Group-18: Inert Gases | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What are Inert Gases?
Members of group 18 in the modern periodic table are known as noble gases. They are colourless, odourless gases at room temperature, isolated by William Ramsay in 1898 from the air.
Inert Gases are:
- Helium (He)
- Neon (Ne)
- Argon (Ar)
- Krypton (Kr)
- Xenon (Xe)
- Radon (Rn)
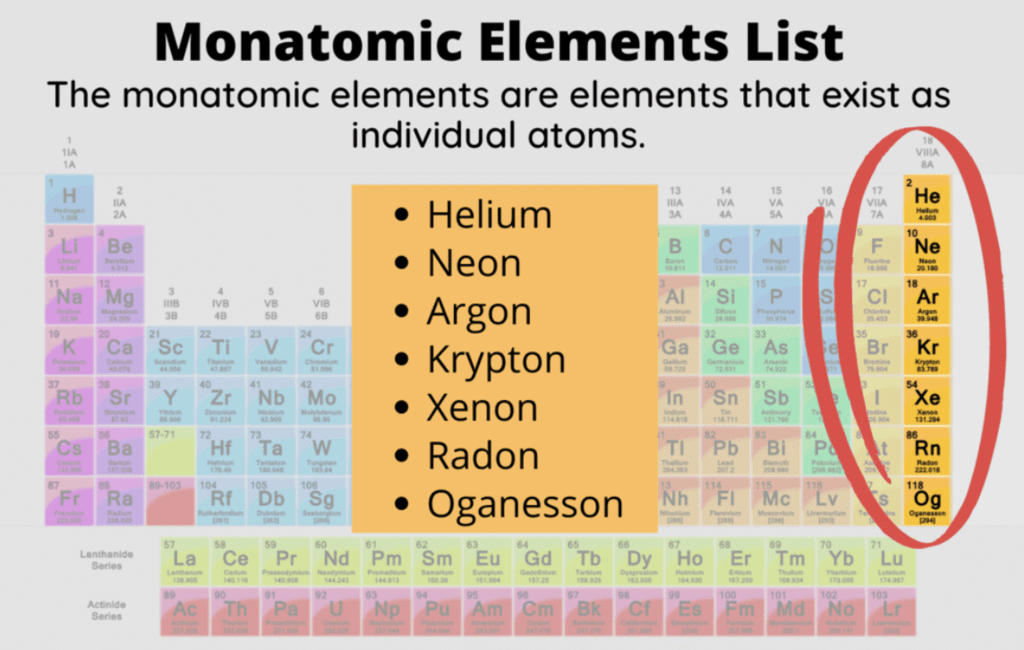
The members of the group have eight electrons in their outermost orbit (except helium which has two electrons). Thus, they have a stable configuration. Group 18 elements are gases and chemically unreactive, which means they don’t form many compounds. Thus, the elements are known as inert gases. Like the other group elements, noble gas elements also exhibit trends in their physical and chemical properties. The general characteristics of noble gases are discussed below.
General/Physical Characteristics of Group 18 Elements:
Electronic configuration:
Their valence shell electronic configuration is ns2 np6 except He.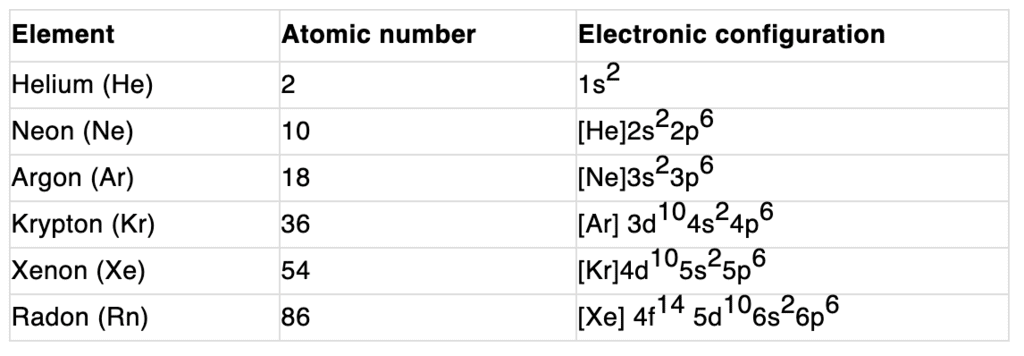
Physical state:
They are all gases under ordinary conditions of temperature and pressure.Abundance:
In 1.0% air, the abundance follows the order: Ar > Ne > He > Kr > XeAtomicity:
The Cp/Cv = 1.67 shows their monoatomic nature.
However, under high energy conditions, several molecular ions such as He+, HeH+, HeH2+and Ar2+ are formed in discharge tubes. They only survive momentarily and are detected spectroscopically.Melting and boiling points:
Due to the increase in the magnitude of Van der Waals’ forces, the melting point and boiling point increase from He to Rn.Atomic radii:
The atomic radii increase from He to Rn. It corresponds to the Van der Waals’ radii. So it has the greatest atomic size in the respective period.Density:
The density of noble gases increases down the group.Heat of vaporisation:
They have very low values of heat of vaporisation due to weak Van der Waals’ forces of attraction. The value increases down the group.Solubility in water:
They are slightly soluble in water and solubility increases from He to Rn.Liquefication:
It is extremely difficult to liquefy inert gases due to weak Van der Waals’ forces of attraction among their molecules. Hence, they possess a low value of critical temperature also.Ionisation energy:
All noble gases possess a very stable (ns2 and ns2 np6) electronic configuration. Therefore, the ionisation energy of noble gases is very high and decreases down the group.Electron affinity:
Due to the presence of stable electronic configuration, they have no tendency to accept an additional electron. Therefore, electron affinity is almost zero.
Chemical Properties of Group 18 Elements:
The noble gases are inert in nature because of their completely filled subshells. In 1962, the first compound of noble gases was prepared. It is hexafluoroplatinate (prepared by Bartlett).
Xe + PtF6 → Xe[PtF6]
Now, many compounds of Xe and Kr are known with fluorine and oxygen.
Preparation of Compounds of Xenon:
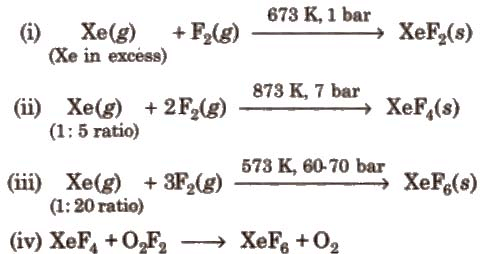
Chemical Reactions of Xenon Compounds:
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Group-18: Inert Gases - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are inert gases? |  |
| 2. What are the general/physical characteristics of Group 18 elements? |  |
| 3. What are the chemical properties of Group 18 elements? |  |
| 4. How are Group 18 elements used in everyday life? |  |
| 5. What are some important properties of radon, an inert gas? |  |























