Himalayas: Physiographic divisions | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Physiographic Divisions of India
India is a country of vast physical diversity. There are high mountain peaks in some areas while in others, lie the flat plains formed by the deposition process of the Himalayan Rivers.
On the basis of varied physiographic features, India is divided into six physiographic divisions:
- The Northern Mountains
- The Northern Plains
- The Peninsular Plateau
- The Indian Desert
- The Coastal Plains
- The Islands
Physiographic Zones of India
The Northern Mountains
The northern mountains of India are a prominent geographical feature, and they are further classified into three distinct groups:
1. The Himalayas
- The Himalayas are a range of very young fold mountains that stretch from the Indus River in the west to the Brahmaputra River in the east, forming the northern boundary of India. These mountains run in a west-east direction and are known for their dramatic and rugged terrain.
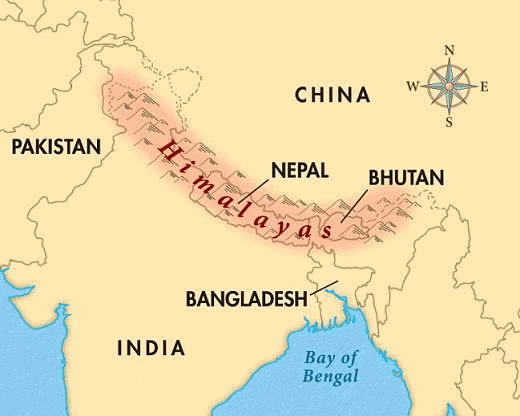 The Great Himalayas
The Great Himalayas
2. The Trans Himalayas
- The Trans Himalayas, located north of the Great Himalayan range, are often referred to as the Tibetan Himalaya because most of these ranges lie in Tibet. The main ranges in this region include the Zaskar, Ladakh, Kailas, and Karakoram ranges.
- Mount Kailash, with an elevation of 6,714 meters, is a notable peak in this region, although it is not the highest peak in the Himalayas. The highest peak in the Himalayas is Mount Everest, standing at 8,848 meters. Another significant peak is Nanga Parbat, which is 8,126 meters tall and located in the Zanskar range.
- The Indus River, an important river in the region, originates from the northern slopes of the Kailash range.
3. The Purvanchal Hills or Northeastern Mountains
The Northeastern Hills, also known as the Purvanchal, are the southern extension of the Himalayas, stretching along the northeastern part of India. These hills run along the India-Myanmar border, from Arunachal Pradesh in the north to Mizoram in the south. The main hills in this region include:
- Patkai Bum, Naga Hills, and Mizo Hills, which are situated along the international boundary with Myanmar.
- Garo, Khasi, and Jaintia Hills, located along the border with Bangladesh.
Some important peaks in the Northeastern Hills are Saramati, standing at 3,826 meters in the Naga Hills, and Blue Mountain, which is 2,157 meters tall in the Mizo Hills.
The Himalayas
- The Himalayas are one of the highest and most rugged mountain ranges in the world, stretching in an arc for about 2,400 km from Jammu & Kashmir in the west to Arunachal Pradesh in the east.
- These mountains are known as 'newest fold mountains,' formed during the Tertiary epoch due to Alpine earth movements. The eastern section has greater height variations, resulting in towering peaks like Mount Everest and Kanchenjunga found in the Eastern Himalayas.
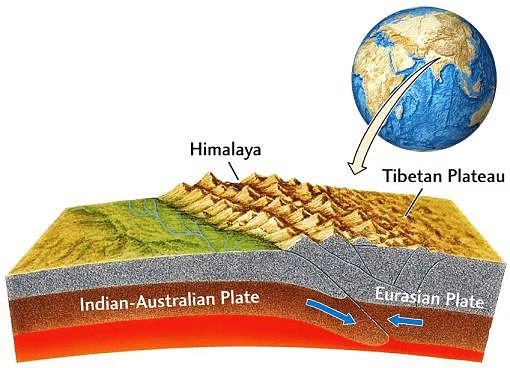 Location of Himalayas on the Earth
Location of Himalayas on the Earth
Formation of the Himalayas
- The Himalayas were formed by the collision of the Eurasian plate and the Indo-Australian plate.
Longitudinal Division of the Himalayas
Western Himalayas consist of three parallel ranges:
- The Great Himalayas or Inner Himalayan Range
- The Lesser Himalayas or Himachal Range
- The Outer Himalayas or Shiwalik Range
1. Greater/Outer Himalayas/Himadri
- Average height: 6000 m.
- Average width: 120 to 190 km.
- Folds are asymmetrical.
- Composed of Archean rocks like granite, gneisses, and schists.
- Highest peak: Mount Everest or ‘Sagarmatha’.
- Rivers like the Ganga, Yamuna, and their tributaries begin in this range, while the Indus, Brahmaputra, and Alaknanda rivers have formed valleys here.
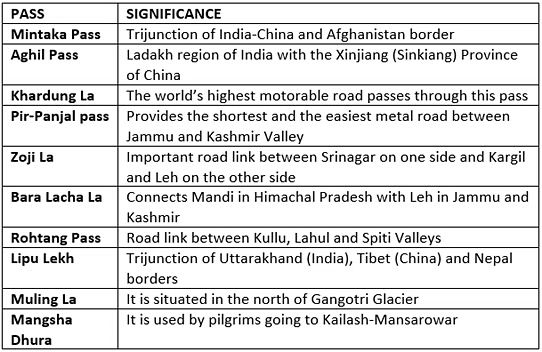
- Many passes exceed 4,500 m in height, including:
- Shipki La and Bara Lapcha La in Himachal Pradesh
- Burzil and Zozi La in Kashmir
- Niti, Lipulekh, and Thag La in Uttarakhand
- Jelep La and Nathu La in Sikkim
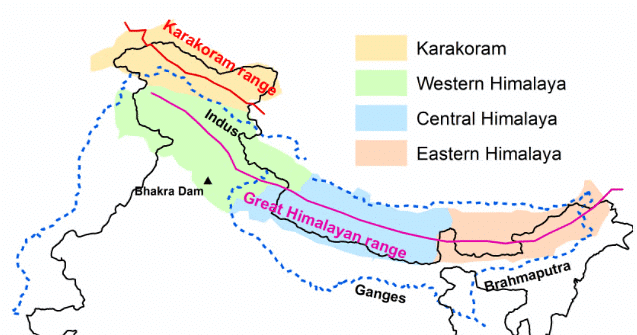 The Great Himalayan Range
The Great Himalayan Range
2. Lesser Himalayas/Himachal
- Average height: 3500-5000 m.
- Average width: 50-80 km.
- Composed of metamorphic rocks.
- Known for popular hill stations like Shimla, Mussoorie, Nainital, and Ranikhet.
- Significant ranges include Pir Panjal, Dhauladhar, and Nag Tibba.
- In Uttarakhand, the Middle Himalayas feature the Mussoorie and Nag Tibba ranges.
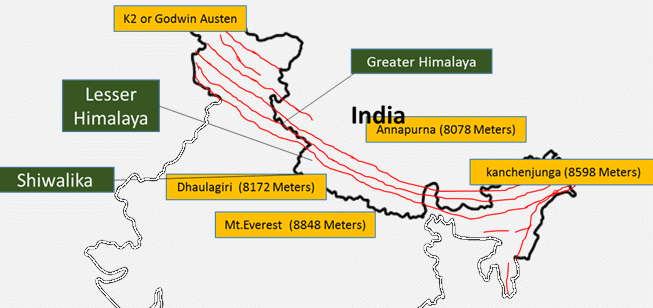 Lesser Himalayan Range
Lesser Himalayan Range
Himalayan Ranges
Pir Panjal is the longest and most important mountain range in India. It starts near PatniTop in Jammu and Kashmir and stretches all the way to Garhwal, passing through Himachal Pradesh along the way.
Dhauladhar Range is another significant mountain range that begins near Dalhousie in the northwestern part of Himachal Pradesh and extends through the state to the Beas River in Kulu.
Sub Himalayas or Shiwaliks
- Height and Width: Average height of 1000 to 1500 meters and a width ranging from 15 to 50 kilometers.
- Composition: Made up of materials like clay, sand, gravel, slate, and boulders.
- Doon Valleys: Includes valleys such as Dehradun, Patlidun, and Kothrud.
1. They had formed due to the collision between the Indian-Australian Plate and the Eurasian plate. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
2. The highest peak of Himalayas the Mount Everest is located in Shivaliks.
3. Lesser Himalayas are composed of metamorphic rocks.
Regional Divisions of Himalayas
The Himalayan region is not only divided into three parallel ranges but can also be categorized into different regions from west to east. These regions are as follows:
- Kashmir / Punjab / Himachal Himalayas
- Kumaun Himalayas
- Central / Nepal Himalayas / Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalayas
- Assam / Eastern Himalayas
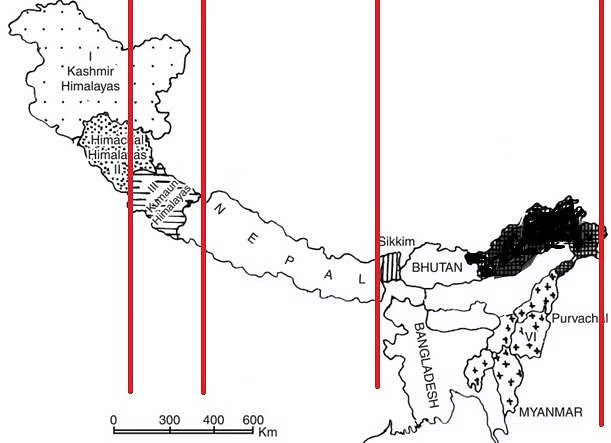 Regional Division of Himalayas
Regional Division of Himalayas
Kashmir / Punjab / Himachal Himalayas
- Areas: This region includes Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and parts of Punjab. It is situated between the Indus and Satluj rivers.
- Features: Known for its high, snow-covered peaks, deep valleys, interlocked spurs, and high mountain passes. The Karewa soil, especially in Kashmir, is famous for saffron cultivation.
- Major Ranges: Includes the Karakoram, Ladakh, Pir Panjal, Zanskar, and Dhauladhar ranges.
Kumaun Himalayas
- Area: Located between the Satluj and Kali rivers.
- Features: Drained by the Indus and Ganga river systems. Distinctive for 'DUN' formations such as Chandigarh-Kalka dun and Dehradun. Inhabitants include the Bhutias, who migrate to summer grasslands known as Bugyals. The famous Valley of Flowers is also located here.
- Important Peaks: Nanda Devi, Trishul, Kedarnath, Dunagiri, Kamet, Badrinath, Jaonli, Gangotri, and Bandarpunch.
- Important Glaciers: Pindari, Gangotri, and Milam glaciers.
- Important Passes: Thaga La, Muling La, Mana, Mangsha Dhura, and Lipu Lekh passes.
Central / Nepal Himalayas / Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalayas
- Area: This region is primarily in Nepal, stretching from the Kali river to the Kosi river in Nepal. The Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalayas extend from the Kosi river to the Teesta river.
- Features: Known for fast-flowing rivers like the Teesta and tea plantations due to abundant rainfall and mild winters. These areas also feature 'DUAR' formations.
- Important Peaks: Mount Everest, Kanchenjunga, Makalu, Dhaulagiri, Annapurna, Manaslu, and Gosainath.
- Important Passes: Nathu La and Jelep La passes.
Eastern Himalayas / The Assam Himalayas
- Area: This region stretches between the Tista river and the Brahmaputra River (Dihang).
- Features: The Himalayas in this region are narrower and show signs of fluvial erosion. The northern area includes Patkai Bum, Naga Hills, and Manipur Hills, while the southern area includes Mizo Hills. The Barak river is the most significant river in this region, and Mizoram is often referred to as the 'Molasses Basin.'
- Important Peaks: Namcha Barwa and Kula Kangri peaks.
- Important Hills: Patkai Bum, Manipur Hills, Blue Mountains, Tripura Range, and Barail Range.
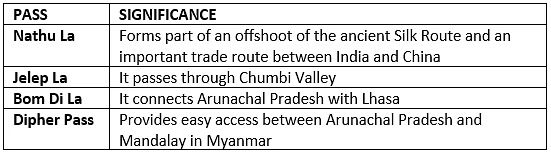
- Important Passes: Bomdi La, Yonggyap, Diphu, Pangsau, Tse La, Dihang, Debang, Tunga, and Bom La passes.
Glaciers and Snowline Glacier
Glaciers are massive ice formations that gradually shift across land, resembling slow-moving rivers of ice. The term "glacier" is derived from the French word "glace," meaning ice.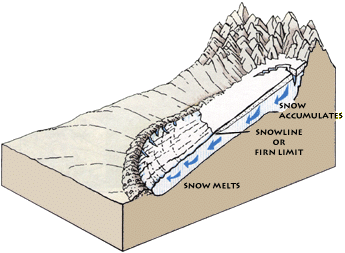
Significant Glaciers in the Himalayas
Karakoram Range:
- Siachen Glacier
- Fedchenko Glacier (the longest glacier outside polar regions)
- Hispar Glacier
- Biafo Glacier
- Baltoro Glacier
Pir Panjal Range:
- Sonapani Glacier
- Bara Shighi Glacier
- Rakhiot Glacier
- Gangri Glacier
Kumaon-Garhwal Range:
- Kafni Glacier
- Kalabaland Glacier
- Kedar Bamak Glacier
- Meola Glacier
- Namik Glacier
- Panchchuli Glacier
- Pindari Glacier
- Ralam Glacier
- Satopanth Glacier
- Chorabari Glacier
The climatic snow line marks the transition between snow-covered and snow-free surfaces. In the Western Himalayas, this line is at a lower altitude compared to the Eastern Himalayas due to the increase in latitude.
1. Fedchenko is the longest glacier in the world outside of the polar regions.
2. The western Himalayas snowline is at a higher altitude than the eastern Himalayas.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Mountain Peaks
The Himalayas are home to some of the tallest mountains in the world, including Nanga Parbat, Annapurna, Mount Everest, Mount K2, and Kanchenjunga. This mountain range features around 9 of the 14 highest peaks globally and boasts over 50 peaks that reach heights greater than 7,000 m.
Mountain Passes
A mountain pass is a route that allows travel through a mountain range or across a ridge. Passes are created when glaciers or streams wear down the land between higher areas. They often offer the easiest paths for people to cross steep mountains.
Important Passes in India
Passes in Western Himalayas:
Passes of the Eastern Himalayas:
 Passes in Southern India:
Passes in Southern India:


Which of the pairs given above is/are correct?
Comparison between Western Himalayas and Eastern Himalayas:
- Extension. Western Himalayas stretch to the west of the River Kali, while Eastern Himalayas extend from Kali to the Brahmaputra River.
- Height. Western Himalayas rise gradually, whereas Eastern Himalayas rise sharply from the plains.
- Vegetation. Western Himalayas are covered with coniferous forests and alpine plants.
- Biodiversity. Western Himalayas have lower biodiversity compared to Eastern Himalayas.
- Precipitation. Western Himalayas receive rain from the northwest monsoon in winter; Eastern Himalayas get rain from the southeastern monsoon in summer.
- Snowline. The snowline is higher in Eastern Himalayas and lower in Western Himalayas.
- Altitude. The altitude is greater in Western Himalayas than in Eastern Himalayas.
Comparison between Northern and Southern slopes of the Himalayas:
- Precipitation. The Southern Slopes receive more rain than the Northern Slopes due to their location in the rain shadow region.
- Vegetation. Southern Slopes are densely forested, while Northern Slopes are usually barren. Rainfall decreases from south to north.
- Snowline. The Southern Slopes have less snow accumulation due to more sunshine compared to the Northern Slopes.
1. Western Himalayas have more biodiversity in comparison to the eastern Himalayas.
2. Southern Slopes of Himalayas are covered with thick vegetation whereas Northern Slopes of Himalayas are generally barren.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
|
182 videos|620 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Himalayas: Physiographic divisions - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main differences between the Northern and Southern slopes of the Himalayas? |  |
| 2. How do the physiographic divisions of the Himalayas affect the biodiversity in the region? |  |
| 3. What role do the Northern Mountains play in influencing the climate of the surrounding regions? |  |
| 4. What are the major rivers that originate from the Northern slopes of the Himalayas? |  |
| 5. How do human activities impact the Northern slopes of the Himalayas? |  |






















