Gravitation | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Gravitation: The Force that Connects the Cosmos
Gravitation, at its core, is the universal force of attraction between all objects in the universe. Regardless of size or composition, every object exerts a gravitational pull on other objects. This force, known as gravitational pressure, is the invisible thread that weaves the fabric of the cosmos, shaping the paths of celestial bodies and governing their interactions.
Centripetal Force: Nurturing Celestial Harmony
To understand the intricacies of celestial motion, we must uncover the concept of centripetal force. Acting towards the center of rotation, the centripetal force keeps objects in circular motion and fuels their perpetual dance through the cosmos. For instance, the Moon's elegant orbit around the Earth is a testament to the power of the centripetal force, which is provided by the Earth's gravitational attraction. Were this force to wane, the Moon would deviate from its celestial path and embark on a uniform straight-line motion.
The Universal Law of Gravitation: Uniting Celestial Bodies
One of the most profound revelations in the field of physics is encapsulated in the universal law of gravitation. This law unveils the intricate nature of gravitational forces between objects and their alignment along the line connecting their centers. For two objects, A and B, with masses M and m respectively, and separated by a distance d, the force of gravitational attraction, F, can be calculated. The law of gravitation has shed light on a multitude of phenomena previously believed to be disconnected, including the force that binds us to the Earth, the motion of the Moon and planets, and the mesmerizing tides caused by the Moon and the Sun.
Importance of Gravitation: The Tapestry of the Universe
Gravitation plays an indispensable role in shaping the cosmos as we know it. Its significance reverberates through the intricate web of celestial phenomena, connecting diverse elements in an awe-inspiring symphony. Some of the crucial roles played by gravitation include:
- Binding us with the Earth: The force of gravity keeps us firmly grounded, enabling us to walk, jump, and experience life on our planet.
- Lunar Elegance: Gravitation is the driving force behind the Moon's mesmerizing orbit around the Earth, illuminating our nights and inspiring poets and dreamers for millennia.
- Planetary Ballet: Gravitation molds the movements of planets in the solar system, guiding them on their majestic paths as they revolve around the Sun.
- Tidal Rhapsody: The harmonious ebb and flow of tides owe their existence to the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and the Sun, influencing the rhythm of life along coastal shores.
Free Fall: Defying Gravity's Hold
When objects plummet towards the Earth under the influence of gravity, they experience a phenomenon known as free fall. This downward motion induces changes in velocity, resulting in acceleration caused by Earth's gravitational force. This acceleration, aptly named the acceleration due to gravity, denoted by 'g,' possesses a magnitude of 9.8 m/s². By multiplying an object's mass, denoted as 'm,' with 'g,' we can determine its weight using the equation F = m × g.
Calculating 'g': The Earth's Gravitational Acceleration
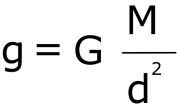
To determine the acceleration due to gravity at different distances from the Earth's surface, we consider the mass of the Earth, denoted as 'M,' and the distance between an object and the Earth, denoted as 'd.' For objects near or on the Earth's surface, where the distance is approximately equal to the Earth's radius ('R'), the value of 'g' can be approximated to 9.8 m/s². Notably, the force of gravity diminishes with increasing altitude and exhibits slight variations across the Earth's surface, gradually decreasing from the poles towards the equator.
Mass: The Inertia of Objects
In the cosmic theater, mass emerges as a pivotal character, defining the degree of an object's inertia. Simply put, mass is the measure of an object's resistance to changes in its state of motion. The greater the mass, the more pronounced the inertia, shaping the object's behavior under the influence of external forces.
Weight: Earth's Irresistible Pull
Every object experiences the gravitational attraction of the Earth, resulting in a force known as weight. Weight is determined by an object's mass, denoted as 'm,' and the acceleration due to gravity, denoted as 'g.' It acts vertically downwards and possesses both magnitude and direction. In the International System of Units (SI), weight is measured in Newtons (N).
Weight's Location Dependency: Unveiling Earth's Secrets
As the Earth's gravitational acceleration, 'g,' varies with location, the weight of an object also fluctuates. The weight of an object on the Moon, for instance, is merely one-sixth of its weight on Earth, highlighting the interplay between celestial bodies and the gravitational forces they exert.
Kepler's Laws: Unraveling Celestial Mysteries
In the pursuit of deciphering the celestial choreography, Johannes Kepler uncovered a set of profound laws that govern the motion of planets. These laws include:
- Elliptical Orbits: Planets gracefully trace elliptical paths around the Sun, with the Sun residing at one of the foci. This revelation shattered the long-held belief that planetary orbits were perfectly circular.
- Equal Areas in Equal Time: The imaginary line connecting a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. This principle reveals the harmonic balance of celestial bodies in motion.
- Period-Radius Relationship: The cube of a planet's mean distance from the Sun ('r') is proportional to the square of its orbital period ('T'). This law elegantly describes the celestial dance, linking orbital parameters in a profound mathematical relationship.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Mysteries of Gravitation
As we gaze upon the night sky, we are reminded of the enigmatic forces that shape our universe. Gravitation, the invisible maestro, guides the celestial ballet, creating awe-inspiring cosmic spectacles and interconnecting the celestial wonders we marvel at. From its role in grounding us to the Earth to its influence on the Moon's graceful orbit and the mesmerizing dance of planets, gravitation is an omnipresent force, beckoning us to unravel its profound secrets. Through the exploration of fundamental principles, laws, and phenomena, we come one step closer to comprehending the majesty of the cosmos and our place within it.
|
745 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
















