Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science Class 10 > Important Equations and Definitions: Electricity
Important Equations and Definitions: Electricity | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Electric Current |

|
| Electric Charge and Potential |

|
| Ohm’s Law |

|
| Combination of Resistors |

|
| Heating Effect of Electric Current |

|
| Electric Power |

|
| Conductors and Insulators |

|
| Current Rating |

|
Electric Current
- Definition: The flow of electric charge is known as Electric Current. It is carried by moving electrons through a conductor.
- Direction: By convention, electric current flows in the opposite direction to the movement of electrons.
- Electric Circuit: A continuous and closed path of electric current.
Expression of Electric Current
- Symbol: Electric current is denoted by the letter ‘I’.
- Formula: If a net electric charge (Q) flows through a conductor in time t, then
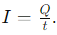
S.I. Units
- Electric Charge: Coulomb (C). 1 C=6×1018 electrons.
- Electric Current: Ampere (A). 1 A=1 C/s.
Small Quantities
- Milliampere (mA): 1 mA=10−3 A
- Microampere (μA): 1 μA=10−6 A
Instruments
- Ammeter: Measures electric current in a circuit.
 Ammeter
Ammeter
Electric Charge and Potential
- Charge: Fundamental property of matter. Two types: Positive and Negative.
- Properties of Electric Charge:
- Unlike charges attract, like charges repel.
- Force between charges varies with the product of charges and inversely with the square of the distance.
Electric Potential and Potential Difference
- Electric Potential: Amount of electric potential energy at a point.
- Potential Difference (Voltage): Difference in electric potential energy between two points.
V=W/Q - S.I. Unit: Volt (V).
Instruments
- Voltmeter: Measures potential difference.
 Voltmeter
Voltmeter
- Galvanometer: Detects current in a circuit.
 Galvanometer
Galvanometer
Ohm’s Law
- Statement: Potential difference is directly proportional to electric current at constant temperature.
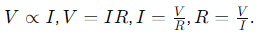
- Resistance: Property resisting electric current. Unit: Ohm (ΩΩ).
Factors Affecting Resistance
- Nature: Good conductors vs. insulators.
- Length:R ∝ l
- Area of Cross Section: R ∝ 1/A
- Specific Resistance (Resistivity):
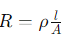 . Unit: Ω⋅m
. Unit: Ω⋅m
Combination of Resistors
Series Combination
- Total Resistance (Rs):Rs=R1+R2+R3.
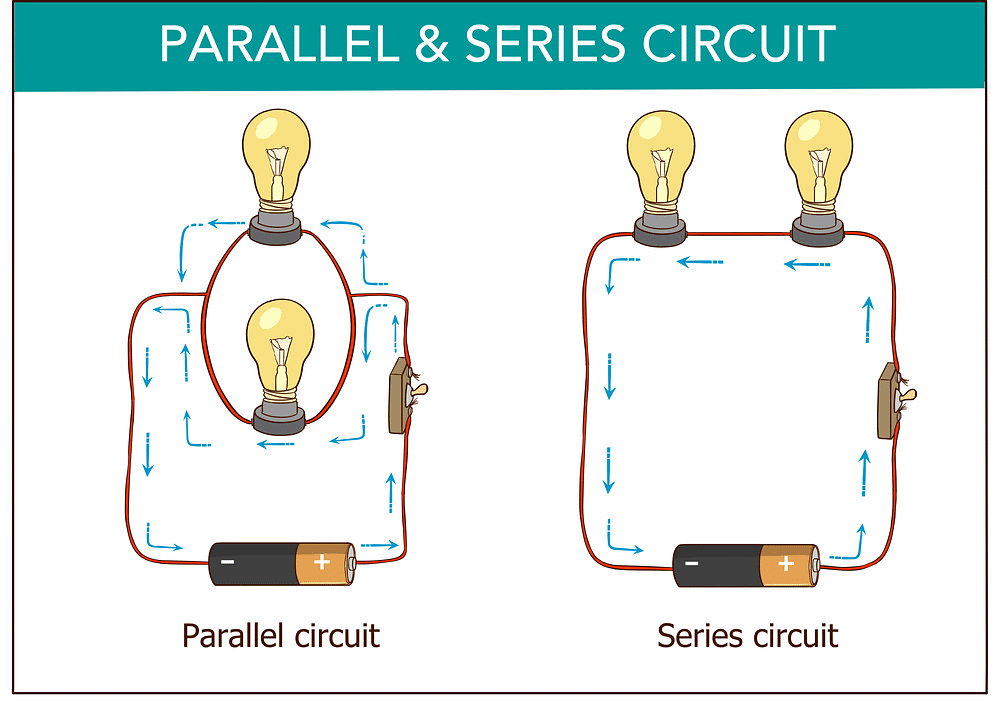
Parallel Combination
- Inverse of Total Resistance
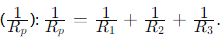
Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Joule’s Law: H=I2Rt
- Applications: Electric bulb, electric iron, electric heater.
Electric Power
- Definition: Work done per unit time. P=VI.
- S.I. Unit: Watt (W). 1 W=1 V×1 A.
- Kilowatt: 1 kW=1000 W.
Electric Energy
- Definition: Amount of work done to maintain continuous electric current.
- Unit: Joule (J).
Electric Power Consumption
- Unit: Kilowatt-hour (kWh). 1 kWh=3.6×106 J.
Conductors and Insulators
- Conductor: Allows flow of electrons. Low opposition to current.
- Insulator: Doesn't allow flow of electrons. High opposition to current.
Current Rating
- Definition: Maximum current without damaging the appliance.
The document Important Equations and Definitions: Electricity | Science Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Science Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Important Equations and Definitions: Electricity - Science Class 10
| 1. What is electric current and how is it measured? |  |
Ans.Electric current is the flow of electric charge in a conductor. It is measured in amperes (A) using an ammeter. One ampere corresponds to one coulomb of charge passing through a point in a circuit per second.
| 2. What is the difference between electric charge and electric potential? |  |
Ans.Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that causes it to experience a force in an electric field, measured in coulombs (C). Electric potential, measured in volts (V), is the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge at a point in a circuit, indicating how much work would be done to move a charge from a reference point.
| 3. How does Ohm’s Law relate voltage, current, and resistance? |  |
Ans.Ohm's Law states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. It is expressed mathematically as V = I × R.
| 4. What are the different ways to combine resistors in a circuit? |  |
Ans.Resistors can be combined in two main ways: in series and in parallel. In a series combination, the total resistance increases and is the sum of individual resistances (R_total = R1 + R2 + ...). In parallel, the total resistance decreases, calculated using the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... .
| 5. What is the heating effect of electric current and its applications? |  |
Ans.The heating effect of electric current, also known as Joule's heating, occurs when electric current passes through a conductor, producing heat due to resistance. This effect is utilized in various applications, such as electric heaters, toasters, and incandescent light bulbs, where heat generation is desired.
Related Searches
















