Indian Society and Social Issues: May 2025 UPSC Current Affairs | Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
Impact of Social Media on Young People

Why in News?
The rise of social media has highlighted significant concerns regarding its effects on youth identity and mental health. As young individuals increasingly seek validation through online interactions, issues such as anxiety and distorted self-image have surged, underlining the need for a critical examination of social media's role in shaping their lives.
Key Takeaways
- Social media influences the self-perception and mental well-being of youth.
- The impact of social media extends to societal, economic, and regulatory dimensions.
Additional Details
- Impact on Indian Society: Social media has disrupted traditional media by empowering citizens to share real-time news and opinions. During the Covid-19 crisis, platforms like Twitter were used by healthcare professionals to address urgent issues, such as oxygen shortages.
- Governments utilize social media for direct engagement with the public, as evidenced during the 2024 Lok Sabha elections in India.
- Social media has amplified marginalized voices, exemplified by movements like the MeTooIndia campaign, where women reported harassment across various sectors.
- Impact on Indian Economy: Social media is a driving force in India's digital economy, benefiting small businesses, startups, gig workers, and influencers. For instance, home chefs leverage platforms like WhatsApp to market their products.
- The creator economy, which includes YouTube and Instagram influencers, expanded significantly, growing from 962,000 creators in 2020 to 4.06 million in 2024, now supporting 8% of the workforce.
- India's creative economy is valued at USD 30 billion in 2024 and contributes 2.5% to the GDP.
- Recent initiatives, such as the government’s USD 1 billion fund, aim to support creators through capital and skill development.
- In addition to these impacts, social media also plays a vital role in promoting digital payments and the formalization of the economy, as seen with WhatsApp Pay streamlining transactions.
How is Social Media Regulated in India?
- Information Technology Act, 2000: This act serves as the primary legislation for electronic governance, including social media. It grants intermediaries liability exemption for third-party content under certain conditions.
- Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021: These rules mandate online safety measures, the removal of inappropriate content, and user education regarding privacy and national security.
- Judicial Stand: Notable cases, such as Shreya Singhal v. Union of India (2015), have upheld freedom of expression on social media, while K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India (2017) emphasized the need for data protection laws.
What Concerns are Associated with Social Media?
- Mental Health Deterioration: Risks include anxiety, depression, and loneliness, exacerbated by the pressure for validation and the fear of missing out (FOMO).
- Performance culture on social media can suppress genuine emotions, making it difficult for young people to express vulnerability or seek help.
- Ethical Concerns: Social media can distort identity among youth, encouraging them to curate their self-presentation for public approval, leading to confusion and emotional distress.
- Parental Disconnect: Many adults lack understanding of the digital landscape their children navigate, leading to increased secrecy among teens.
- Child Exploitation: Young influencers can be exploited for content generation, facing performance pressure before reaching emotional maturity.
- Cyberbullying: Issues such as anonymous harassment and deepfake abuse are prevalent, posing significant risks to young users.
What Measures can Address the Challenges of Social Media for Young People?
- Social Media Policy for Youth Protection: Platforms should adjust algorithms to promote educational and positive content for users under 18.
- Prohibit behavioral profiling of minors for targeted ads, ensuring users can customize their content preferences.
- Digital Literacy: Implement a National Digital Literacy Program to include cyber safety courses in school curricula.
- Strengthen Governance & Accountability: Enforce the DPDP Act, 2023, to protect children's data and establish rapid response mechanisms for cyberbullying complaints.
- Promoting Mental Health Awareness: Social media platforms should introduce tools like screen time reminders and well-being resources.
In conclusion, the growing influence of social media necessitates urgent regulation, digital literacy, and ethical platform design. While it presents opportunities for innovation, unchecked use can cause harm. A collaborative approach that involves parental engagement is essential to ensure meaningful and safe digital experiences for young people.
Mains Question
Q: Social media is both a tool for empowerment and a threat to mental health. Examine.
Participation of Women in Cooperatives

Why in News?
Despite India being one of the largest cooperative movements in the world, with approximately 8.5 lakh cooperatives, women-only cooperatives still account for only 2.52% of the total, according to a NITI Aayog report (2023). The UN has declared 2025 as the International Year of Cooperatives with the theme “Cooperatives Build a Better World,” launching it globally in 2024 in India.
Key Takeaways
- India has a significant cooperative movement, yet women's representation in cooperatives is minimal.
- The UN's International Year of Cooperatives in 2025 aims to promote cooperative principles globally.
Additional Details
- Cooperative Societies: A cooperative society is a voluntary, member-owned organization designed to meet common economic, social, and cultural needs through self-help, mutual assistance, and community welfare, distinct from profit-driven enterprises.
- Evolution of the Cooperative Movement:
- Pre-Independence Era: Informal cooperatives like chit funds and nidhis existed, formalized through the Cooperative Credit Societies Act, 1904, and expanded by the Cooperative Societies Act, 1912.
- Post-Independence Era: Strengthened through Five-Year Plans and the establishment of National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) in 1963 and NABARD in 1982.
- Legal and Constitutional Backing: Key legislations include the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act (1984 & 2023) and the National Policy on Cooperatives (2002).
- Recent Developments: The Ministry of Cooperation was established in 2021, emphasizing the government’s commitment to enhancing cooperative societies.
Cooperatives play a vital role in empowering women economically and socially, yet significant challenges exist. The International Year of Cooperatives in 2025 provides a crucial opportunity to address these challenges and enhance women's roles in cooperative movements.
What is the Significance of Cooperatives in Women Empowerment?
- Pathway to Socio-Economic Empowerment: Cooperatives provide rural women with low-threshold entry into income-generating activities, accessible livelihood options, fair pricing, skill development, and inclusive governance.
- Successful Models: Examples include the Self-Employed Women's Association (SEWA) and Lijjat Papad, showcasing how cooperatives foster economic self-reliance and social upliftment for women.
- Access to Services & Financial Inclusion: Women’s cooperatives enhance access to credit, banking, insurance, healthcare, and education, bridging service delivery gaps.
- Social Capital and Community Resilience: Cooperatives foster trust, reciprocity, and shared responsibility, helping women build resilience against socio-economic challenges.
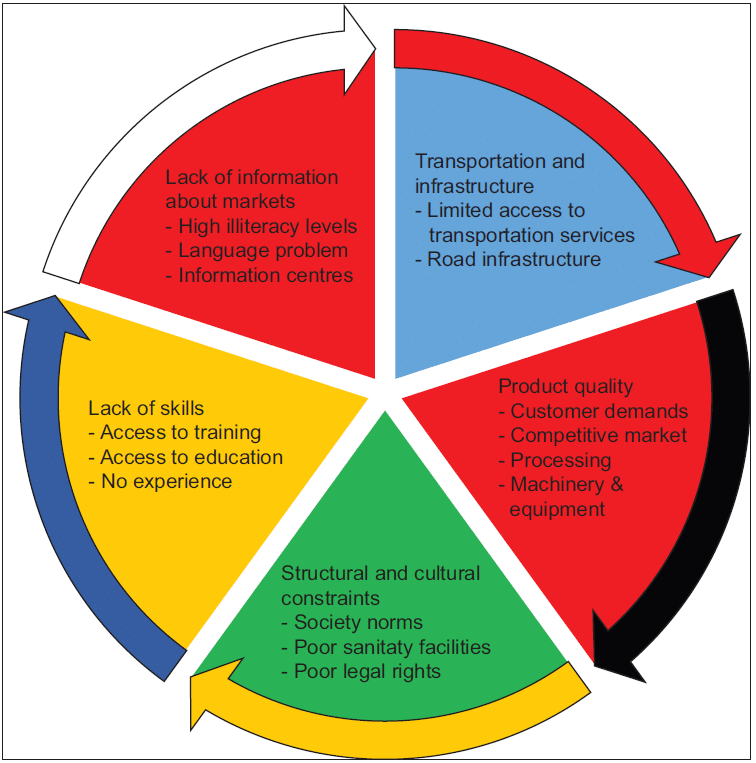
What are the Challenges Faced by Women’s Cooperatives in India?
- Structural Constraints: Approximately 50% of women’s cooperatives are dormant due to inadequate institutional support and poor financial linkages.
- Time Poverty and Unpaid Labour: Women disproportionately bear the burden of unpaid domestic work, limiting their participation in cooperative activities.
- Lack of Skills & Underrepresentation: Low literacy and limited training hinder women’s involvement in leadership and decision-making roles.
- Cultural and Social Norms: Deep-rooted societal norms often restrict women’s autonomy, particularly in rural areas, affecting their ability to engage in cooperatives.
What Measures Can be Taken to Empower Women Cooperatives in India?
- Institutional and Financial Support: Revive dormant cooperatives through professional guidance and ensure dedicated funding and market linkages.
- Capacity Building and Training: Provide training in governance, finance, digital literacy, and marketing to boost women’s participation.
- Recognizing Unpaid Work: Promote shared domestic roles and community childcare to reduce the unpaid work burden on women.
- Policy Integration and Technological Innovation: Ensure policy convergence across various ministries to streamline support for women’s cooperatives.
Cooperatives have the potential to transform the socio-economic landscape for women in India. Empowered women-only cooperatives, with proper resources and training, can drive significant economic and social change. The International Year of Cooperatives in 2025 offers a timely opportunity to reshape policies and empower women at the forefront of this movement.
Mains Question
Q: Examine the role of women cooperatives in empowering rural women in India. Discuss the challenges they face and suggest measures to improve their effectiveness.
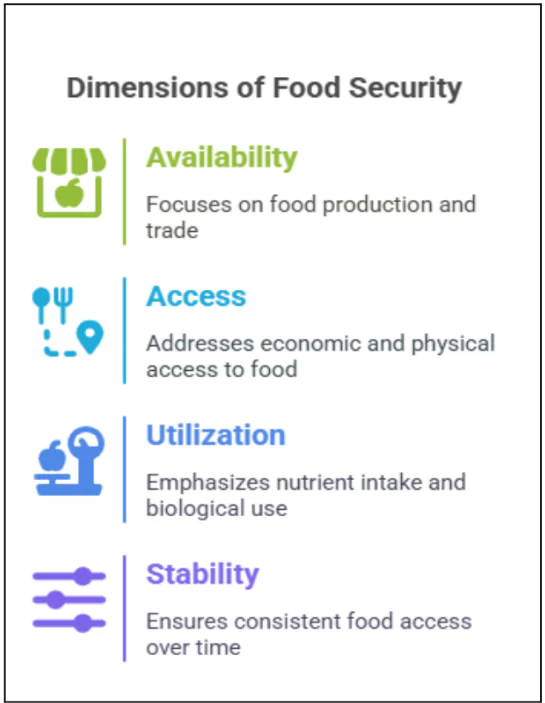
Key Findings of the Global Report on Food Crises 2025

Why in News?
In 2024, a staggering 295 million people across 53 countries experienced acute hunger, marking a troubling increase in global food insecurity for the sixth consecutive year. This report highlights the alarming state of food crises worldwide, necessitating urgent attention and action.
Key Takeaways
- The number of acutely food-insecure individuals rose by 13.7 million from the previous year.
- Catastrophic hunger (IPC Phase 5) has more than doubled, affecting nearly 1.9 million people, the highest level since 2016.
- Approximately 38 million children under five are suffering from acute malnutrition, particularly in regions like Gaza, Mali, Sudan, and Yemen.
Additional Details
- Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC): An annual publication that analyzes acute food insecurity globally, aimed at informing humanitarian responses.
- Published By: The report is jointly published by the Global Network Against Food Crises (GNAFC), which includes significant organizations such as the European Union, FAO, and WFP.
- Purpose: The report’s main goal is to identify the severity, causes, and geographic distribution of food crises to inform humanitarian and development responses.
- Significance: It plays a crucial role in coordinating efforts to prevent famine and address the root causes of food insecurity, guiding policy and resource allocation.
Conflict remains a predominant driver of hunger, affecting around 140 million people across 20 countries, while factors like forced displacement and climate extremes exacerbate the crisis.
Understanding Hunger and Food Crisis Definitions
- Hunger: Defined by the FAO as a regular intake of insufficient calories, failing to meet the body’s minimum dietary energy needs.
- Types of Hunger:
- Acute Hunger: A severe form of undernourishment occurring over a short period, often triggered by emergencies such as conflicts or natural disasters.
- Chronic Hunger: A long-term condition where individuals consistently consume less food than needed, typically due to persistent poverty.
- Hidden Hunger: A deficiency of vital micronutrients like vitamin A or iron, leading to health issues without visible symptoms.
Global Initiatives to Address Hunger
- FAO: Through the Hand-in-Hand Initiative, it targets 20 low-income countries for urgent food system reforms.
- UNICEF: Scaled its No Time to Waste strategy to support 7 million malnourished children in 2024.
- World Food Programme: The largest humanitarian organization, assisting 152 million people in 2023, notably restoring school feeding programs in post-COVID zones.
- World Bank: Committed over $1 billion in 2024 to fragile states to rebuild food systems and provide cash transfers.
Challenges in Addressing Global Hunger
- Conflict and Political Instability: Ongoing wars in regions like Sudan and Gaza obstruct food access.
- Climate Extremes: Droughts, floods, and rising temperatures have led to widespread crop failures.
- Economic Shocks: Inflation and currency collapse have driven hunger levels up, affecting millions.
- Forced Displacement: Over 95 million displaced individuals live in hunger-affected countries.
- Funding Shortfall: A projected 45% drop in humanitarian aid threatens nutrition services for millions.
Way Forward
- Evidence-Based Interventions: Responses must be data-driven, focusing on scalable solutions that deliver measurable outcomes.
- Investing in Local Food Systems: Strengthening indigenous agriculture will reduce dependency on imports.
- Integrated Nutrition Services: Coordination between health, sanitation, and food services is essential to combat malnutrition.
- Protecting the Most Vulnerable: Strategies must focus on children and conflict-affected communities to ensure global food security.
- Global Cooperation and Accountability: Urgent international action is needed to meet Sustainable Development Goal 2 and create a hunger-free world.
The situation of global food insecurity demands immediate and coordinated responses to ensure the well-being of vulnerable populations and work towards sustainable solutions for food security.
Hooch Tragedies in India
Why in News?
A recent hooch tragedy in Amritsar district, Punjab, has resulted in 21 deaths and numerous hospitalizations due to the consumption of spurious liquor believed to contain methanol, an extremely toxic substance.
Key Takeaways
- The tragedy highlights ongoing issues with illicit liquor in India.
- Methanol, a hazardous chemical, is often misused in the production of illegal alcohol.
- There is an urgent need for effective regulation and public awareness.
Additional Details
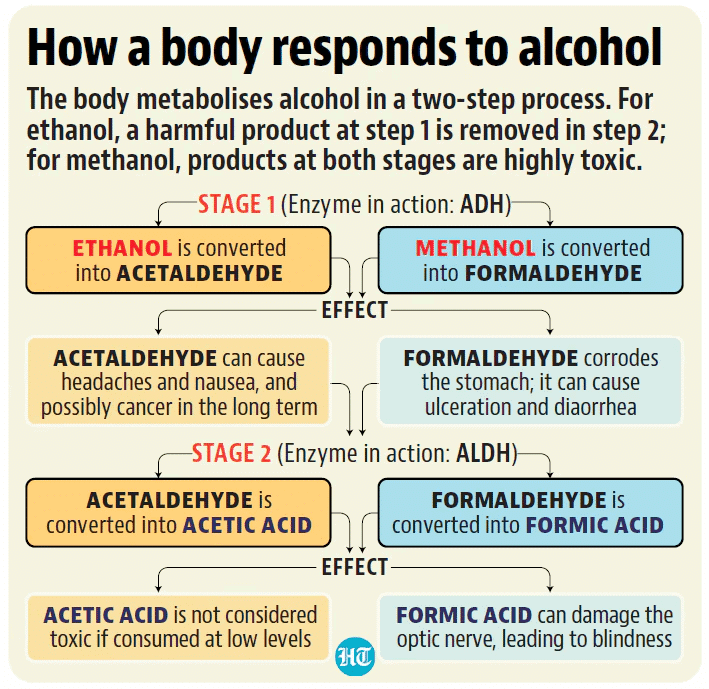
- Methanol: Known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, methanol (CH3OH) is a clear, volatile liquid that is completely soluble in water. It is used in various applications, including as a solvent and fuel additive.
- Health Impact: Ingesting methanol can lead to severe health issues, including metabolic acidosis, organ damage, and blindness, potentially resulting in coma or death.
- Regulatory Framework: The Food Safety and Standards (Alcoholic Beverages) Regulations 2018 aim to control methanol levels in liquors, while the Excise Act, 1944 regulates alcohol production, yet enforcement remains weak.
Causes of Hooch Tragedies in India
- Economic Vulnerability: Individuals from poorer backgrounds often resort to cheap, unsafe alcohol due to financial constraints.
- Misuse of Methanol: Methanol is frequently added to illicit liquor to enhance potency, despite its dangers.
- Weak Regulation: Poor enforcement of existing laws allows illegal liquor production and distribution to thrive.
- Political and Bureaucratic Influence: Corruption and political connections protect illegal operations from law enforcement.
- Lack of Awareness: Many rural residents are unaware of the risks associated with unregulated alcohol consumption.
- Community Reporting Issues: Fear of retaliation from local mafias prevents reporting of illegal activities.
- Supply Chain Monitoring Flaws: Insufficient tracking of methanol distribution facilitates illegal activities.
Case Studies of Major Hooch Tragedies
- Mumbai (2015): Approximately 100 fatalities due to methanol poisoning.
- Punjab (2020): Over 100 deaths linked to adulterated liquor.
- Bihar (2022): 40 lives lost in Saran from spurious alcohol despite prohibition.
- Tamil Nadu (2024): An illicit liquor tragedy resulted in over 50 deaths in Kallakurichi.
Prevention Measures
- Enhanced Enforcement: Successful initiatives like Operation Moonshine demonstrate the efficacy of coordinated law enforcement efforts.
- Centralized Methanol Tracking: Establish a portal to monitor methanol production and distribution.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educate communities on the dangers of spurious liquor through focused awareness programs.
- Access to Quality Alcohol: Ensure the availability of safe and regulated alcoholic beverages to reduce demand for illicit options.
- Socio-Economic Support: Provide skill development programs to help communities transition away from dependence on illicit liquor.
- Accountability Measures: Implement performance audits for law enforcement to ensure accountability in curbing illegal alcohol trade.
- International Best Practices: Follow WHO guidelines on alcohol harm reduction to strengthen prevention efforts.
The recurring hooch tragedies in India underscore systemic socio-economic issues and governance challenges. The recent incident in Amritsar serves as a critical reminder of the need for a comprehensive approach that integrates strict regulations, community engagement, and public education to combat the illicit liquor trade effectively.
Enrolment Drop in Government Schools and PM-POSHAN
Why in News?
The Ministry of Education (MoE) has recently held discussions with various States and Union Territories (UTs) to evaluate the performance, planning, and budget of the Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman (PM-POSHAN) scheme. This discussion unveiled a notable decline in government school enrolment across 23 States.
Key Takeaways
- The MoE reported a significant drop in enrolment for 2024-25, with some states experiencing a decrease of over 100,000 students.
- Major contributors to this decline include Uttar Pradesh (21.83 lakh), Bihar (6.14 lakh), Rajasthan (5.63 lakh), and West Bengal (4.01 lakh).
Additional Details
- Factors Behind Enrolment Decline:
- Change in Data Collection Methodology: The shift from school-wise to student-wise reporting may have led to the removal of outdated records, including the identification of 'ghost' students who were not actually attending school.
- Shift to Private School: Post-Covid trends indicate a movement of students from government schools to private institutions, reversing earlier patterns observed during the pandemic.
- What is the PM-POSHAN Scheme?
- PM-POSHAN is a centrally sponsored initiative that provides one hot cooked meal to students up to Class 8 in government and government-aided schools.
- It was launched for an initial five-year period from 2021-22 to 2025-26, replacing the previous midday meal scheme (MDM), which has been the largest school meal program globally since its inception in 1995.
- Cost Sharing: The costs of the scheme are shared between the Centre and the States on a 60:40 basis, with the Centre responsible for supplying food grains.
- Entitlements: Students in primary (Class 1-5) and upper primary (Class 6-8) receive 100g and 150g of food grains daily, ensuring a nutritional intake of 700 calories, along with additional nutrition such as milk or eggs in areas with high anemia rates.
- Key Provisions:
- Nutritional Gardens: The scheme promotes the establishment of school nutritional gardens to enhance the micro-nutrient intake of students.
- Tithi Bhojan: This initiative encourages communities to provide special food to children during festivals and other significant occasions.
- Nutrition Expert: Schools are required to appoint a nutrition expert to monitor students' Body Mass Index (BMI), weight, and hemoglobin levels.
- Social Audit: Mandatory social audits in all schools are conducted to evaluate the implementation of the scheme, with college students participating in local monitoring.
- Vocal for Atmanirbhar Bharat: The initiative promotes the involvement of Farmers Producer Organizations (FPOs) and Women Self Help Groups (SHGs), along with the promotion of locally grown traditional foods to enhance local economies.
In summary, the decline in government school enrolment poses significant challenges that need to be addressed, particularly in light of the transition to the PM-POSHAN scheme, which aims to ensure that students receive adequate nutrition and support for their educational needs.
Tuberculosis in India – Cases, Challenges & National Eradication Plan
 Why in the News?
Why in the News?
A recent paper titled 'Progress and challenges in achieving tuberculosis elimination in India by 2025: A systematic review and meta-analysis' highlights the significant challenges India faces in combating tuberculosis (TB).
Key Takeaways
- Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection primarily affecting the lungs but can impact other body parts.
- India has the largest share of the global TB burden, with over 24 lakh cases recorded in 2022.
- The National TB Elimination Programme aims to eradicate TB in India by 2025, five years ahead of global goals.
Additional Details
- About Tuberculosis (TB): TB is a bacterial infection spread via inhalation of droplets from an infected person. It can affect various body parts, including the lungs, abdomen, glands, bones, and nervous system.
- Symptoms of TB: Common symptoms include a persistent cough lasting more than 3 weeks, weight loss, night sweats, high fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, and swelling in the neck.
- Types of TB:
- Pulmonary TB: The most contagious form, primarily affecting the lungs.
- Latent TB: A dormant form where the bacteria remain but do not cause symptoms and are not infectious.
- Active TB: Occurs when the immune system cannot contain the infection, leading to symptoms.
- Treatment: TB can be cured with a course of antibiotics lasting 6-18 months, especially since some TB strains are antibiotic-resistant.
Despite the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program's efforts, which include free diagnosis and treatment, challenges persist. These include poor healthcare infrastructure, unregulated private healthcare, and social determinants such as poverty and malnutrition. The mortality rate from TB was approximately 450,000 in 2021, showcasing the ongoing public health crisis.
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is revising TB treatment protocols to achieve a TB-free initiative with zero deaths and poverty associated with the disease.
|
112 videos|390 docs
|
FAQs on Indian Society and Social Issues: May 2025 UPSC Current Affairs - Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes)
| 1. What are the positive effects of social media on young people? |  |
| 2. What are the negative impacts of social media on young individuals? |  |
| 3. How does social media influence the participation of women in cooperatives? |  |
| 4. What steps can be taken to mitigate the negative effects of social media on youth? |  |
| 5. How can women leverage social media for economic empowerment through cooperatives? |  |





















