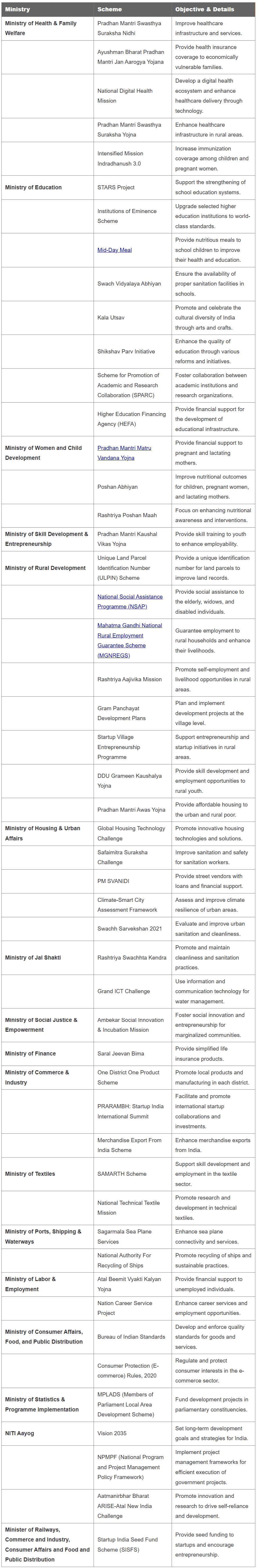
List of Government Schemes Ministry-wise
Latest Government Schemes in India
Important Government Schemes in Detail
Several programs are launched by the central ministries on behalf of the Indian government to promote the social and economic well-being of the nation. These schemes are crucial for preparation in government employment exams, such as the UPSC Civil Services Exam.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY)
- Objective: Provide affordable housing to urban and rural residents.
- Launch: June 25, 2015.
- Details: Interest rates starting at 6.5% per annum for up to 20 years. Eligibility for EWS and LIG categories extended until March 31, 2028, with a focus on eco-friendly construction materials.
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana
- Objective: Ensure food security for ration card holders.
- Launch: March 26, 2020.
- Details: Provides 5 kg of rice or wheat and 1 kg of dal per ration card holder, covering 90 crore beneficiaries until December 2026.
Meri Policy Mere Hath
- Objective: Deliver crop insurance to farmers' doorsteps.
- Launch: February 18, 2016 (under Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana).
- Details: Integrated with mobile apps for real-time claim processing and farmer support.
Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA)
- Objective: Enhance efficiency and access to quality higher education.
- Details: Provides strategic funding for state universities, including virtual reality-based learning labs and AI-driven academic programs.
Support for Marginal Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE)
- Objective: Provide recovery, medical assistance, and skill development for marginalized communities.
- Details: Includes mental health support programs and vocational training for sustainable livelihoods.
Jal Jeevan Yojana
- Objective: Connect 6 crore rural households to the public water system by 2027.
- Details: Allocation of Rs. 90,000 crore for smart water meters and community water management systems.
Jal Shakti Abhiyan
- Objective: Promote water conservation and management.
- Launch: March 22, 2021.
- Details: "Catch the Rain 3.0" campaign extended to urban and rural areas, running from March to November 2026, with IoT-based water monitoring.
Ayushman Bharat Yojana
- Objective: Provide health insurance of up to Rs. 5 lakh per family per year.
- Launch: 2018.
- Details: Covers over 10 crore vulnerable families, including geriatric care and telemedicine services.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana (PM-KISAN)
- Objective: Provide Rs. 8,000 annually to small and marginal farmers.
- Launch: 2019.
- Details: Disbursed in three equal installments of Rs. 2,667 each, directly into farmers' bank accounts.
Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
- Launched in 2014, the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan aims to eliminate open defecation, promote waste management, and improve sanitation across the country.
- It has been a successful program in improving India's sanitation system.
Solar Charkha Scheme
- Announced in June 2018 by the Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises, this initiative focuses on creating solar charkha clusters.
- These clusters will benefit 200 to 2042 artisans (spinners, weavers, seamstresses, etc.) and promote economic development through the use of solar power.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
- Objective: Develop the fisheries sector.
- Launch: September 10, 2020.
- Details: Investment of Rs. 30,050 crore to increase fish production by 80 lakh tonnes and boost export revenues to Rs. 1,20,000 crore by 2026-27.
Public Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM-WANI)
- Objective: Improve wireless access nationwide.
- Launch: December 9, 2020.
- Details: Targets 1.5 crore Wi-Fi hotspots by 2028 to enhance digital connectivity.
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana
- Launched on October 11, 2014, the Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana encourages MPs to develop a village by addressing issues like agriculture, education, health, sanitation, and livelihood.
- MPs are required to select one village with a population of 3,000-4,000 in the plains and 1,000-3,000 in the hills.
Mission Karmyogi
- Objective: Enhance civil service capacities.
- Launch: September 20, 2020.
- Details: Incorporates AI-based training modules for civil servants to improve governance efficiency.
VAN DHAN Yojana
- Objective: Support tribal communities in Minor Forest Produce collection.
- Launch: 2018.
- Details: Provides e-commerce platforms for marketing tribal products and sustainable income generation.
State Government Schemes
Karnataka
- Vajpayee Arogyasri Yojana: A health insurance program providing financial assistance for the treatment of serious illnesses for economically disadvantaged families.
- Shaadi Bhagya Scheme: Aimed at helping financially weaker sections of society, this scheme provides financial aid for the marriage of girls from minority communities.
- Karnataka Green Farming Initiative: Subsidies for organic farming and sustainable agricultural practices.
Madhya Pradesh
- Bhavantar Bhugtan Yojana: A price stabilization scheme that ensures fair prices for farmers by compensating them when market prices fall below the minimum support price (MSP).
- Deen Dayal Antyoday Upchar Yojna: A health initiative aimed at providing medical care to the underprivileged sections of society through affordable treatment options.
- Deen Dayal Mobile Health Clinic: A mobile health service that delivers healthcare to remote and underserved areas in Madhya Pradesh, ensuring access to basic medical services.
- Ladli Laxmi Yojana: A program designed to support the girl child by providing financial assistance for her education and well-being until she reaches adulthood.
- Madhya Pradesh Rural Livelihoods Project: A project aimed at improving the livelihoods of rural households by promoting skill development, entrepreneurship, and access to financial services.
- Mukhya Mantri Yuva Swarozgar Yojana: A youth employment scheme designed to encourage young entrepreneurs by providing financial assistance and support to start their own businesses.
- MP Digital Farmer Connect: Real-time market price updates and e-commerce integration for farmers.
Maharashtra
- Jalyukt Shivar Abhiyan: A water conservation initiative aimed at improving water availability in Maharashtra’s rural areas by focusing on watershed management, water storage, and ground water recharge.
- Maharashtra Arthik Vikas Mahamandal: This economic development program provides financial support to small-scale industries, rural entrepreneurs, and other key sectors to boost the state's economy.
- Mahatma Jyotiba Phule Jan Arogya Yojana: A health insurance scheme designed to provide free medical treatment for low-income families, particularly for major health ailments.
- Maharashtra Skill Connect: Trains 1.5 lakh youth in AI, robotics, and green technologies.
Telangana
- Aarogya Lakshmi Scheme: A healthcare initiative that provides free nutritional supplements to pregnant women and young children in Telangana to improve maternal and child health.
- Aasara Pension: A social welfare program that provides a monthly pension to elderly, disabled, and widowed individuals to ensure financial security.
- Amma Odi & KCR Kit: These programs aim to provide support for pregnant women and newborns by providing financial assistance and necessary healthcare items.
- Double Bedroom Housing Scheme: A housing initiative aimed at providing affordable housing with two-bedroom units for economically disadvantaged families in urban and rural areas.
- Kalyana Lakshmi – Shaadi Mubarak: A welfare scheme that offers financial assistance for the marriage of girls from economically weaker sections, encouraging social inclusion.
- Mission Bhagiratha: An ambitious scheme to provide tap water to every household in Telangana, ensuring access to clean drinking water.
- Rythu Bandhu Scheme: A farmer welfare initiative providing financial assistance to farmers to support agricultural activities, particularly for purchasing seeds and fertilizers.
- Telangana Ku Haritha Hāram: A green initiative focused on increasing the state’s green cover by planting trees across urban and rural areas to combat climate change.
- Telangana Sheep Distribution Scheme: Aimed at providing sheep to shepherds and enhancing their livelihood through livestock-based activities.
- 2 Rupees per Kg Rice: A scheme that provides rice at an affordable price of ₹2 per kg to economically disadvantaged families in Telangana.
- Telangana Smart Village Mission: IoT-based agricultural solutions for rural development.
Tamil Nadu
Amma Unavagam: A program offering affordable and nutritious meals to the public at subsidized rates, with the goal of tackling hunger and promoting good health.
Samathuvapuram: This initiative promotes social equality by establishing model villages with equal opportunities for all, regardless of caste or economic status.
Uzhavar Santhai: A farmers' market program that allows farmers to sell fresh produce directly to consumers at reasonable prices, eliminating middlemen and improving farmers' incomes.
West Bengal
- Kanyashree Prakalpa: A scheme that provides financial incentives to girls for completing education, aimed at reducing dropout rates and improving female education in the state.
Uttar Pradesh
Kamdhenu Yojna: A welfare scheme designed to promote cattle rearing and improve the income of farmers by providing them with dairy cows and other livestock.
Free Laptop Distribution Scheme: A program that provides free laptops to meritorious students in Uttar Pradesh to encourage digital learning and bridge the technology gap.
UP Rural Broadband Yojana: High-speed internet for 60,000 villages to enhance digital connectivity.
|
63 videos|175 docs|37 tests
|

















