Important Definition: How do Organisms Reproduce? | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Reproduction |

|
| Asexual Reproduction |

|
| Sexual Reproduction |

|
| Reproduction in Flowering Plants |

|
| Reproduction in Humans |

|
| Contraception |

|
Reproduction
Reproduction is the biological process through which new individuals of the same species are created, ensuring life continues.
Asexual Reproduction
A mode of reproduction where offspring are produced by a single parent, and they are genetically identical to the parent. Examples include binary fission, budding, and spore formation.
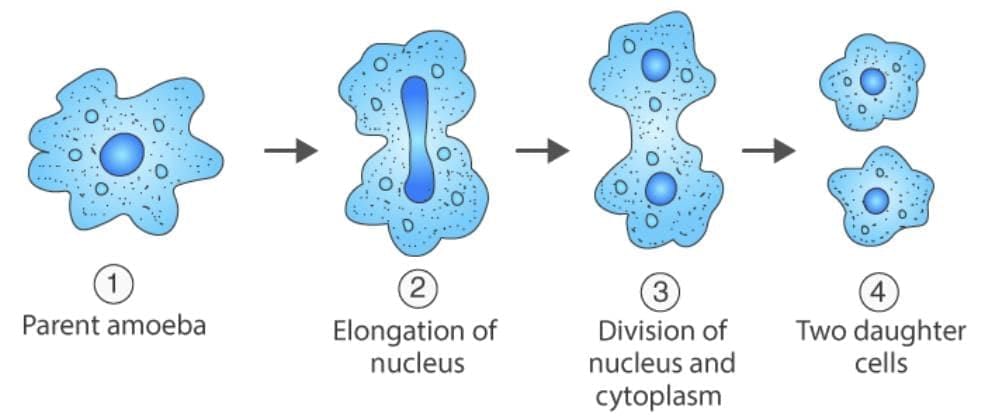
- Binary Fission: A type of asexual reproduction where a single organism divides into two identical individuals. Common in unicellular organisms like bacteria and amoeba.
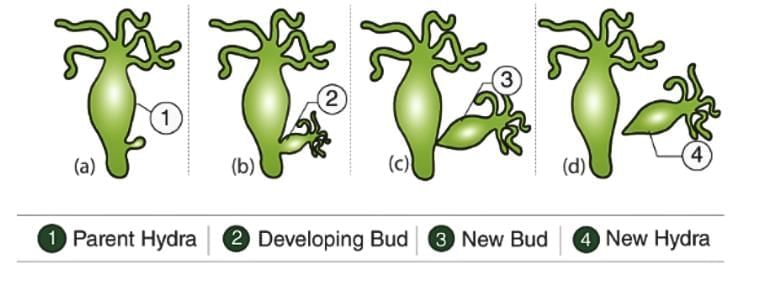
- Budding: A form of asexual reproduction in which a new individual develops as an outgrowth or bud on the parent organism. It eventually detaches to become a separate organism.
- Spore Formation: A method of asexual reproduction where specialized reproductive cells called spores are produced. These spores can develop into new individuals under suitable conditions.
- Fragmentation: A process of asexual reproduction in which an organism breaks into fragments, and each fragment can grow into a complete new organism. Common in organisms like Spirogyra.
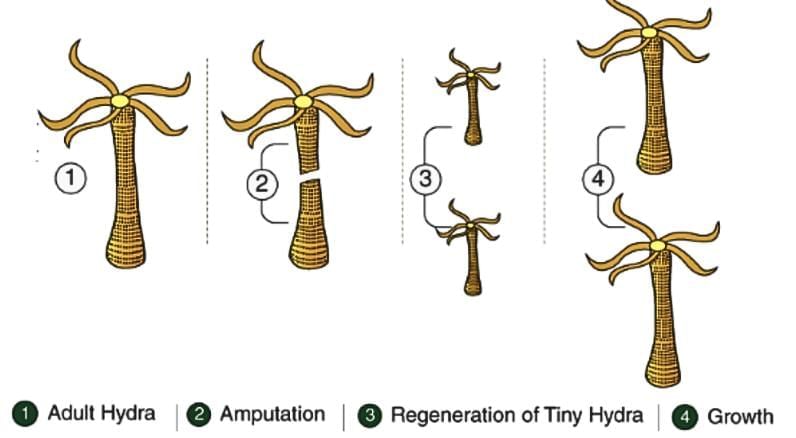
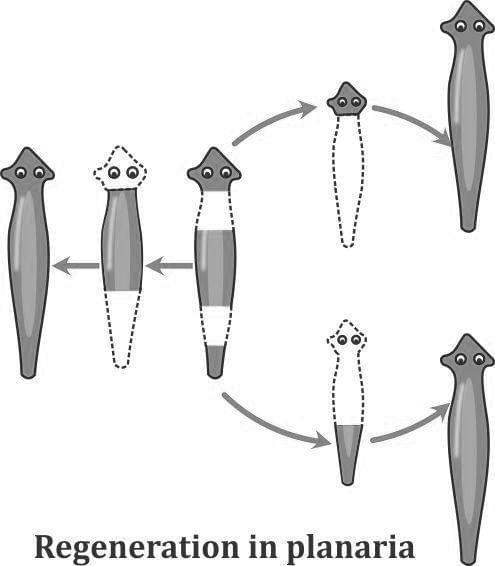
- Regeneration: The ability of an organism to regrow lost or damaged body parts and develop into new individuals. It is common in some lower animals like planaria.
- Vegetative Propagation: A method of asexual reproduction in plants where new plants develop from vegetative parts like roots, stems, or leaves. It is used in crops like sugarcane and rose.
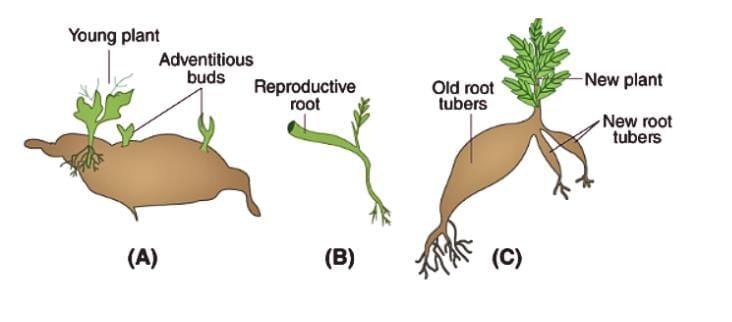
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves two parents, typically one male and one female, who provide genetic material to create offspring with variations.
- Gametes: Gametes are specialized reproductive cells that contain half the number of chromosomes. Fusion of these leads to the formation of a zygote. Gametes are of two types:
Male gamete: Sperm
Female gamete: Egg or ovum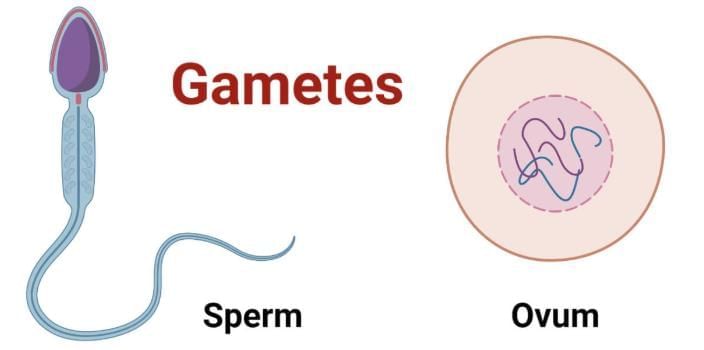
- Fertilization: The process by which male and female gametes (sperm and egg) combine to create a zygote, which is the first cell of a new individual.
Zygote A zygote is the first cell of the new organism formed after fertilization. It contains a complete set of chromosomes (half from each parent).
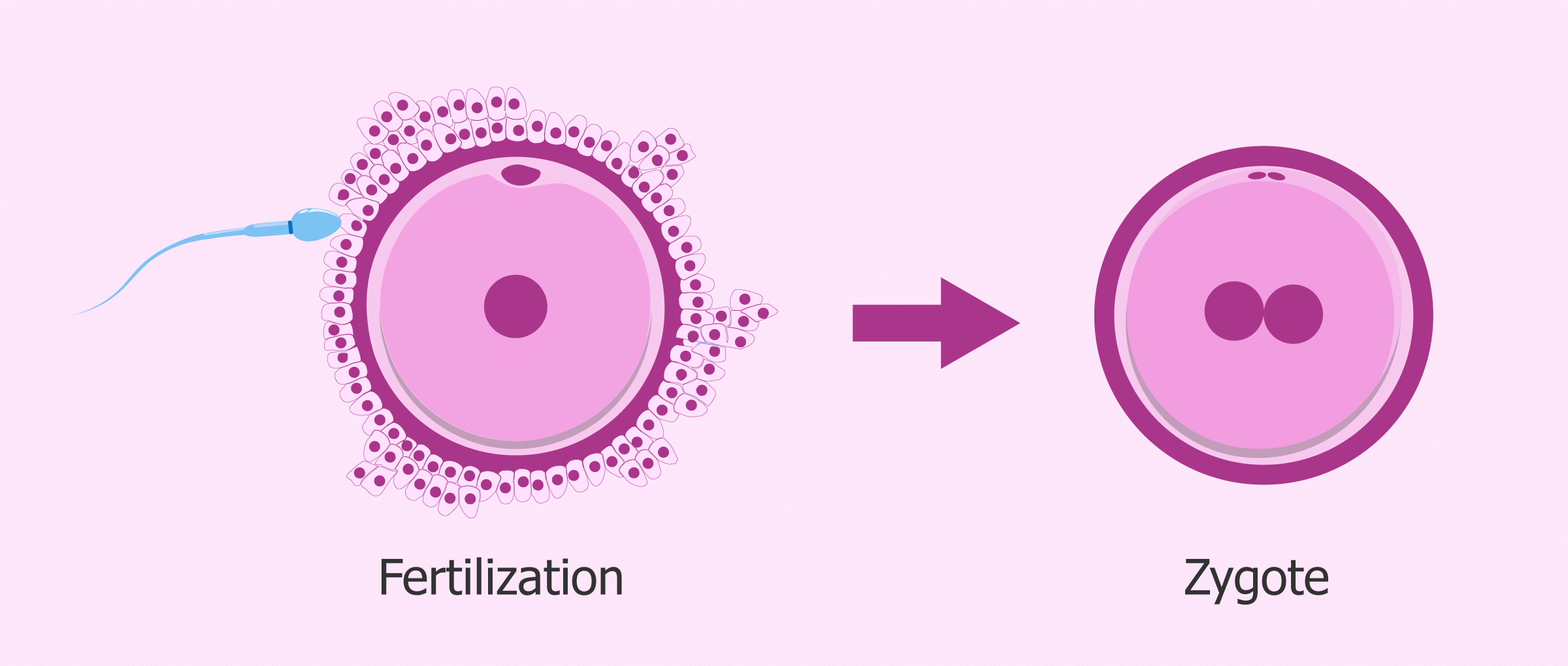
Embryo: The embryo is the early developmental stage of an organism. It forms after multiple divisions of the zygote and gradually develops into a mature organism.
Reproduction in Flowering Plants
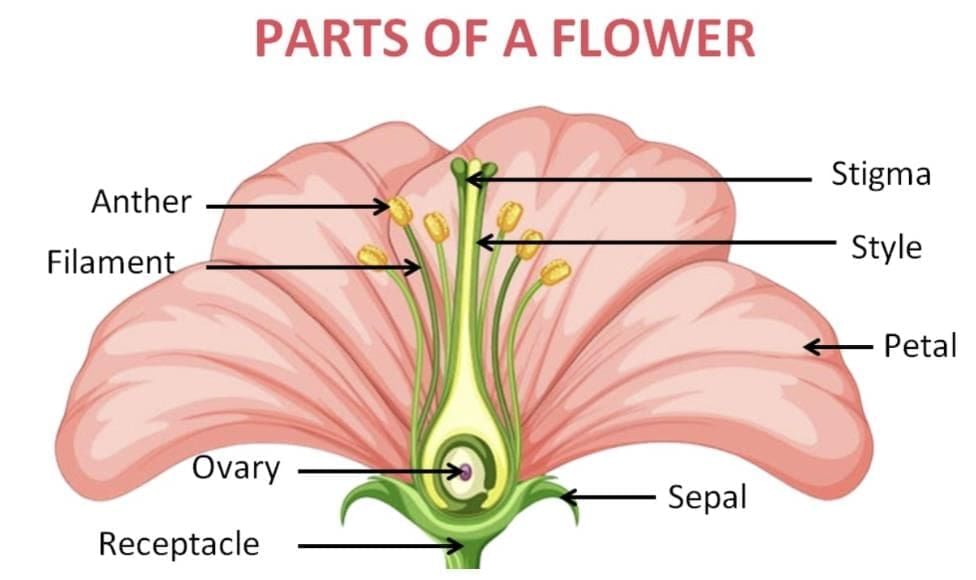
- Pollination: Pollination is the process of transferring pollen grains from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) of a flower. Pollination are of two types:
Self-pollination: Pollen lands on the stigma of the same flower or plant.
Cross-pollination: Pollen is transferred to a flower on another plant of the same species. - Ovary: The ovary is the basal part of the pistil (female reproductive part of a flower). It contains one or more ovules and later develops into a fruit after fertilisation.
- Ovule: The ovule is the structure inside the ovary where the egg cell is present. After fertilization, the ovule becomes the seed.
- Germination: It is the process by which a seed develops into a new plant.
Reproduction in Humans
- Puberty: The stage of development in humans when reproductive organs become functional, marked by physical and hormonal changes enabling reproduction.
Girls: 10–14 years
Boys: 12–16 years Menstruation: If fertilization does not occur, the thickened lining of the uterus along with blood is shed through the vagina. This cycle, called menstruation, occurs roughly every 28 days in females.
- Menarche: The first instance of menstruation in a girl, usually during puberty.
- Menopause: The time in a woman's life when menstruation ceases, typically between the ages of 45 and 55, indicating the end of her reproductive years.
Placenta: The placenta is a special organ that forms during pregnancy and connects the developing embryo to the mother’s uterus. This facilitates the exchange of nutrients, gases, and wastes without mixing the mother’s and baby's blood
- Gonads: The main reproductive organs in animals. In males, these are testes; in females, they are ovaries.
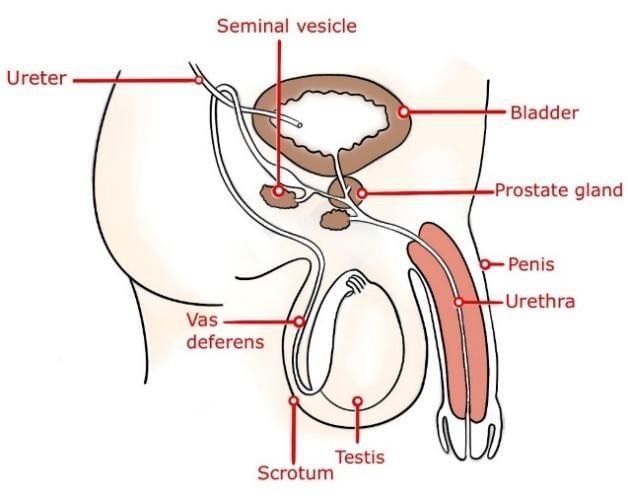
1. Male Reproductive System
The main organs of the male reproductive system include:
Testes – produce sperm and the hormone testosterone
Vas deferens – carries sperm from testes to urethra
Seminal vesicles – add fluid to nourish sperm
Penis – organ that transfers sperm to the female body
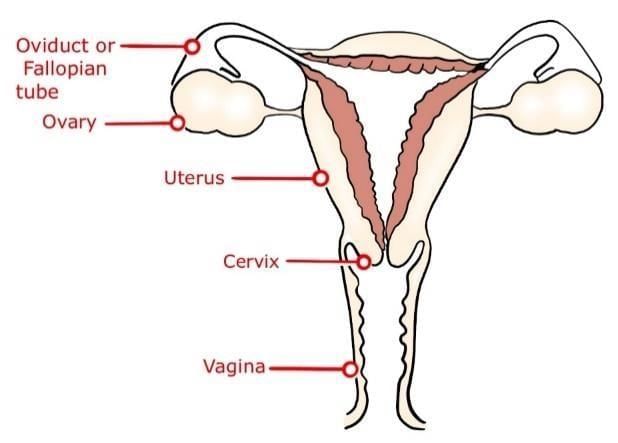
2. Female Reproductive System
The main organs of the female reproductive system include:
Ovaries – produce eggs and hormones (estrogen, progesterone)
Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts) – site of fertilization
Uterus – where embryo implants and develops
Vagina – receives the sperm and serves as the birth canal.
Contraception
Contraception refers to methods used to prevent pregnancy by stopping fertilization or preventing implantation of the embryo. Some methods are also effective in preventing sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Types of Contraceptive Methods:
1. Barrier Methods: These prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
Condoms (male/female): Thin covers worn over the penis or inserted into the vagina to block sperm.
Diaphragm: A dome-shaped device placed inside the vagina to cover the cervix and stop sperm entry.
2. Hormonal Methods: These use hormones to prevent ovulation or fertilization.
Birth control pills: Oral tablets that stop the release of eggs (ovulation).
Intrauterine devices (IUDs): Small devices placed inside the uterus to prevent fertilization or implantation.
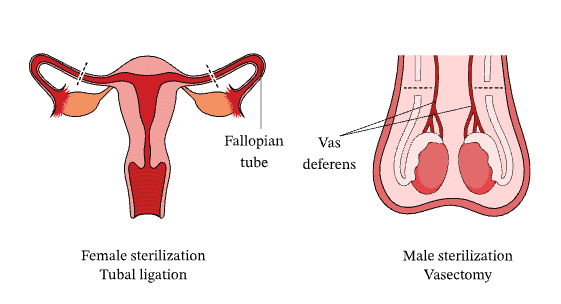
3. Surgical Methods: These are permanent methods to prevent the transport of gametes.
- Vasectomy: A surgical method of contraception in males involving the cutting and tying of the vas deferens to prevent the passage of sperm.
- Tubectomy: A surgical method of contraception in females, which involves the cutting and sealing of the fallopian tubes to prevent the passage of eggs.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Important Definition: How do Organisms Reproduce? - Science Class 10
| 1. What is asexual reproduction and how does it differ from sexual reproduction? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of organisms that reproduce asexually? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction? |  |
| 4. What are some common contraceptive methods and how do they work? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding reproduction important in biology? |  |
















