History, Art & Culture: July 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| National Maritime Heritage Complex |

|
| Lambani Art |

|
| Buddha’s Relevance to the Modern Youth |

|
| Alluri Sitarama Raju |

|
| Bal Gangadhar Tilak |

|
National Maritime Heritage Complex
The government has announced the development of a National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) in Lothal, Gujarat under the Sagarmala program (under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW)). The project aims to showcase India’s maritime heritage from ancient to modern times.
It will include world’s highest light house museum, world’s largest open aquatic gallery, India’s largest naval museum. It is funded by MoPSW and Ministry of Culture through National Culture Fund by way of grant.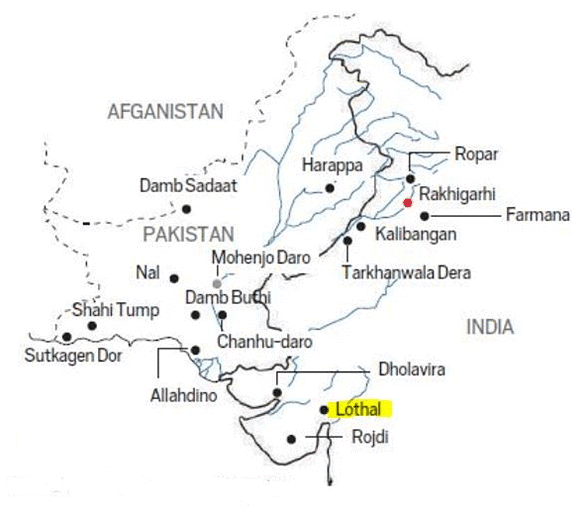
Lambani Art
Context
- At the 3rd G20 Culture Working Group, In Hampi, Karnataka, Guinness World Record was set for the largest display of Lambani items.
- A total of 1755 items were on display.
Other Details
- It was an effort/initiative to popularize Lambani art, craft and culture.
- This initiative is also expected to encourage the participation of Nari Shakti in such cultural activities.
Lambani Embroidery
- Also known as Banjara embroidery, it is an intricate embroidery art done on a piece of cloth.
- This art is mainly practiced by the community of Lambanis.
- This art comprises various processes such as –
- Firstly Basic tools and materials are collected – for eg – Fabric, needles, thread, accessories etc.
- Then there is selection of patterns, types and shapes of stitches, color combinations
- Accessories like beads, mirror are added in the later stage.
- Finally it is ironed to give the cloth piece a desired look.
- The final piece of cloth can be used in clothing, curtain, pillow cover, bedcovers, bags, etc.
- Sandur Lambani Embroidery is recognized with a Geographical Indication tag in 2010.
Features
- Done on a loosely woven piece of cloth.
- It includes –
- Around 14 types of stitches with various geometric shapes like - squares, circles, triangles, diagonal lines etc.
- Parallel lines of multi color threads.
- Patchwork.
- Mirror work, Beads, Metal buttons, Ghungroo etc.
- Quilting.
- Applique, an ornamental needlework.
- Overlaying
- Most commonly used colors are red, yellow and blue
Who are Lambanis
- These are nomadic tribes that are spread across India.
- Regarding the origins of the Lambani community, there are many theories, some are -
- They are considered to be the descendants of the Romanis of Europe.
- Came from the Ghor province of Afghanistan and then settled in Rajasthan, Gujarat and then migrated down south.
- These tribal communities of Banjara or Lambani mainly reside in -
- Sanduru, Bellary and Bijapur in Karnataka, and
- Hyderabad in Andhra Pradesh.
Significance of Lambani Art
- Empower marginalised communities like Lambani
- Contribution to economy of the country.
- Preserve the rich cultural traditions in line with the constitutional provisions.
- It can also contribute to improving biodiversity of their region as
- Indigenous fibres are required.
- Native plant dyes are used. and
- Locally sourced materials are preferred.
- It is sustainable practice which works on the principle of recycle and reuse. No fabric or material is wasted in the process.
- Potential to enhance India’s soft power.
Efforts for Conservation
- More exhibitions to make people interested in the art.
- The artisans should be financially supported.
- There should be a formal course to learn this art.
- More promotion and brand engagement would help to revive this indigenous art.
- More efforts by government are needed to rehabilitate and reform
- GI tag will help in creating a unique selling proposition.
- More awareness about indigenous textiles and fashion will help this art to gain momentum.
Buddha’s Relevance to the Modern Youth
Why in News?
The President of India, urged the youth to draw inspiration from the teachings of Lord Buddha, on the occasion of Dharma Chakra Pravartana Divas (3rd July 2023).
- The President reflected on how Lord Buddha's first sermon on Asadha Purnima planted the seeds of the middle path of the Dhamma.
How can Youth Draw Inspiration from Buddha to Navigate Life's Challenges?
- Mindfulness as a Foundation: One of the central tenets of Buddha's teachings is the practice of mindfulness.
- Mindfulness encourages individuals to cultivate a deep awareness of the present moment, fostering an enhanced understanding of their thoughts, emotions, and actions.
- In a world saturated with distractions, young people can draw inspiration from Buddha's emphasis on being fully present and engaged.
- By practicing mindfulness, youth can learn to manage stress, improve focus and concentration, and nurture a greater sense of self-awareness, leading to improved mental well-being and personal growth.
- Impermanence and Non-Attachment: Buddha's teachings emphasize the impermanence (the state or fact of lasting for only a limited period of time) of all phenomena and the futility of attachment.
- In a materialistic society driven by instant gratification, youth can find solace and inspiration in the understanding that everything is transient.
- By recognizing the impermanence of both joy and suffering, young individuals can cultivate a mindset that is adaptable, resilient, and open to change.
- Learning to let go of attachment to outcomes, possessions, and even relationships can free the youth from unnecessary suffering and allow them to embrace life with greater equanimity.
- Compassion and Empathy: In a world where divisions and conflicts persist, young people can find inspiration in Buddha's teachings on loving-kindness and compassion.
- By cultivating empathy, youth can develop a deeper understanding of others' struggles, fostering a sense of unity and connection.
- Self-Discovery and Inner Transformation: Young people, often grappling with questions of identity and purpose, can draw inspiration from Buddha's teachings on self-exploration.
- By engaging in introspection and self-reflection, youth can gain insights into their true nature, passions, and aspirations.
- Engaging in Social and Environmental Responsibility: Buddha's teachings emphasize the interconnectedness of all beings and advocate for responsible action.
- The youth can actively engage in social and environmental responsibility by working towards equality, justice, and sustainable practices.
- They can participate in community initiatives, advocate for marginalized groups, and champion environmental conservation.
- By embodying these teachings, they contribute to building a more equitable, harmonious, and environmentally conscious society.
Alluri Sitarama Raju
Why in News?
Recently, the President of India attended the closing ceremony of the 125th Birth Anniversary of Alluri Sitarama Raju in Hyderabad.
- The 125th ceremony of Alluri Sitha Rama Raju was a year-long celebration of the birth anniversary of the legendary freedom fighter. The ceremony was launched by the Prime Minister on July 4, 2022.
Who was Alluri Sitarama Raju?
- About:
- Alluri Sitarama Raju was an Indian revolutionary who fought against the British colonial rule in India.
- He led a guerrilla campaign in the Eastern Ghats region of present-day Andhra Pradesh, mobilizing the tribal people against the oppressive forest laws and policies of the British government.
- He is widely regarded as a hero of the jungle or Manyam Veerudu by the local people for his bravery and sacrifice.
- Early Life and Background:
- He was born on 4 July 1897 or 1898 in Pandrangi village, Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh.
- He belonged to a Telugu-speaking Kshatriya family.
- Rampa Rebellion (or Manyam Rebellion) of 1922-1924:
- Alluri Sitarama Raju joined the Non-cooperation movement led by Mahatma Gandhi and witnessed the exploitation of tribal people in the Eastern Ghats region by British authorities.
- The tribal people practiced podu or shifting cultivation, which involved clearing patches of forest land for agriculture and moving to another area after a few years. This was their traditional and sustainable way of life, which also ensured their food security and cultural identity.
- The Madras Forest Act of 1882 imposed restrictions on the tribal people's movement and prohibited their collection of minor forest produce, forcing them into low-wage labor for the forest department or contractors.
- Alluri Sitarama Raju formed a guerrilla army and used Guerrilla warfare to launch attacks on British police stations and outposts.
- Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics, and mobility, to fight a larger and less-mobile traditional military.
- He aimed to liberate the tribal people and drive the British out of the Eastern Ghats.
- Death and Legacy:
- Alluri Sitarama Raju was captured and killed by British forces in Koyyuru village on 7 May 1924, marking the end of the Rampa Rebellion.
- Alluri Sitarama Raju's life exemplified the unity of society without discrimination based on caste and class.
- A postal stamp issued by the Government of India in 1986 featuring Alluri Sitarama Raju.
- A biographical film titled Alluri Seetharama Raju was released in 1974.
Bal Gangadhar Tilak
Why in News
On 23rd July, India paid tribute to the freedom fighter and educationist Bal Gangadhar Tilak on his birth anniversary.
Key Points
- Birth: He was born on 23rd July 1856 in Ratnagiri, Maharashtra.
- Freedom fighter and lawyer, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, is also known as Lokmanya Tilak.
- Educationist:
- Founder of the Deccan Education Society (1884) along with his associate Gopal Ganesh Agarkar and others.
- One of the founders of the Fergusson College (1885) in Pune through the Deccan Education Society.
- Ideology:
- He was a devout Hindu and used Hindu scriptures to rouse people to fight oppression.
- Stressed on the need for self-rule and believed that without self-rule or swarajya, no progress was possible.
- Slogan: “Swaraj is my birthright and I shall have it!”
- A book ‘Indian Unrest’ written by Valentine Chirol, an English journalist, stated Tilak the ‘father of Indian unrest’.
- Emphasised the importance of a cultural and religious revival to go with the political movements.
- Popularised the Ganesh Chaturthi festival in the Maharashtra region.
- Propounded the celebration of Shiv Jayanti on the birth anniversary of the monarch Chhatrapati Shivaji.
- Political Life: He was one of the earliest and the most vocal proponents of complete independence or swarajya (self-rule).
- Along with Lala Lajpat Rai and Bipin Chandra Pal, he was part of the Lal-Bal-Pal trio of leaders with extremist outlooks.
- Joined the Indian National Congress (INC) in 1890.
- Surat Split: It was the splitting of the INC into two groups - the Extremists and the Moderates - at the Surat session in 1907.
- Reason: The extremists wanted either Tilak or Lajpat Rai to be president, so when Rasbehari Ghose was announced as president, the extremist resorted to violence. Hence Surat Split happened.
- While extremists wanted to end the tyranny rule of British through protest, Moderates were aimed at administrative and constitutional reforms.
- The Extremist camp was led by Lal Bal and Pal and the moderate camp was led by Gopal Krishna Gokhle.
- Contribution to Freedom Movement:
- Propagated swadeshi movements and encouraged people to boycott foreign goods.
- Indian Home Rule Movement:
- It was a movement in British India on the lines of Irish Home Rule movement.
- Started in 1916, it is believed to have set the stage for the independence movement under the leadership of Annie Besant and Bal Gangadhar Tilak for the educated English speaking upper class Indians.
- All India Home Rule League: Founded by Tilak in April 1916 at Belgaum.
- It worked in Maharashtra (except Bombay), the Central Provinces, Karnataka and Berar.
- Lucknow Pact (1916): Between the INC headed by Tilak and All-India Muslim League led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah for hindu-muslim unity in nationalist struggle.
- Jail: Between 1908 and 1914, he spent 6 years in Mandalay Prison for defending the actions of revolutionaries Khudiram Bose and Prafulla Chaki.
- Khudiram Bose and Prafulla Chaki had tried to assassinate the District Judge, Mr. Kingsford by throwing bombs at the carriage in which he was supposed to travel.
- Newspapers: Weeklies Kesari (Marathi) and Mahratta (English)
- Books: Gita Rhasya and Arctic Home of the Vedas.
- Death: He died on 1st August 1920.
|
63 videos|5408 docs|1146 tests
|















