Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science Class 10 > Important Definitions : Life Processes
Important Definitions : Life Processes | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Life Processes
"Life Processes" refers to the essential functions that living organisms carry out to maintain their existence and sustain life. These processes are fundamental for the survival and growth of living organisms.
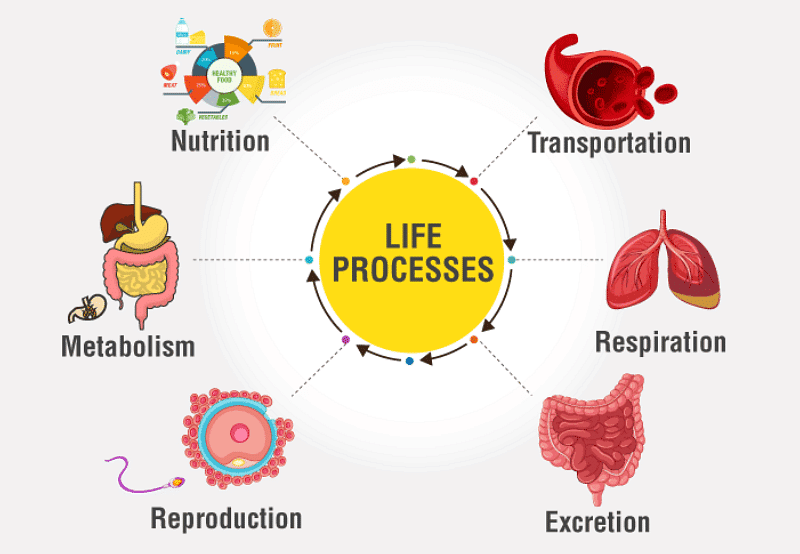
The main life processes taught at this level typically include the following:
- Nutrition: Nutrition is the process by which organisms obtain and utilize food for energy and growth. It involves the following sub-processes:
- Ingestion: The intake of food or organic materials.
- Digestion: The breakdown of complex food molecules into simpler, usable substances.
- Absorption: The uptake of digested nutrients by cells.
- Respiration: Respiration is the process of obtaining energy from the breakdown of nutrients, typically involving the use of oxygen (aerobic respiration) or occurring in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration).
- Transportation: Transportation involves the circulation of substances (e.g., nutrients, oxygen, and waste products) within an organism's body. I
- Excretion: Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste products, such as carbon dioxide and nitrogenous wastes, from the body.
- Synthesis: Living organisms carry out various biochemical reactions to produce complex molecules required for growth and maintenance.
- Growth and Development: Growth involves an increase in size, while development refers to the process of maturing and becoming more complex.
- Reproduction: Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce offspring, ensuring the continuity of their species. It can be asexual (single parent) or sexual (two parents).
- Response to Stimuli: Living organisms can sense and respond to changes in their environment, which is essential for their survival. This includes actions like movement or altering metabolic activities in response to external factors.
- Adaptation: Over time, living organisms evolve and adapt to their environments through natural selection, ensuring that they are better suited to survive and reproduce.
Question for Important Definitions : Life ProcessesTry yourself: Which life process involves the breakdown of complex food molecules into simpler, usable substances?View Solution
The document Important Definitions : Life Processes | Science Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Science Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Important Definitions : Life Processes - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the essential life processes required for living organisms? |  |
Ans.The essential life processes required for living organisms include nutrition, respiration, transport, excretion, reproduction, and growth. These processes enable organisms to maintain homeostasis and ensure survival.
| 2. How does the process of nutrition differ between plants and animals? |  |
Ans.Nutrition in plants involves photosynthesis, where they convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. In contrast, animals obtain nutrition by consuming food, which is then broken down into simpler substances for energy.
| 3. What is the significance of respiration in living organisms? |  |
Ans.Respiration is crucial as it provides energy for various cellular activities. It involves the exchange of gases, where oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is released, allowing organisms to convert glucose into usable energy (ATP).
| 4. Why is excretion important for living organisms? |  |
Ans.Excretion is vital as it helps remove waste products generated from metabolic processes. By eliminating harmful substances, organisms can maintain a stable internal environment and prevent toxicity that could lead to health issues.
| 5. What role does reproduction play in the continuity of life? |  |
Ans.Reproduction is essential for the continuation of species. It ensures the transfer of genetic material from parents to offspring, allowing for variation and adaptation to changing environments, ultimately contributing to evolutionary processes.
Related Searches

















