Human Geography: Introduction | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Human Geography
Human geography is a wide-ranging discipline that draws together many of the strands important for understanding the world today. It examines human societies and how they develop, their culture, economy and politics, all within the context of their environment.
- Each and every event or phenomenon which varies over space and time can be studied geographically.
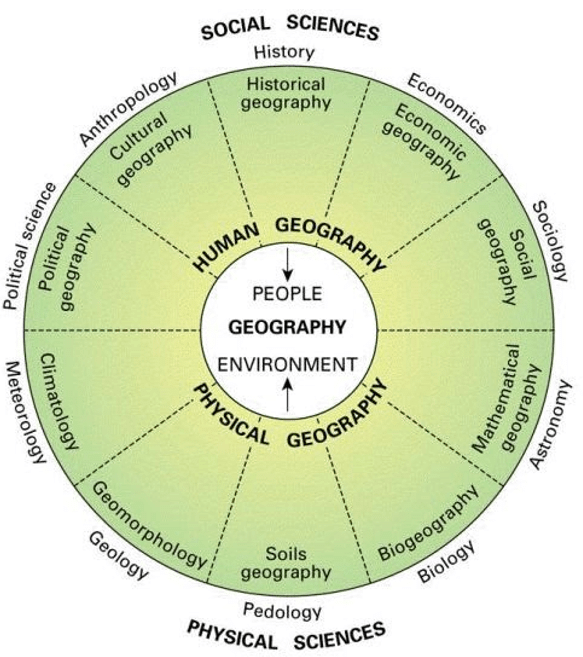
- Physical geography studies the physical environment.
- Human geography studies the inter-relationship between the physical environment and sociocultural environment created by human beings through mutual interaction with each other.
- The dichotomy (contrast) between physical and human is not a very valid one because nature and humans are inseparable elements and should be seen holistically.
Schools of thought in Human Geography
The three different Schools of thought in Human Geography are:
1. Welfare or Humanistic school of thought
- The welfare or humanistic school of thought in human geography was mainly concerned with the different aspects of the social well-being of the people.
- These included aspects such as housing, health, and education.
2. Radical School of Thought
- The radical school of thought employed Marxian theory to explain the basic cause of poverty, deprivation, and social inequality.
- Contemporary social problems were related to the development of capitalism.
3. The Behavioural School of Thought
- The behavioral school of thought laid great emphasis on lived experience and also on the perception of space by social categories based on ethnicity, race and religion, etc.
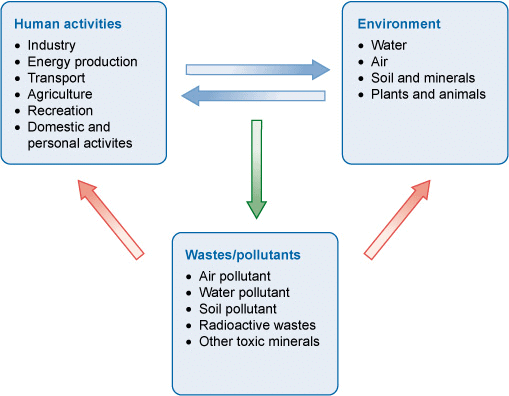
Environment and Human Inter-Relationship
Humans need to interact with the environment to obtain our food, water, fuel, medicines, building materials, and many other things.
- Advances in science and technology have helped us to exploit the environment for our benefit, but we have also introduced pollution and caused environmental damage.
1. Naturalization of Humans: Determinism
During the early periods of human history, men and women were greatly influenced by their surrounding environment. Thus, humans were naturalized because they were afraid of nature and worshipped it. This is known as naturalization of humans.
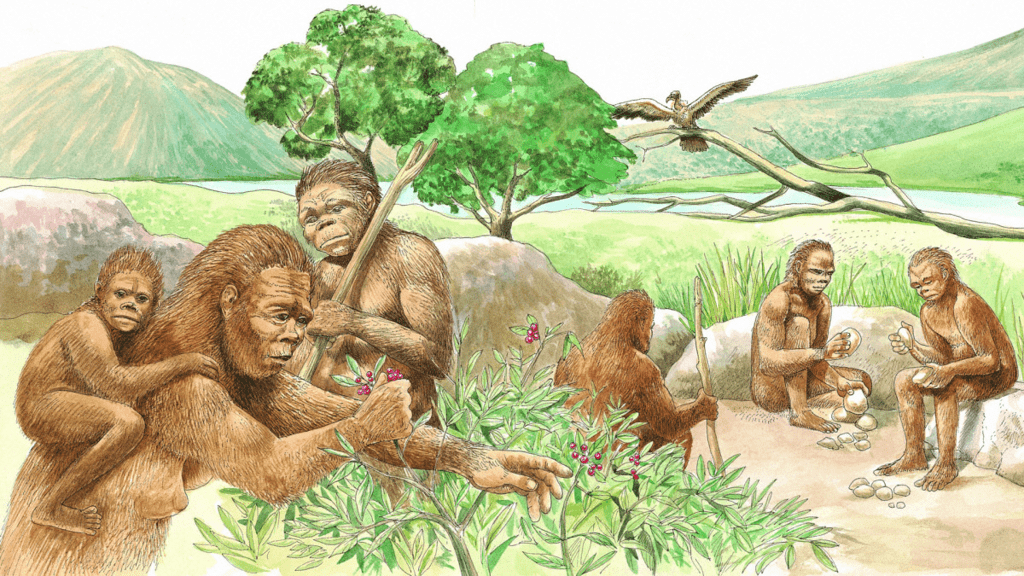 Early Men and Nature
Early Men and Nature
- In the early stages of their interaction with their natural environment, humans adapted to the dictates of nature.
- This type of interaction between primitive human society and the strong forces of nature was termed environmental determinism.
- Environmental determinism considers humans as passive agents as their decisions, attitudes, and way of life are affected by nature.
- For example, forest dwellers and tribal societies who live deep in the forest or in secluded mountainous regions.Question for Human Geography: IntroductionTry yourself:Which school was mainly concerned with the different aspects of the social well-being of the people.View Solution
2. Humanisation of Nature: Possibilism
Nature provides opportunities and human beings make use of these and slowly nature gets humanized and starts bearing the imprints of human endeavor.
- The earlier scholars termed this as possibilism.
- With the passage of time, humans began to understand their natural surroundings and the forces of nature.
- As humans began to form social groups and settled at a place, they developed new and efficient means of technology which helped them to use natural resources.
- Humans create possibilities with the resources obtained from nature. For example, they create orchards and entertainment resorts near adventurous places.
3. Neo Determinism
Another concept which reflects a middle path between the two ideas of environmental determinism and possibilism is termed as Neo Determinism or stop and go determinism.
- The concept shows that neither is there a situation of absolute necessity (environmental determinism) nor is there a condition of absolute freedom (possibilism).
- It means that human beings can conquer nature by obeying it and that possibilities can be created within the limits which do not damage the environment and there is no free run without accidents.
- The free run which the developed economies attempted to take has already resulted in the greenhouse effect, ozone layer depletion, global warming, receding glaciers and degrading lands.
- Neo-determinism conceptually attempts to bring a balance nullifying the ‘either’ ‘or’ dichotomy.
Broad Stages and Thrust of Human Geography
Exploration and Description
- Imperial and trade interests prompted the discovery and exploration of new areas.
- An encyclopaedic description of the area formed an important aspect of the geographer’s account.
Regional Analysis
- An elaborate description of all aspects of a region were undertaken.
- The idea was that all the regions were part of a whole, i.e. (the earth); so, understanding the parts in totality would lead to an understanding of the whole.
Areal Differentiation
- The focus was on identifying the uniqueness of any region and understanding how and why it was different from others.
Spatial Organisation
- Marked by the use of computers and sophisticated statistical tools.
- Laws of physics were often applied to map and analyse human phenomena.
- This phase was called the quantitative revolution.
- The main objective was to identify mappable patterns for different human activities.
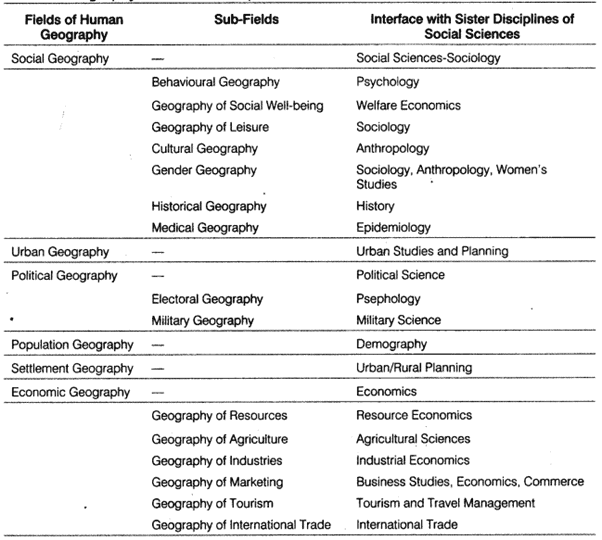
Human Geography and Sister Disciplines of Social Sciences
|
180 videos|620 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Human Geography: Introduction - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main schools of thought in human geography? |  |
| 2. What is the concept of determinism in human geography? |  |
| 3. How does possibilism differ from determinism in human geography? |  |
| 4. What is neo-determinism in human geography? |  |
| 5. What are the broad stages and thrust of human geography? |  |






















