Important Organic Chemistry & Organic Formulas for JEE and NEET
1. (Alkane)
Wurtz reaction : e.g., R1 X + R2X + 2 Na → R1- R2 + 2NaX
Decarboxylation :
General reaction 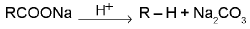
Mechanism 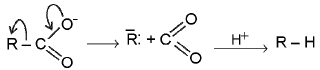
The thermal decarboxylation of free acids may be :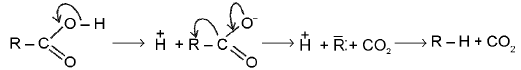
(2. Alkyl halide)
Nucleophilic substitution Reaction (SN1, SN2)
SN1 reaction :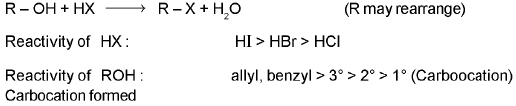
Mechanism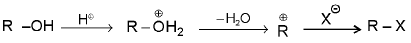
e.g.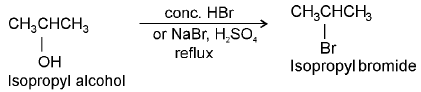
SN2 reaction : Alkylhalide are hydrolysed to alcohol very solwly by water, but rapidly by silver oxide suspended in boiling water.
RX + KOH → ROH + KX
Mechanism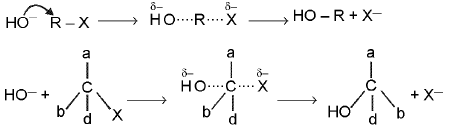
Williamson’s synthesis: It is the reaction in which sodium or potassium alkoxide is heated with an alkyl halide (SN2).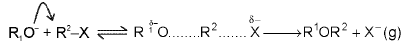
This method is particularly useful for preparing mixed ethers.
3. Grignard Reagents
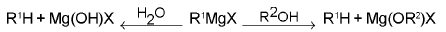
The majority of Grignard reactions fall in to two groups
(i) Addition of the Grignard reagent to a compound containing a multiple - bond group e.g.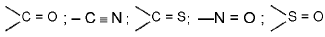
(ii) Double decompsition with compounds containing an active hydrogen atom or a reactive halogen atom.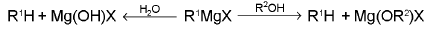
Important chemical synthesis by Grignard reagent
1. Hydrocarbons: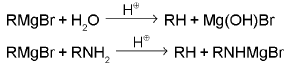
2. Alcohols:
(a) Primary alcohols 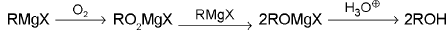
(b) Secondary alcohols 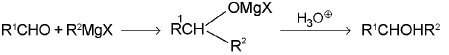
(c) Tertiary alcohols: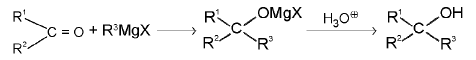
3. Ethers: R1OCH2CI + R2MgX → R1OCH2R2 + MgXCI
4. Aldehydes: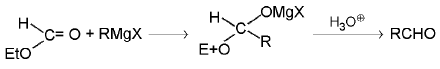
5. Ketones: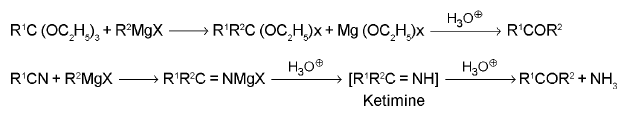
6. Acids: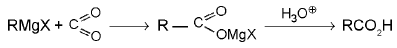
7. Esters: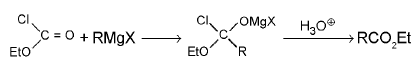
8. Alkyl Cyanides:
RMgX + (CN)2 → RCN + Mg(CN)x
9. Primary amines :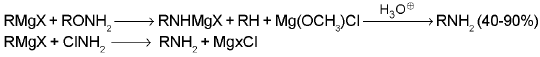
4. Alkene & Alkyne
Electrophilic addition reactions :
Mechanism
Step 1 : Attack of the electrophile on k bond forms a carbocation.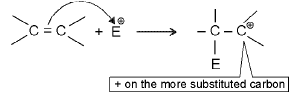
Step 2 : Attack by a nucleophile gives the product of addition.
e.g. (a) Addition of water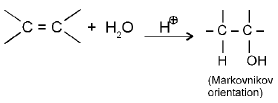
(b) Addition of hydrogen halides (where HX = HCI, HBr, HI)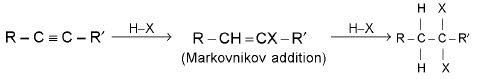
5. Aromatic compounds
Electrophilic aromatic substitution :
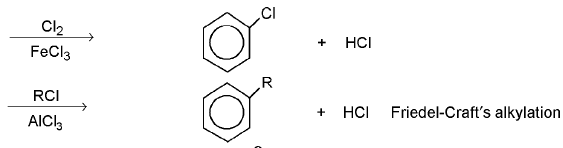
(a) Bromination of Benzene : Bromination follows the general mechanism for electrophilic aromatic substitution. Bromine itself is not sufficiently electrophilic to react with benzene, but a strong Lewis acid such as FeBr3 catalyzes the reaction.
Step 1 : Formation of a stronger electrophile.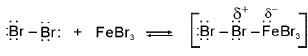
Step 2 : Electrophilic attack and formation of the sigma complex.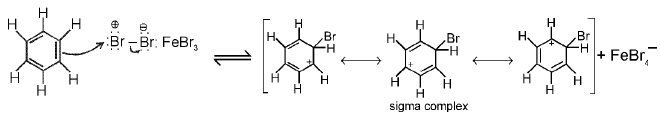
Step : 2 Loss of a proton gives the products.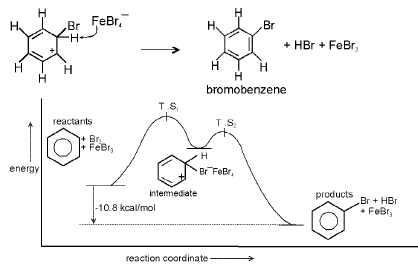
(b) Nitration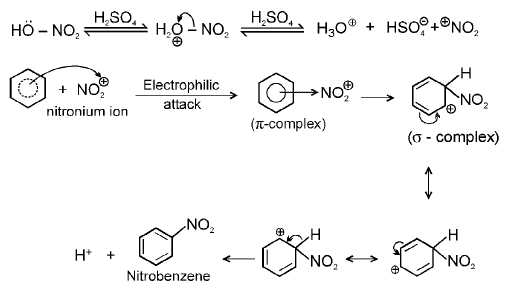
(c) Sulphonation: The electrophilic reagent, SO3, attacks the benzene ring to form the intermediate carbocation.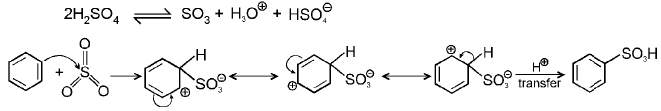
(d) Friedel Craft reaction : Alkylation mechanism
(i) 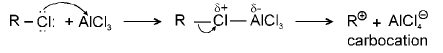
(ii) 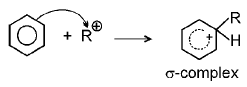
(iii) 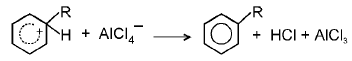
Acylation mechanism
Acylation of benzene may be brought about with acid chlorides or anhydrides in presence of Lewis acids.
Step 1 : Formation of an acylium ion.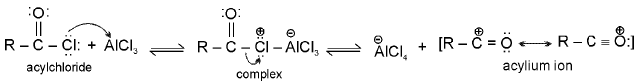
Step 2 : electrophilic attack.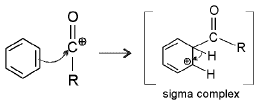
Step 3 : Loss of a proton. Complexation of the product.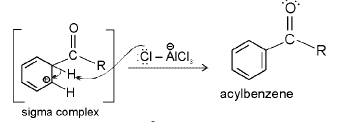
e.g. 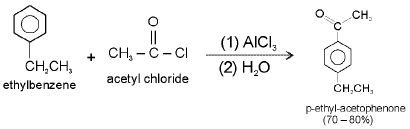
Note : Friedal - Crafts acylations are generally free from rearrangements and multiple substitution. They do not go on strongly deactivated rings.
e.g. 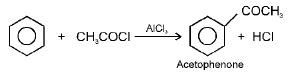
Chemical Reactions of Benzene :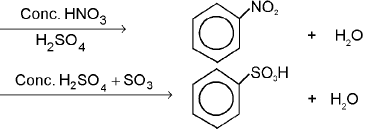
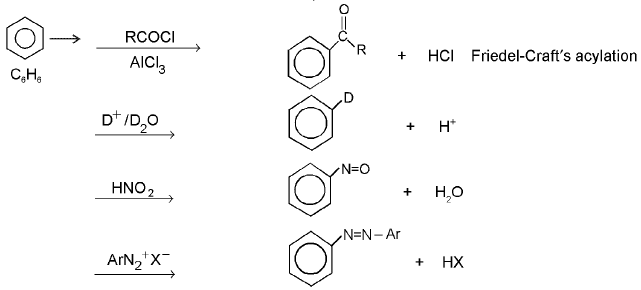
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution : The reaction is second-order in which nucleophilic sbustitution occurs on benzene ring. It is generally accepted that the reaction proceeds via an intermediate o-complex, the benzenonium carbanion (or the pentadienyl anion), e.g.,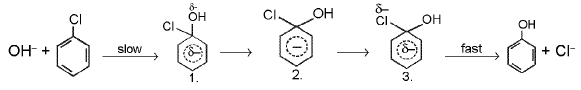
6. Chemical Reactions of Phenol
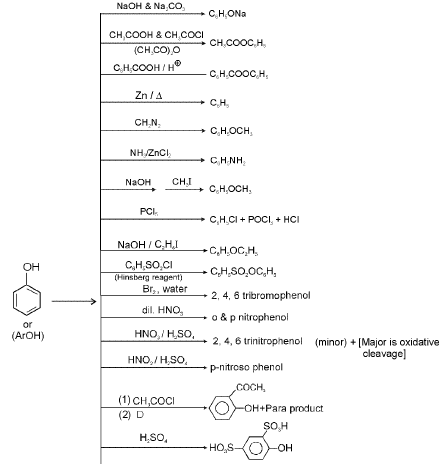
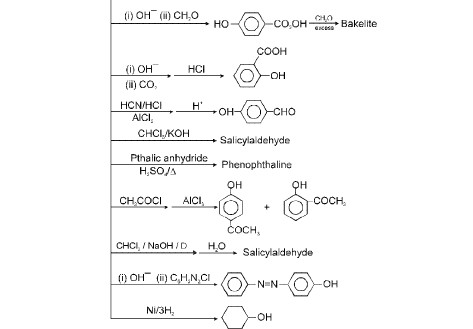
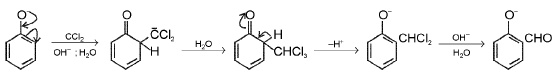
Reimer-Tiemann reaction : The reaction is conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde. The mechanism of the Reimer-Tiemann reaction is believed to involve the formation of dichloromethylene.
Kolbe Reaction : It is the industrial method of preparation of salicylic acid from phenol.
General reaction: 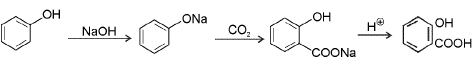
Mechanism 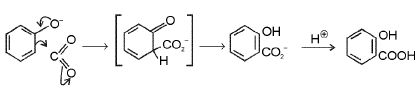
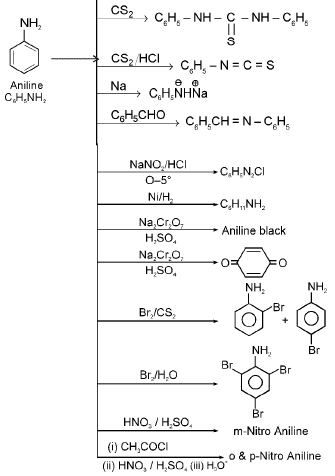
7. Chemical reactions of aniline
Sandmyer’s Reaction : When a diazonium salt solution is run into a solution of cuprous halide dissolved in the corresponding halogen acid, the diazo-group is replaced by a halogen atom.
m - Chloronitrobenzene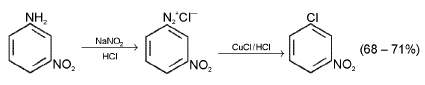
p-Bromotoluene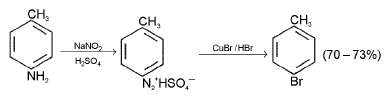
Chemical Reactions of Aniline :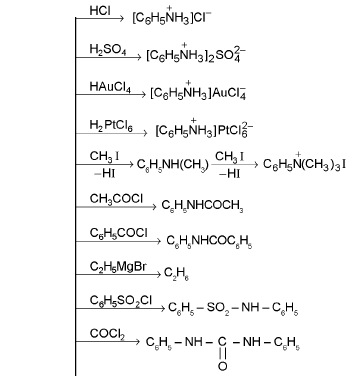
8. Aldehyde & ketone
Aldol condensation: Carbonyl compounds having acidic α - H shows this reaction in presence of dil. NaOH or dil. acid.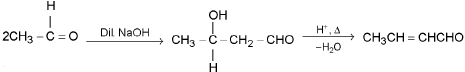
Crossed aldol condensation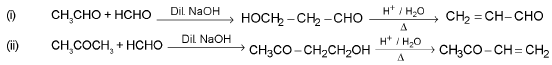
Cannizzaro reaction :
Carbonyl compounds not having α-H shows following disproportion reaction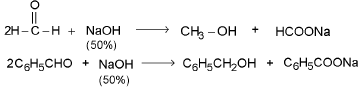
Crossed Cannizzaro reaction: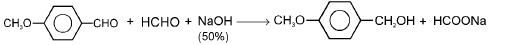
Formation of hydrzones and azines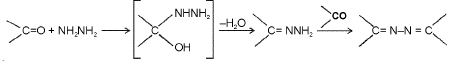
Amides formation: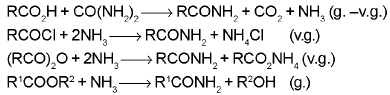
Carbyl amine reaction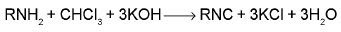
Perkin reaction :
When benzaldehyde (or any other aromatic aldehyde) is heated with the anhydride of an aliphatic acid (containing two α-hydrogen atoms) in the presence of its sodium salt, condensation takes place to form a β-arylacrylic acid ; e.g., with acetic an hydride and sodium acetate, cinnamic acid is formed.
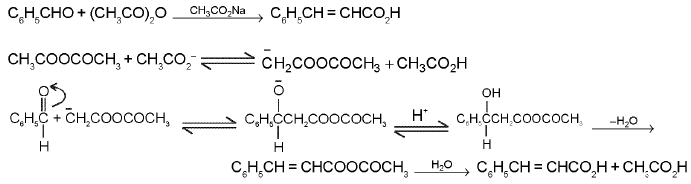
9. Ester formation
General reaction 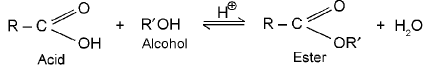
Hydrolysis of ester 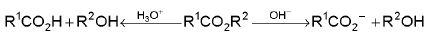
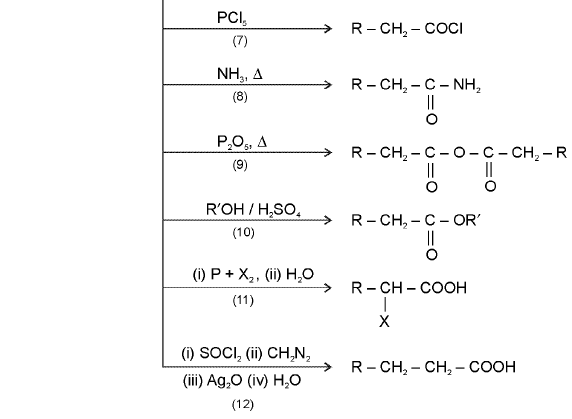
10. Carboxylic Acids
Chemical Reactions of acids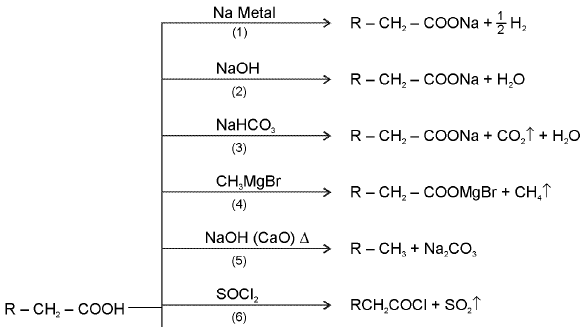
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|

















