NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physics Class 12 > Important Derivations: Electromagnetic Induction
Important Derivations: Electromagnetic Induction | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Important Derivations
(1) Derivation of Emf induced in a rod moving in a uniform magnetic field.
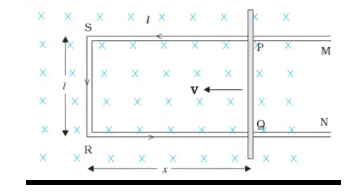
The magnetic flux linked with the area SPQR is:
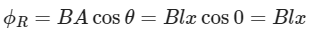 As the rod PQ is moving towards left with a velocity , x is changing and
As the rod PQ is moving towards left with a velocity , x is changing and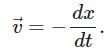 Here
Here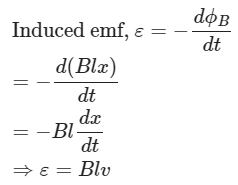 This emf is induced in the rod because of the motion of the rod in the magnetic field. Therefore this emf is called motional emf.
This emf is induced in the rod because of the motion of the rod in the magnetic field. Therefore this emf is called motional emf.
(2) Derivation of EMF induced in a rotating metallic rod in a uniform magnetic field
Let the rotating metallic rod subtends an angle θ in time t with the centre of the circle.
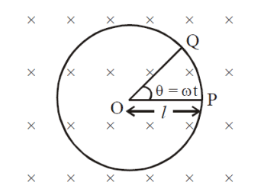
The area of the sector OPQ is given by,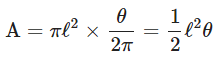
The induced emf is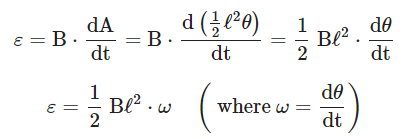
The document Important Derivations: Electromagnetic Induction | Physics Class 12 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physics Class 12.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Important Derivations: Electromagnetic Induction - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is electromagnetic induction? |  |
Ans. Electromagnetic induction is the process where a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in a conductor, resulting in the production of an electric current.
| 2. How is electromagnetic induction used in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Electromagnetic induction is used in various applications in our daily lives. Some examples include electric generators, transformers, induction cooktops, and wireless charging technologies.
| 3. What is Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction? |  |
Ans. Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction states that the magnitude of the induced EMF in a circuit is directly proportional to the rate at which the magnetic field changes through the circuit.
| 4. What is Lenz's law? |  |
Ans. Lenz's law states that the direction of the induced current in a conductor is such that it opposes the change in magnetic field causing it. In simple terms, it follows the principle of conservation of energy.
| 5. What is the difference between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC)? |  |
Ans. Direct current (DC) flows in only one direction, while alternating current (AC) periodically changes its direction. DC is commonly used in batteries and electronic devices, whereas AC is used for power transmission over long distances.
Related Searches





















