Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science Class 10 > Important Equations and Definitions: Heredity
Important Equations and Definitions: Heredity | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Definitions
- Genetics is the branch of biology that studies how traits and characteristics are passed down and how they differ among individuals in a population.
- Heredity is the process of passing traits from one generation to the next, while variation refers to the differences in these traits among individuals.
- Somatic Variation: Changes in body cells that are not inherited and do not get passed to offspring; these are also known as acquired traits and can result from environmental influences.
- Gametic Variation: Changes in reproductive cells (gametes) that are inherited, contributing to the diversity of traits in offspring.
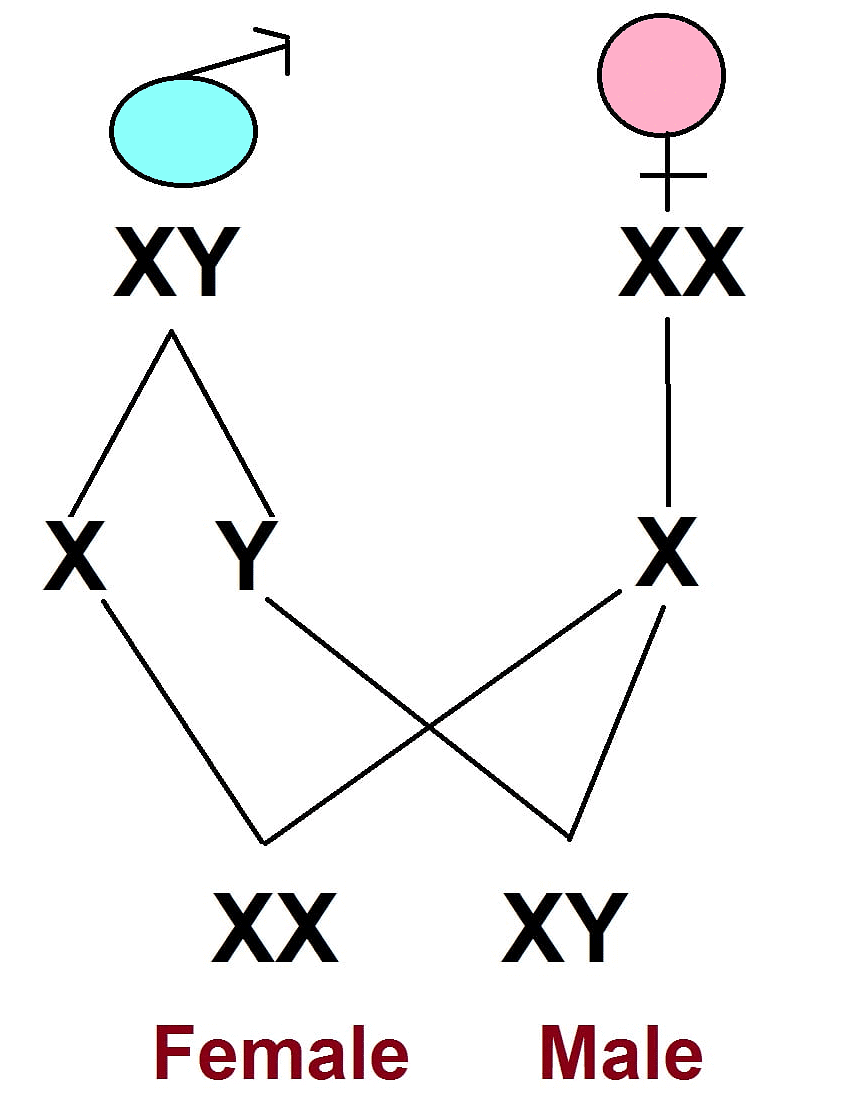
- Determination of sex: The method by which the gender of an offspring is decided, influenced by genetic and environmental factors. A child's sex is determined by whether the paternal chromosome is X (for girls) or Y (for boys).
- Factors responsible for Sex Determination: Environmental factors like temperature in some species or genetic factors such as sex chromosomes (XX for females and XY for males) influence sex determination.
- Acquired Traits: Characteristics developed in an individual due to specific conditions or experiences that are not passed on to offspring, unlike inherited traits.
- Inherited Traits: Traits passed down through genetics from one generation to the next, which can affect the evolution of species.
- Gene Flow: The movement of genes between partially separated populations, allowing for the exchange of genetic material.
- Genetic Drift: Random changes in the frequency of genes in a population over generations, often due to chance events.
- Natural Selection: A process where nature favours organisms with beneficial variations, enhancing their chances of survival.
- Geographical Isolation: Occurs when physical barriers, like mountains or rivers, divide populations, leading to reproductive isolation and potential new species.
- Variation: Differences among individuals of the same species, resulting from either heredity or environmental influences.
- Heredity: The passing of traits from parents to offspring through genetic information.
- Reproduction: The biological process of creating new individuals of the same species.
- Asexual Reproduction: Involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to that parent.
- Sexual Reproduction: Involves combining genetic material from two parents, resulting in offspring with a unique mix of traits.
- Trait: A specific characteristic or feature of an organism, like height, colour, or shape.
- Dominant Trait: A trait that appears in an individual's phenotype even if only one copy of the gene is present.
- Recessive Trait: A trait that shows in the phenotype only when two copies of the gene are present.
- Genes: DNA segments with instructions for making proteins and determining specific traits.
- Chromosomes: Thread-like structures made of DNA and proteins in the cell nucleus that carry genetic information.
- Sex Chromosomes: Chromosomes that determine an individual's sex; in humans, these are the X and Y chromosomes.
- Genetic Linkage: The tendency of genes on the same chromosome to be inherited together.
Principles Of Inheritance And Variation
- Gamete Calculation
The types of gametes produced can be calculated using a formula:
Number of gametes: 2n, where 'n' is the number of heterozygous alleles, which refer to different alleles at a locus. - Recombination Frequency
A numerical value that describes the proportion of recombinant offspring produced in a genetic cross is referred to as recombinant frequency. It is calculated as:
Recombinant Frequency: (Number of Recombinant Offspring / Total Number of Offspring) × 100. - Genetic Linkage
Learn about the formula to determine the possibility of genetic linkage concerning the position of genes on a chromosome through an interesting GIF. Each gene set exists not as a single long thread of DNA but as separate independent pieces called chromosomes. Thus:- Each cell has two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent.
- When two germ cells combine, they restore the normal number of chromosomes in the progeny, ensuring the stability of the DNA of the species.
Equations:
- Number of Gametes: 2n, where 'n' is the number of heterozygous alleles.
- Recombinant Frequency: The proportion of recombinant offspring in a genetic cross, calculated as (Number of Recombinant Offspring / Total Number of Offspring) × 100.
The document Important Equations and Definitions: Heredity | Science Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Science Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Important Equations and Definitions: Heredity - Science Class 10
| 1. What is heredity and how does it work? |  |
Ans.Heredity is the process by which traits and characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring through genes. Each parent contributes one set of genes to their offspring, which determines various physical and behavioral traits. The fundamental unit of heredity is the gene, which is located on chromosomes.
| 2. What are the main principles of inheritance? |  |
Ans.The main principles of inheritance are formulated by Gregor Mendel and include the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment. The Law of Segregation states that allele pairs separate during gamete formation, ensuring that offspring receive one allele from each parent. The Law of Independent Assortment states that the segregation of one allele pair is independent of the segregation of another pair, resulting in genetic variation.
| 3. What is the difference between dominant and recessive traits? |  |
Ans.Dominant traits are expressed in the phenotype even if only one copy of the allele is present, while recessive traits require two copies of the allele to be expressed. For example, if a dominant allele (A) is present with a recessive allele (a), the dominant trait will be shown in the organism.
| 4. How do variations occur in offspring? |  |
Ans.Variations in offspring occur due to several factors, including genetic recombination during meiosis, mutations, and environmental influences. Genetic recombination shuffles the genes during the formation of gametes, while mutations introduce new genetic variations. Environmental factors can also influence the expression of genes, leading to phenotypic differences.
| 5. What are genotypes and phenotypes? |  |
Ans.Genotypes refer to the genetic makeup of an organism, specifically the alleles it possesses for a trait (for example, AA, Aa, or aa). Phenotypes, on the other hand, are the observable characteristics or traits of an organism that result from the interaction of its genotype with the environment (for example, flower color or height).
Related Searches

















