NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Important Diagrams: Locomotion and Movement
Important Diagrams: Locomotion and Movement | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Parts of the Axial Skeleton
1. Bones of the Cranium
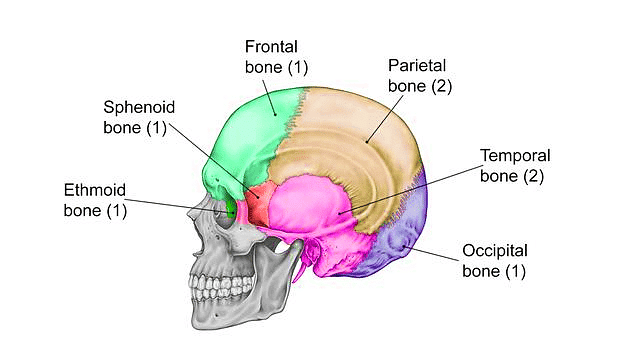
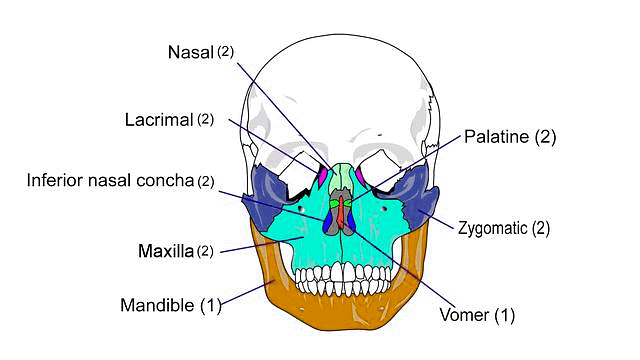
2. Bones of the Face
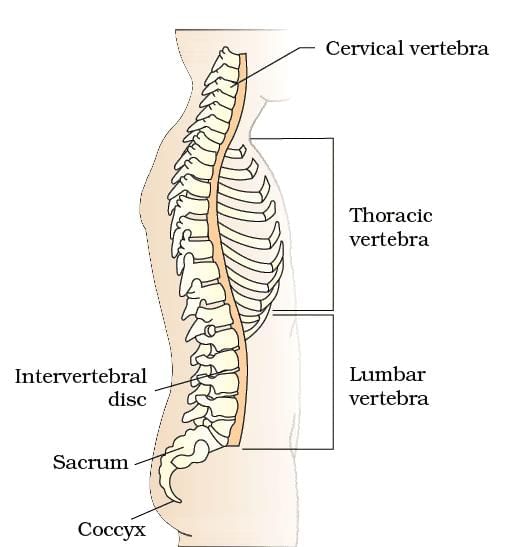
3. Vertebral Column
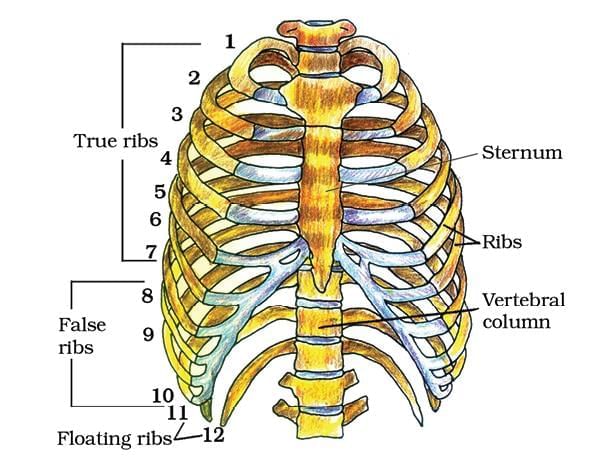
4. Rib Cage
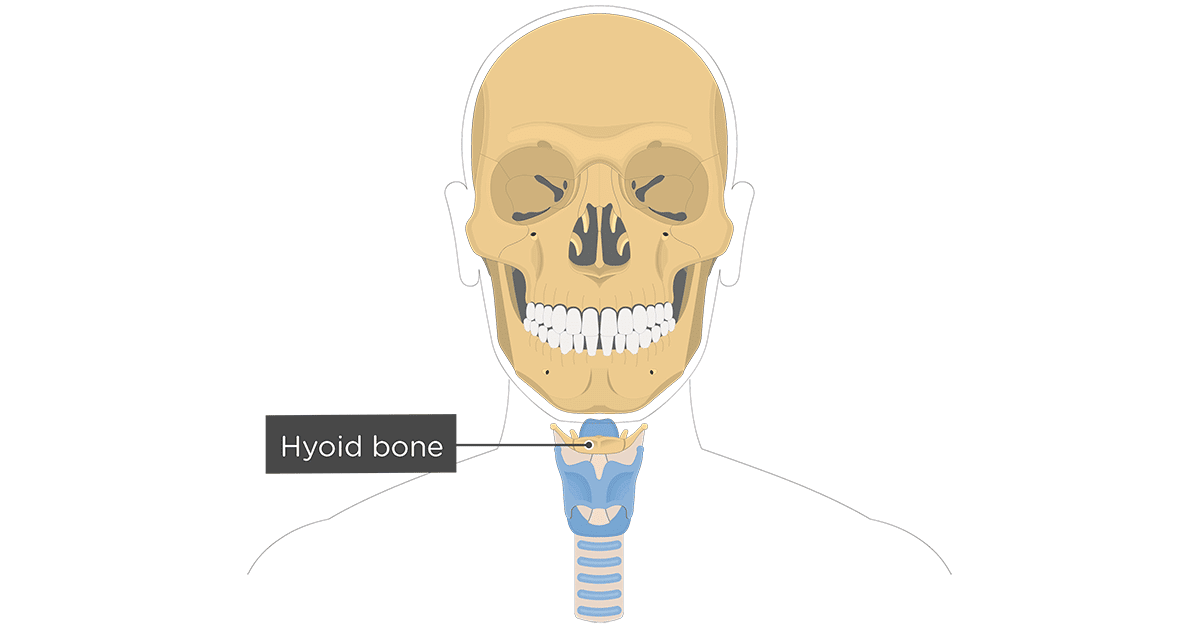
5. Hyoid Bone
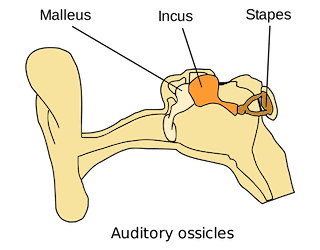
6. Ear Ossicles
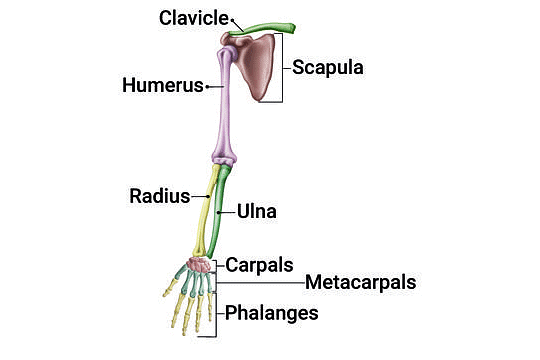
Parts of the Appendicular Skeleton
1. Right Pectoral Girdle and Upper Arm
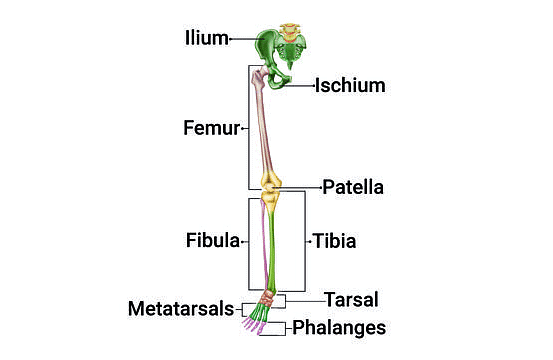
2. Right Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limb Bone
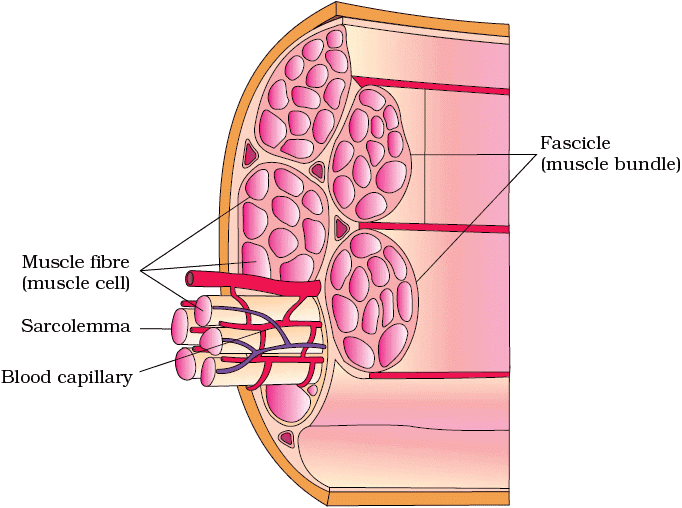
Structure of Skeletal Muscle
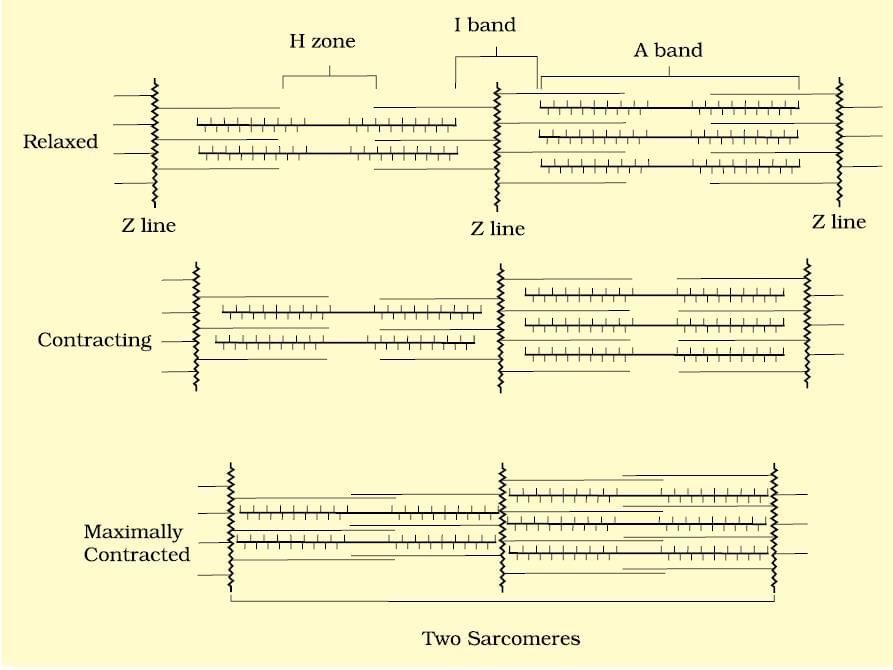
Structure of the Sarcomere
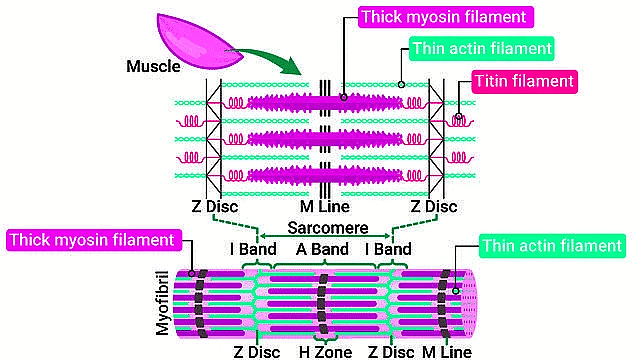
Structure of Contractile Proteins
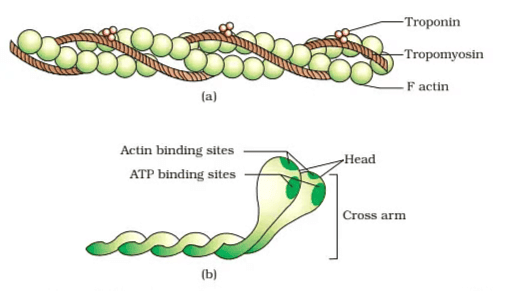 (a) An actin (thin) filament (b) Myosin monomer (Meromyosin)
(a) An actin (thin) filament (b) Myosin monomer (Meromyosin)
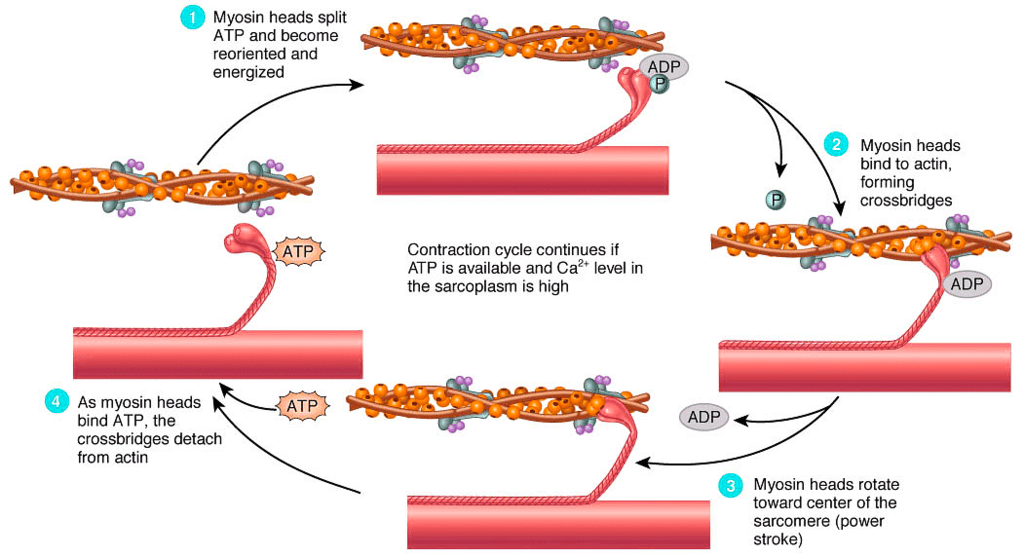
Sliding Filament Theory
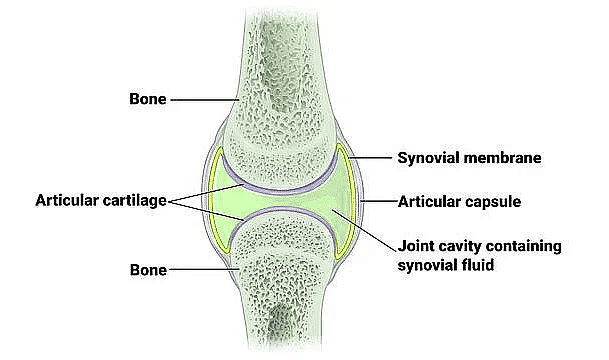
Synovial Joint Structure
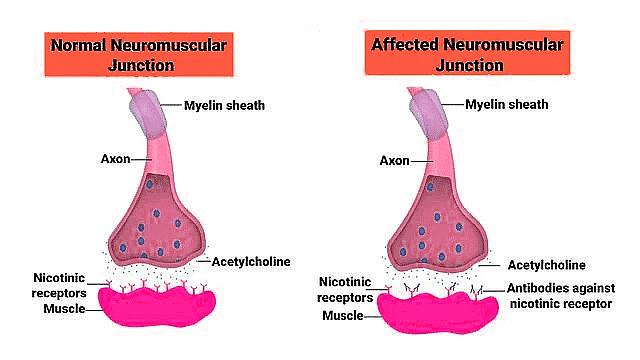
Myasthenia Gravis
The document Important Diagrams: Locomotion and Movement | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Locomotion and Movement - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the basic structure of skeletal muscle? |  |
Ans. Skeletal muscle is composed of long, cylindrical cells known as muscle fibers. These fibers are multinucleated and contain myofibrils, which are the contractile elements of the muscle. The myofibrils are organized into repeating units called sarcomeres, which are responsible for muscle contraction. The skeletal muscle is also surrounded by connective tissue, including epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium, which provide support and structure.
| 2. What is a sarcomere and its function in muscle contraction? |  |
Ans. A sarcomere is the fundamental contractile unit of striated muscle tissue, defined by the area between two Z discs. It contains overlapping thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments. During muscle contraction, the sarcomeres shorten as the actin filaments slide over the myosin filaments, leading to the overall shortening of the muscle fiber.
| 3. How are contractile proteins structured in skeletal muscle? |  |
Ans. Contractile proteins in skeletal muscle include actin and myosin. Actin is a globular protein that polymerizes to form thin filaments, while myosin is a motor protein that forms thick filaments. Myosin molecules have a head that interacts with actin to form cross-bridges, enabling muscle contraction. The arrangement of these proteins within the sarcomere is crucial for the contractile function of the muscle.
| 4. What is the mechanism of muscle contraction? |  |
Ans. Muscle contraction occurs through a process known as the sliding filament theory. When a muscle receives a signal from a motor neuron, calcium ions are released, allowing myosin heads to attach to binding sites on actin filaments. The myosin heads pivot, pulling the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, which shortens the muscle fiber. ATP is necessary for this process, as it provides the energy required for the myosin heads to detach and reset for another contraction cycle.
| 5. What are the differences between the axial and appendicular skeleton? |  |
Ans. The axial skeleton consists of the bones that form the central axis of the body, including the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage. Its primary function is to protect vital organs and support the body. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the limbs (arms and legs) and the girdles (shoulder and pelvic) that attach them to the axial skeleton. This part of the skeleton is primarily involved in movement and locomotion.
Related Searches
















