Index: Chemical Kinetics | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the rates of chemical reactions and the factors that influence those rates. It focuses on understanding how and why reactions occur at different speeds and how reactants are transformed into products over time.
 Graph Depicting Activation Energy
Graph Depicting Activation Energy
The following Index outlines the essential Key Concepts and Terms that we will explore and grasp in this section.
1. Rate of a chemical reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction is the change in concentration of reactants or products per unit of time. It is often expressed as the rate of disappearance of a reactant or the rate of appearance of a product.
You can understand the Rate of Reaction through:
2. Factors influencing rate of a reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction can be influenced by various factors. Some of the key factors that affect the rate of a reaction are mentioned here:
- Video: Effect of a Catalyst on the Rate of a Reaction
- Doc: Rate of a Chemical Reaction and Factors affecting Rate
3. Rate expression, order and molecularity
The rate expression, order, and molecularity are key concepts in chemical kinetics that describe and quantify how chemical reactions occur. Explore the concepts here:
- Video: Rate of a Reaction- 1
- Video: Rate of a Reaction (part - 2)
- Video: The Rate Constant
- Video: Order of a Reaction
- Video: Molecularity of a Reaction
- Doc: Rate of a Reaction
- Doc: Order & Molecularity of a Reaction
- Test: Rate Law, Molecularity & Order of Reaction
- Test: Rate Of Chemical Reaction
4. Integrated rate equation
The integrated rate equation is an expression that relates the concentrations of reactants or products in a chemical reaction to time. Here are the most common integrated rate equations for different reaction orders:
- Video: Integrated Rate Equation: Zeroth Order Reactions
- Video: Integrated Rate Equation for First order Reactions
- Doc: Integrated Rate Equations: Zero, First, Second-Order Reactions- Graphs & Half-lives
- Test: Integrated Rate Equation
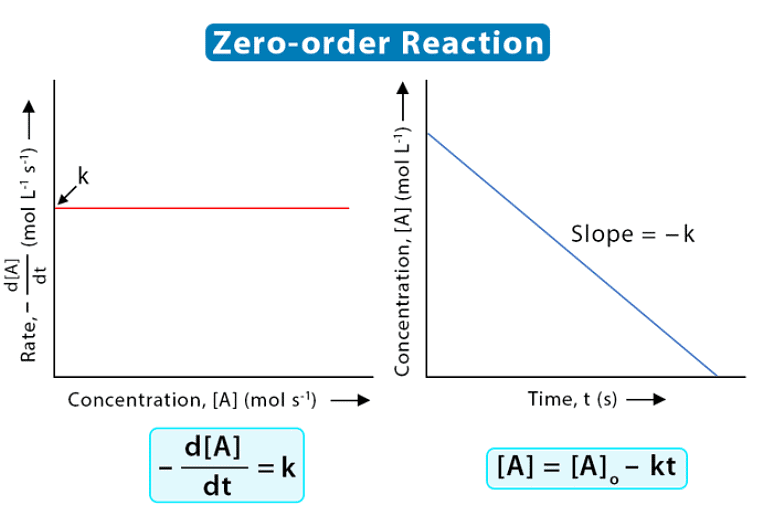
5. Zero order reaction
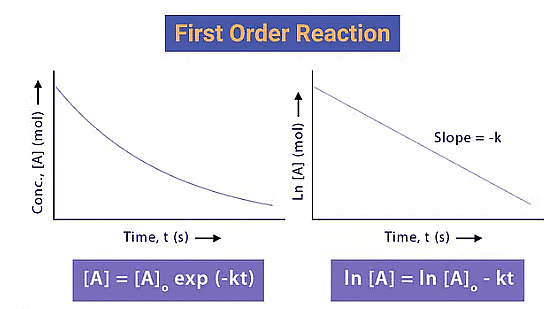
6. First order reaction
- Video: Pseudo First Order Reaction
- Doc: Arrhenius Equation & Pseudo First Order Reaction
- Test: Zeroth Order & First Order Reactions
7. Energy of activation
- Test: Energy of Activation
8. Temperature dependence on reaction
9. Half life of a reaction
- Video: Half - Life of a Reaction
10. Collision theory of chemical reaction
- Video: Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions- 1
- Video: Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions- 2
- Video: The Arrhenius Equation
- Doc: Collision Theory and Variations in Arrhenius Equation
- Doc: Arrhenius Equation & Pseudo First Order Reaction
- Test: Collision Theory & Reaction Mechanism
11. NEET Questions
- Test: 28 Year NEET Questions: Chemical Kinetics- 1
- Test: 28 Year NEET Questions: Chemical Kinetics- 2
- Doc: NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-21): Chemical Kinetics
12. NCERT Materials
- Doc: NCERT Textbook - Chemical Kinetics
- Doc: NCERT Solutions: Chemical Kinetics
- Doc: NCERT Exemplar - Chemical Kinetics
13. Chapter tests and other docs
- Test: Chemical Kinetics- 1
- Test: Chemical Kinetics- 2
- Test: Chemical Kinetics- Assertion & Reason Type Questions
- Test: Chemical Kinetics- Case Based Type Questions
- Test: Previous Year Questions: Chemical Kinetics
- Test: Level - 1 Chemical Kinetics - 1
- Test: Level - 1 Chemical Kinetics - 2
- Test: Chemical Kinetics 1 - From Past 28 Years Questions
- Test: Chemical Kinetics 2 - From Past 28 Years Questions
- Doc: Solved Subjective Problems: Chemical Kinetics
- Doc: Solved Objective Problems: Chemical Kinetics
- Test: R.C. Mukherjee Test: Chemical Kinetics
- Test: P. Bahadur Test: Chemical Kinetics
- Doc: MCQs Question Bank Solutions (Competition Preparation): Chemical Kinetics
- Doc: Short & Long Answer Question: Chemical Kinetics
- Doc: Previous year Questions (2016-20) - Chemical Kinetics & Nuclear Chemistry
- Doc: Important Formulas & Rapid Revision: Chemical Kinetics
- Doc: Mindmap: Chemical Kinetics
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Index: Chemical Kinetics - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is chemical kinetics? |  |
| 2. What are the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction? |  |
| 3. How can the rate of a chemical reaction be determined experimentally? |  |
| 4. What is the order of a chemical reaction? |  |
| 5. How do catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction? |  |
















