UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Science & Technology for UPSC CSE > Human Genome Project
Human Genome Project | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
- Human Genome Project is a publicly funded international collaborative research project aimed at determining the sequence of chemical base pairs which make up human DNA, & identifying & mapping all of the genes of the human genome.
- A base pair (bp) is a unit consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds.
- They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix & contribute to the folded structure of both DNA & RNA.
- Human Genome Project was formally launched in 1990, & finally declared complete in 2003.
- The mapping of the human genome involves sequencing multiple variations of each gene.
- The HGP has revealed that there are probably about 20,500 human genes.
Applications & Benefits of Human Genome Project
It can help us
- understand diseases including genotyping of specific viruses to direct appropriate treatment,
- in the identification of mutations linked to different forms of cancer,
- understand the design of medication & more accurate prediction of their effects,
- in the advancement of forensic applied sciences, biofuels, animal husbandry, etc.
- understand evolution much more accurately.
- Another proposed benefit is the commercial development of genomics research related to DNA based products, a multibillion-dollar industry.
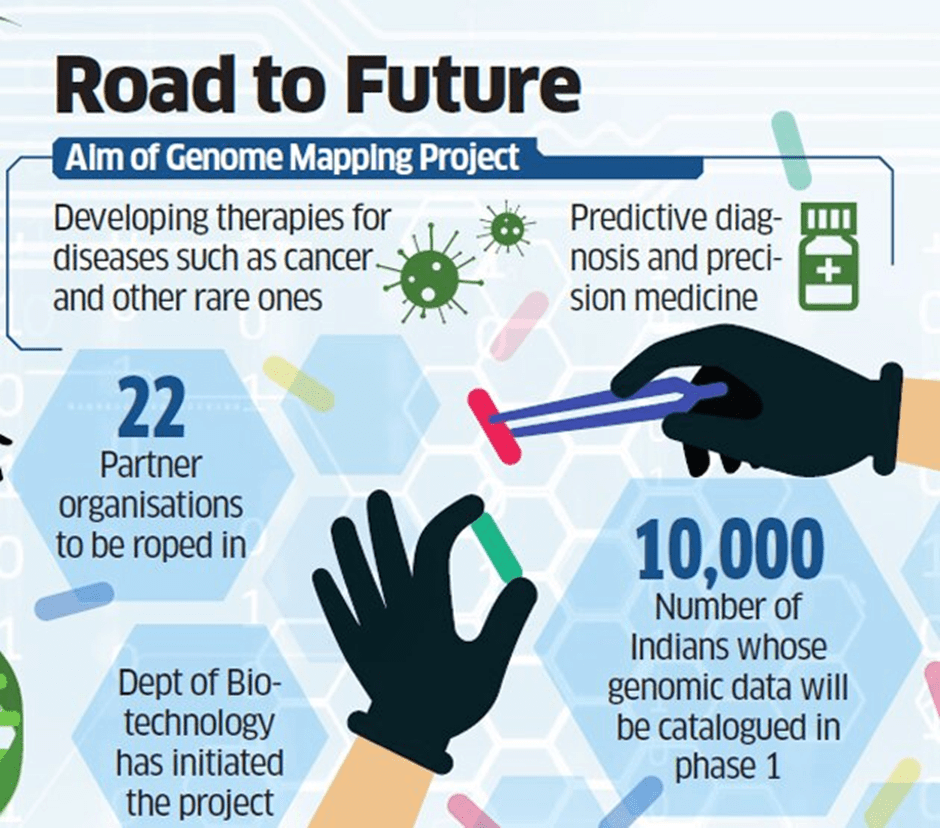
Genome India Project
- Taking inspiration from the Human Genome Project, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) initiated the ambitious Genome India Project” (GIP) in 2020.
- As of January 2025, the project has successfully sequenced the genomes of 10,000 individuals from 99 distinct populations across India, creating a comprehensive reference genome.
- The Genome India Project involved collaboration among over 20 institutions across the country, including the Indian Institute of Science's Centre for Brain Research, Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, and National Institute of Biomedical Genomics
 Genome India Project
Genome India Project
IndiGen: India’s Genome Sequencing Project
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) concluded the six-month-long exercise of conducting a “whole-genome sequence” of a 1,008 Indians that beloged to diverse ethnicities.
- The project is part of a programme called “IndiGen” and is a precursor to Genome India Project” (GIP).
- The project involved the Hyderabad-based Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) and the CSIR-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology (IGIB).
Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG)
- It is a network of 10 laboratories established in December 2020.
- INSACOG has expanded to include 28 laboratories as of July 2021.
- It aims at continuously monitoring the genomic changes of SARS-CoV-2 in India.
- Monitoring is done through Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS).
- Knowledge generated through this research consortium will assist in developing diagnostics & potential therapeutics & vaccines in the future.
Goals & Objectives of Genome India Project” (GIP)
- Whole-genome sequencing and subsequent data analysis of the genetic data of these 10,000 individuals has been successfully carried out as of January 2025.
- It aims to aid understanding of the nature of diseases affecting the Indian population.
- It allows India to draw upon its tremendous genetic diversity, given the series of large migrations historically, and thus, add greatly to the current information about the human species.
- This initiative would help lay the foundation of personalized healthcare for a very large group of persons on the planet.
Priority Areas
Some of the priority areas are:
- Precision health
- Rare genetic disorders
- Mutation spectrum of genetic and complex diseases in the Indian population
- Genetic Epidemiology of Multifactorial Lifestyle Diseases
- Translational Research.
Key Terms
- DNA: hereditary material of most of the living beings.
- RNA: hereditary material of some microorganisms (virus).
- Genes: specific section of DNA which encodes the synthesis of gene product either RNA or for proteins, i.e., it is involved in making RNA (transcription) or proteins (translation).
- Chromosome:are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal & plant cells.
- The DNA is coiled to make thread-like structure called chromosomes.
- Human beings have 46 chromosomes (23 from each parent).
- Each chromosome is made of protein & a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
- Genome sequencing:Deciphering the exact order of bases pairs (complete DNA sequence) in an organism’s genome.
- This entails sequencing all of an organism’s chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast.
The document Human Genome Project | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Science & Technology for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Human Genome Project - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the Human Genome Project? |  |
Ans. The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project that aimed to map and sequence the entire human genome, which is the complete set of genetic information present in humans.
| 2. What are the applications of the Human Genome Project? |  |
Ans. The Human Genome Project has several applications, including identifying genes responsible for diseases, predicting the risk of developing certain conditions, understanding genetic variations among individuals, and aiding in the development of personalized medicine.
| 3. What are the benefits of the Human Genome Project? |  |
Ans. The Human Genome Project has numerous benefits, such as advancing medical research, facilitating the development of targeted therapies, improving disease diagnosis and treatment, enabling the identification of genetic predispositions, and enhancing our understanding of human evolution and biology.
| 4. How has the Human Genome Project contributed to personalized medicine? |  |
Ans. The Human Genome Project has played a crucial role in personalized medicine by providing insights into individual genetic variations that influence disease susceptibility, drug responses, and treatment outcomes. This information helps doctors tailor medical interventions to each patient's specific genetic makeup.
| 5. How does the Human Genome Project impact genetic research and discoveries? |  |
Ans. The Human Genome Project has revolutionized genetic research by providing a comprehensive reference for studying the human genome. It has facilitated the discovery of numerous disease-related genes, improved understanding of genetic variations, and accelerated the development of new diagnostic tools and treatments.
Related Searches
















