India-Sri Lanka Relations - 3 | UPSC Mains: International Relations PDF Download
India’s efforts to counter China:
In 2014 India abstained from voting on a UNHRC resolution calling for a probe into alleged war crimes by Sri Lanka. And it helped to revamp the century-old relationship with Sri Lanka. (While Pakistan and China voted against the resolution).
- In a sign of a closer strategic partnership between Sri Lanka and India, they signed civil nuclear cooperation agreement which is Sri Lanka’s first nuclear partnership with any country.
- In the wake of China’s economic dominance in the island, India is also entering into Sri Lanka’s mega project business in a big way by focusing on infrastructure development in the Northern and Eastern provinces.
- India is also planning to build Trincomalee Port. The port is envisioned as an Indian counterweight to Chinese developments at Hambantota Port.
Fisherman Problem:
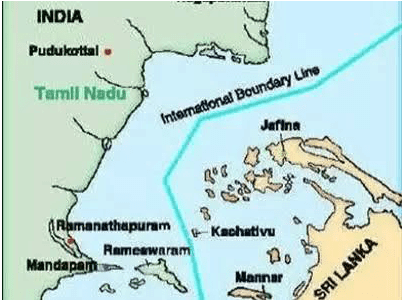
- Indian boats have been fishing in the troubled waters of Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar for centuries.
- In 1974 and 1976 treaties were signed between the two countries to demarcate International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL).
- However, the treaties failed to factor in the hardship of thousands of traditional fishermen who were forced to restrict themselves to a meagre area in their fishing
forays.
However, the treaties failed to factor in the hardship of thousands of traditional fishermen who were forced to restrict themselves to a meagre area in their fishing
forays.
- Fishermen often risk their lives and cross the IMBL rather than return empty-handed.
- However, the high alert Sri Lankan Navy have either arrested or destroyed fishing nets and vessels of those who have crossed the line.
To deal with the issue of detention of fishermen in a humane manner, India and Sri Lanka have set up a Joint Working Group (JWG) on Fisheries as the mechanism to help find a permanent solution. The first meeting took place in December 2016 in New Delhi and second meeting in Colombo on April 07, 2017. The next round of Ministerial-level talks and JWG meetings were held during October 2017 at New Delhi.
Katchatheevu Island:
It is an uninhabited island that India ceded to Sri Lanka in 1974 based on a conditional agreement called “Kachchativu island pact”.
Later on, Sri Lanka declared Katchatheevu, a sacred land given the presence of a Catholic shrine.
- The central government recognizes Sri Lanka’s sovereignty over the island as per the 1974 accord. But Tamil Nadu claimed that Katchatheevu falls under the Indian territory and Tamil fishermen have traditionally believed that it belongs to them and therefore want to preserve the right to fish there.
Significance of India –Sri Lanka relations:
- Sri Lanka is strategically located in the Indian Ocean, just a few kilometers from the Indian coast and near one of the busiest sea lanes in the world – one that carries much of the oil.
- Indo-Chinese competition in the Indian Ocean: India believes that China’s interest in Sri Lanka and its growing footprint there is part of an encirclement strategy to contain India.
- India’s ‘Neighbourhood First’ Policy : Sri Lanka is at the core of our 'Neighbourhood First' policy and Sagar doctrine.
- The Sri Lankan Tamils — India is concerned about the plight of Sri Lankan Tamils devastated by war and is working for their rehabilitation.
- Maritime interests: it is important for the coast guards of the two countries to establish the safety and security of the Indian Ocean region.
- “Strategic significance” of the nuclear agreement : Sri Lanka’s decision to sign a nuclear agreement with India rather than Pakistan, with which it had explored a similar pact two years ago, “shows the importance Sri Lanka attaches to its relations with New Delhi.”
- International cooperation:
(i) Sri Lanka is an active partner in South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
(ii) Sri Lanka, with its geo-strategic location as well as its diverse experience in maritime safety and security issues, contributes much to Indian Ocean Rim Association – IORA.
Both countries also cooperate in the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting.
Way forward:
- The Sri Lankan President has described India as “our closest neighbour and longstanding friend”. He assured that cooperation with India is multifaceted with priority given to security-related matters while cooperation with other countries are largely economic and commercial.
- Given the mutual trust and historical ties, both countries should work together to strengthen their multi-dimensional partnership. In line with India’s ‘neighbourhood first’ policy and SAGAR doctrine, primacy should be given to relationship with Sri Lanka.
- Meanwhile Srilanka should carry forward the process of reconciliation, to fulfill the aspirations of the Tamils for equality, justice, peace and respect. Counter-terrorism will be a big area of cooperation between Colombo and New Delhi which requires detailed intelligence sharing.
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) must be signed to improve the economic cooperation between both countries.
- The biggest advantage that India has over China when it comes to bilateral ties with Sri Lanka is its deep civilizational and cultural connect.
- Sri Lanka’s first nuclear partnership with any country was signed with India.
- Chinese funding in infrastructure projects is blamed of lacking transparency, pushing participating smaller nations in a debt-trap (e.g. Hambantota port deal), having devastating social and environmental impact and even serving to undermine sovereignty.
- Counter-terrosism: the two countries must improve cooperation in counter-terror training as India has vast experience in this arena.
- Maritime cooperation: It "may include measures such as joint naval patrolling, controlling of smuggling and piratical activities, and the strengthening of communication networks."
|
88 videos|120 docs
|
FAQs on India-Sri Lanka Relations - 3 - UPSC Mains: International Relations
| 1. What are the key aspects of India-Sri Lanka relations? |  |
| 2. How are India's efforts countering China in the context of India-Sri Lanka relations? |  |
| 3. What challenges does India face in countering China in Sri Lanka? |  |
| 4. How does India's relationship with Sri Lanka impact its overall strategy in countering China? |  |
| 5. How does India's development assistance to Sri Lanka contribute to countering China? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















