NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Important Diagrams: Breathing and Exchange of gases
Important Diagrams: Breathing and Exchange of gases | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
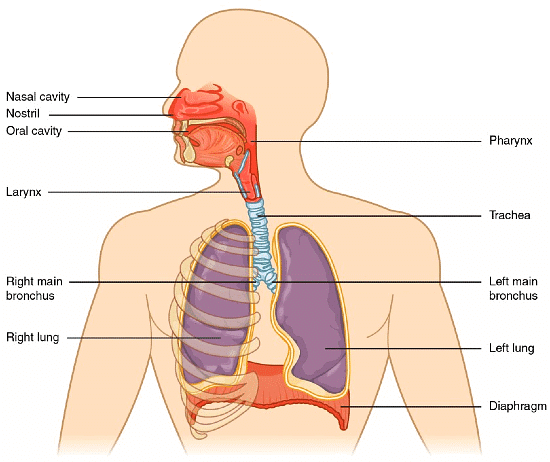
Human Respiratory System
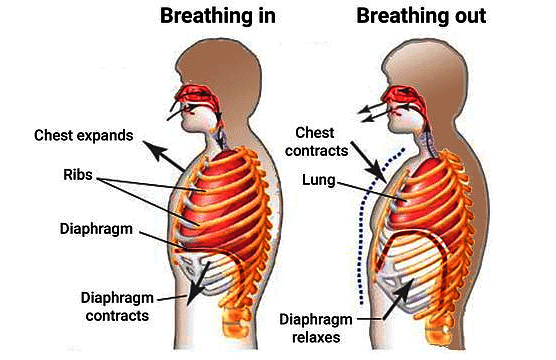
Mechanism of Inspiration and Expiration
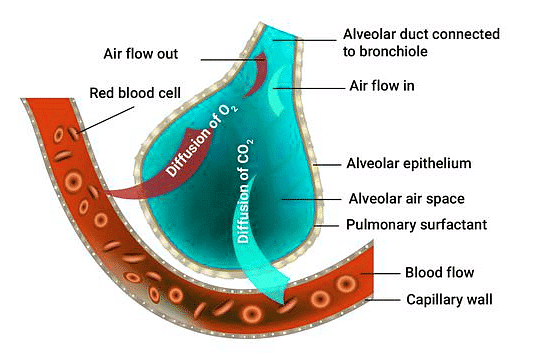
Gaseous Exchange at the Site of Alveoli
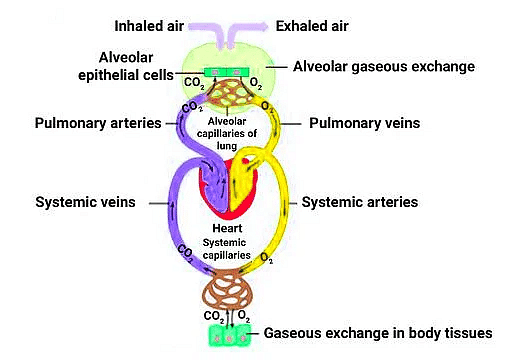
Transport of Gases between the Alveoli and Body Tissues
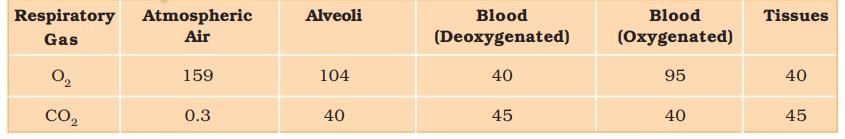 Partial Pressures (in mm Hg) of Oxygen and Carbon dioxide at Different Parts Involved in Diffusion in Comparison to those in Atmosphere
Partial Pressures (in mm Hg) of Oxygen and Carbon dioxide at Different Parts Involved in Diffusion in Comparison to those in Atmosphere
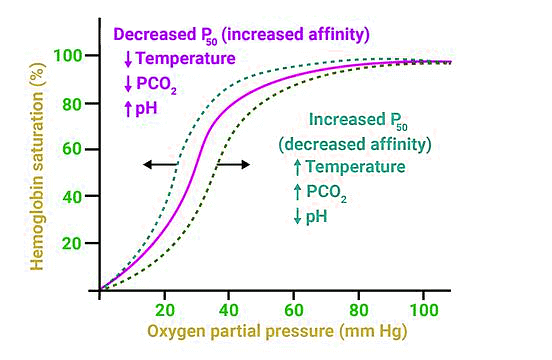
Oxygen-Dissociation Curve
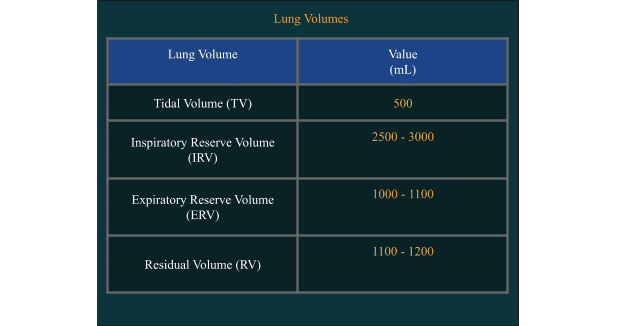
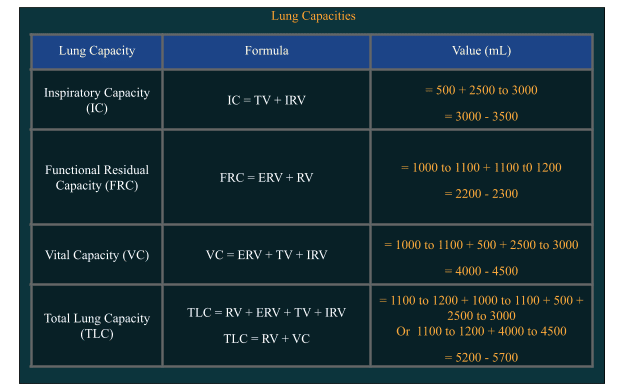
Lung Volumes and Capacities
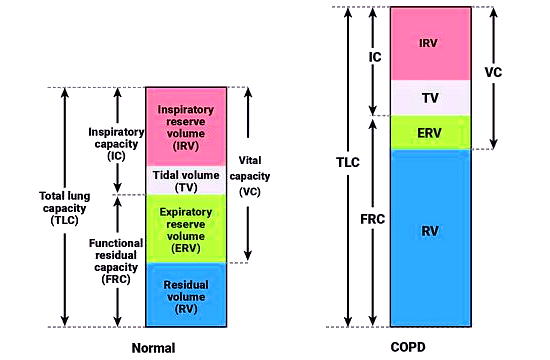 Disorders related to lung volumes and capacities
Disorders related to lung volumes and capacities
Respiratory Disorder
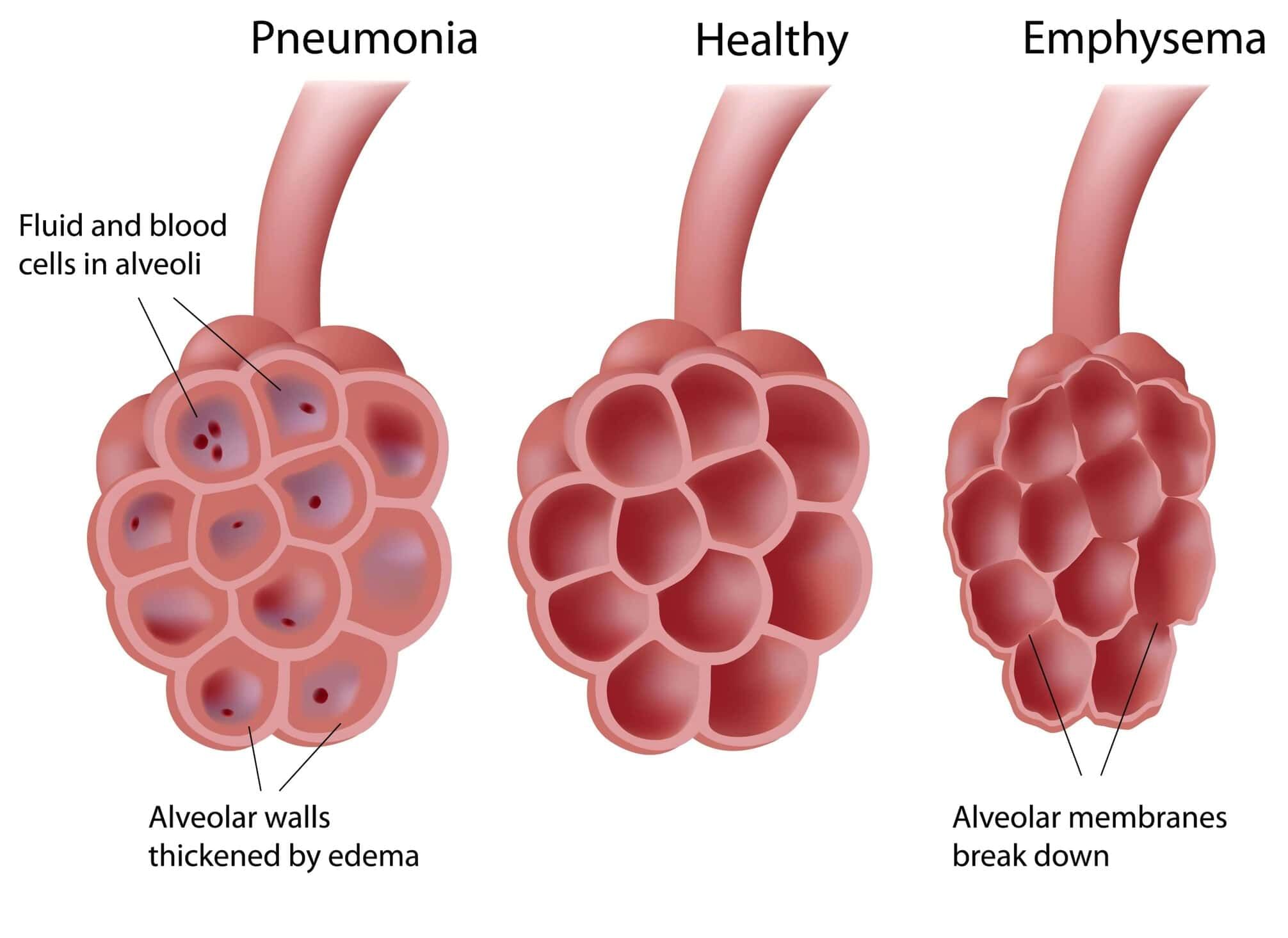
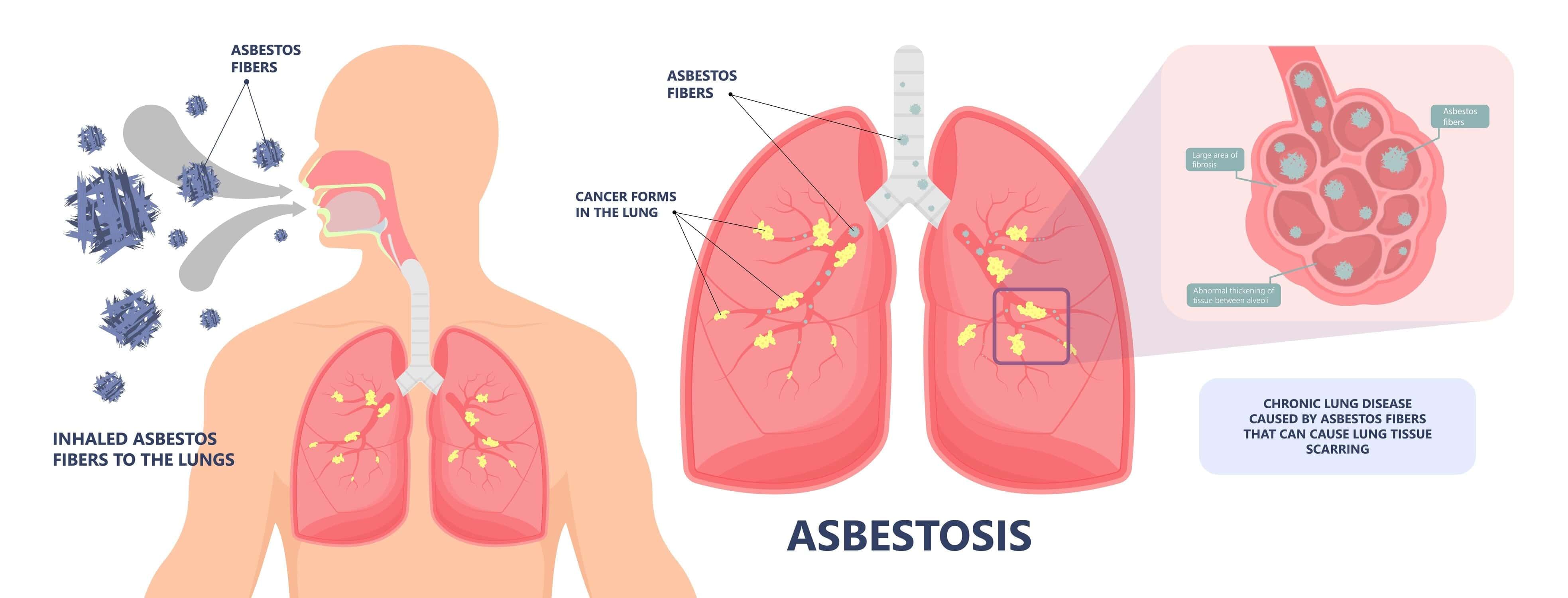
The document Important Diagrams: Breathing and Exchange of gases | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
169 videos|524 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Breathing and Exchange of gases - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the mechanism of inspiration in the human respiratory system? |  |
Ans. The mechanism of inspiration involves the contraction of the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward, increasing the thoracic cavity's volume. Simultaneously, the intercostal muscles contract, raising the rib cage. This combination of movements reduces the pressure inside the thoracic cavity, allowing air to flow into the lungs from the atmosphere.
| 2. How does expiration occur in the respiratory system? |  |
Ans. Expiration is primarily a passive process where the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax. As the diaphragm moves upward and the rib cage lowers, the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases. This increase in pressure inside the thoracic cavity pushes air out of the lungs and into the atmosphere. In forced expiration, additional muscles, such as the abdominal muscles, may contract to expel air more rapidly.
| 3. What is the role of the oxygen-dissociation curve in gas exchange? |  |
Ans. The oxygen-dissociation curve illustrates how hemoglobin binds to oxygen at various partial pressures of oxygen (pO2). It shows that at high pO2 levels, such as in the lungs, hemoglobin binds more oxygen, while at lower pO2 levels, like in tissues, it releases oxygen. This curve is important for understanding how oxygen is transported in the blood and how efficiently it is delivered to tissues that need it.
| 4. What are the important diagrams related to breathing and gas exchange that are commonly found in NEET? |  |
Ans. Important diagrams include the structure of the respiratory system (showing the trachea, bronchi, and lungs), the mechanism of breathing (illustrating diaphragm and intercostal muscle movements), the oxygen-dissociation curve of hemoglobin, and diagrams depicting gas exchange in the alveoli. These visuals help in understanding the anatomy and physiology involved in respiration and gas exchange.
| 5. How does the body adapt to high altitudes in terms of respiration and gas exchange? |  |
Ans. At high altitudes, the partial pressure of oxygen is lower, leading to reduced oxygen availability. The body adapts by increasing the breathing rate (hyperventilation) to enhance oxygen intake. Additionally, over time, there is an increase in red blood cell production (erythropoiesis) to improve oxygen transport. These adaptations help maintain adequate oxygen levels in the blood and tissues despite the lower atmospheric oxygen pressure.
Related Searches

















