UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly > Indian Society and Social Issues: September 2023 UPSC Current Affairs
Indian Society and Social Issues: September 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
Maratha Quota
Why in News?
Recently, in Maharashtra, the demand for reservations in educational institutions and government jobs by the Maratha community has once again taken center stage.
What is the History and Status of the Maratha Reservation Demand?
- History:
- The Marathas are a group of castes comprising peasants and landowners among others constituting nearly 33% of the state’s population.
- While most Marathas are Marathi-speaking, not all Marathi-speaking people belong to the Maratha community.
- Historically, they have been identified as a ‘warrior’ caste with large land holdings.
- However, over the years, due to factors such as land fragmentation, agrarian distress, unemployment and lack of educational opportunities, many Marathas have faced social and economic backwardness. The community still plays an important role in the rural economy.
- Therefore, they have been demanding reservation in government jobs and educational institutions under the category of Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (SEBC).
- Status of the Maratha Reservation Demand:
- 2017:
- A 11-member commission headed by Retired Justice N G Gaikwad recommended Marathas should be given reservation under Socially and Educationally Backward Class (SEBC).
- 2018:
- Maharashtra Assembly passed a Bill proposing 16% reservation for Maratha community.
- 2019:
- The Bombay High Court while upholding the reservation pointed out that instead of 16% it should be reduced to 12% in education and 13% in jobs.
- 2020:
- The Supreme Court of India stayed its implementation and referred the case to the Chief Justice of India for a larger bench.
- 2021:
- Supreme Court struck down the Maratha reservation in 2021 citing the 50% cap on total reservations it had set in 1992.
- The Maratha reservation of 12% and 13% (in education and jobs) had increased the overall reservation ceiling to 64% and 65%, respectively.
- In the Indira Sawhney judgment 1992, SC had categorically said 50% shall be the rule, only in certain exceptional and extraordinary situations for bringing far-flung and remote areas' population into mainstream said 50% rule can be relaxed.
- The Supreme Court said that there were no “exceptional circumstances” or an “extraordinary situation” in Maharashtra for the state government to breach the limit.
- In addition, the court ruled that the state had no authority to accord socially and economically backward status to a community: only the president can tweak the central list of socially and backward classes, said the court. States can only make “suggestions”.
- The Bench unanimously upheld the constitutional validity of the 102nd Constitution Amendment but differed on the question of whether it affected the power of states to identify SEBCs.
- The Supreme Court highlighted that a separate reservation for the Maratha community violates Articles 14 (right to equality) and 21 (due process of law).
- 2022:
- In November 2022, after the SC upheld the 10% quota for the Economically Weaker Sections, the state government said that until the issue of Maratha reservation is resolved, economically weaker members of the community can benefit from the EWS quota.
Global Fund Secures Deal to Slash HIV Treatment Price
Introduction
The Global Fund, partners, and generic drug makers achieved a 25% cost reduction for first-line HIV treatment, now priced at under $45 per person annually. This has the potential to expand HIV services in resource-limited areas.
First-line HIV Treatment – TLD
- Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate, Lamivudine, and Dolutegravir (TLD) is a single-pill antiretroviral treatment.
- WHO endorsed TLD in 2018 due to its effectiveness, fewer side effects, and simplicity.
Historical Progress and Collaboration
- 2017: TLD was introduced at $75 annually in low- and middle-income countries with global support.
- Partnerships led to 19 million in resource-limited settings receiving TLD, promoting efficiency and sustainable pricing.
Future Initiatives and Impact
- Global Fund’s NextGen approach focuses on affordable HIV treatment through collaborations, particularly in India and Africa.
- Pooled Procurement Mechanism and Reach
- Mechanism negotiated $1.5 billion in 2021 orders, serving 90 countries, and providing access to essential health products.
The Global Fund
- The Global Fund is an international financing and partnership organization.
- It was created in 2002 and its secretariat is located in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The Global Fund aims to attract, leverage, and invest additional resources to end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria to support the attainment of the Sustainable Development Goals.
- It is designed to promote innovative solutions to global health challenges. It works in partnership with governments, civil society, technical agencies, and people affected by the diseases.
- Public sector contributions have constituted 95 percent of all financing raised; the remaining 5 percent comes from the private sector or other financing initiatives such as Product Red.
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI) 2023
Why in News?
‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World' (SOFI) 2023, a report by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), has shed light on a concerning issue in India.
- It highlights the growing disparity between the cost of a nutritious meal and the economic realities faced by a significant portion of the Indian population.
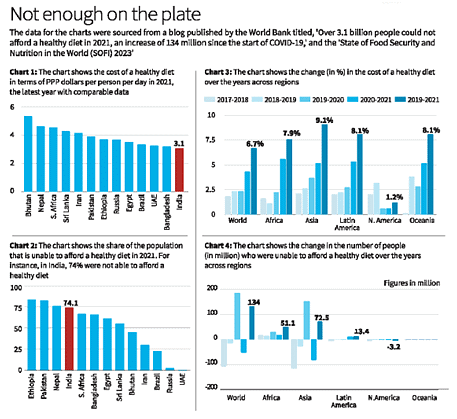
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Global Hunger: While global hunger numbers have remained stagnant between 2021 and 2022, the number of people facing hunger worldwide has increased by over 122 million since 2019 due to the pandemic, repeated weather shocks, and conflicts, including the war in Ukraine.
- Nutritional Access: Approximately 2.4 billion individuals, largely women, and residents of rural areas, did not have consistent access to nutritious, safe, and sufficient food in 2022.
- Child Malnutrition: Child malnutrition is still alarmingly high. In 2021, 22.3% (148.1 million) children were stunted, 6.8% (45 million) were wasted, and 5.6% (37 million) were overweight.
- Urbanization’s Impact on Diet: As urbanization accelerates, there is a noticeable increase in the consumption of processed and convenience foods, leading to a spike in overweight and obesity rates across urban, peri-urban, and rural areas.
- Rural Dependence on Global Markets: Previously self-sustaining rural regions, especially in Africa and Asia, are now found to be increasingly dependent on national and global food markets.
- Regional Trends: The SOFI report also tracks changes in the cost of a healthy diet and affordability across regions.
- Between 2019 and 2021, Asia witnessed the highest increase in the cost of maintaining a healthy diet, rising by almost 9%.
- The growth in the number of people unable to afford a nutritious diet was highest in Asia and Africa, with South Asia and Eastern and Western Africa facing the greatest challenges.
- South Asia's Struggle: South Asia, with 1.4 billion people, recorded the highest number (72%) of individuals unable to afford a healthy diet.
- Africa's Challenge: In Africa, Eastern and Western Africa were particularly affected, with 85% of the population unable to afford a healthy diet. These two continents (Asia and Africa) accounted for 92% of the global increase in this statistic, underscoring the severity of the issue on the African continent.
- Future Outlook: By 2050, it’s projected that 70% of the global population will reside in cities. This significant demographic shift necessitates a reorientation of food systems to cater to these new urban populations and eradicate hunger, food insecurity, and malnutrition.
What are the Key Highlights related to the Report on India?
- Cost of a Healthy Diet in India: According to the SOFI report, India has the lowest cost of a healthy diet among BRICS nations and its neighbours. In 2021, a healthy diet in India costs approximately 3.066 Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) per person per day, making it seemingly affordable on the surface.
- A diet is considered unaffordable if it costs more than 52% of a nation's average income. India has a low average income compared to other countries.
- This makes it difficult for a substantial portion of the population to afford the recommended diet.
- The Mumbai Case Study: The report also highlights a specific case study in Mumbai, where the cost of meals has risen by a staggering 65% in just five years. In contrast, salaries and wages have only increased by 28%-37% during the same period.
- Mumbai, chosen for its consistent data availability, serves as a stark example of the challenges faced by urban populations in India.
- Global Comparisons: Comparing India to other countries in the report, it becomes evident that while the cost of a healthy diet in India remains relatively low, it remains unattainable for a substantial portion of the population due to income disparities.
- In 2021, 74% of Indians could not afford a healthy diet, ranking India fourth among the nations considered.
Why is Ensuring Food Security Important for India?
- Meeting the Nutritional Needs of the Population:
- India is home to a significant population that is malnourished or undernourished, which affects their physical and mental growth.
- According to the Global Food Security Index 2022, India has a prevalence of undernutrition of 16.3%. Further, 30.9% of children in India are stunted, 33.4% are underweight, and 3.8% are obese.
- Supporting Economic Growth:
- Agriculture is a crucial sector that contributes significantly to India's economy. By ensuring food security, the government can support farmers and increase their income, which can help drive economic growth.
- With over 70% of the population engaged in agriculture-related activities, it is the backbone of India’s economy.
- Reducing Poverty:
- Food security can play a vital role in reducing poverty levels. By providing access to affordable and nutritious food, people can better manage their expenses, reduce their healthcare costs, and improve their overall quality of life.
- According to the Global Multidimensional Poverty Index MPI 2023, India still has more than 230 million people who are poor.
- Ensuring National Security:
- Food security is also essential for India's national security. A stable food supply can prevent social unrest and political instability, which can threaten national security.
- Combating Climate Change:
- Climate change poses a significant threat to India's food security. By adopting sustainable farming practices and investing in climate-resilient crops, India can better adapt to the changing climate and ensure food security for its population.
- The International Food Security Assessment for 2022-2032 indicates that India's large population has a significant impact on food insecurity trends. It is projected that around 333.5 million people will be affected in India during 2022-23.
What are the Challenges of Food Security in India?
- Inadequate Infrastructure:
- Inadequate infrastructure makes it difficult for farmers to transport their produce to the market and store them properly. This leads to high wastage and lower profits for farmers.
- Poor Agricultural Practices:
- Poor agricultural practices like over-cultivation, excessive use of pesticides, and improper irrigation techniques have led to decreased soil fertility and reduced crop yields.
- Extreme Weather Conditions:
- The extreme weather conditions due to climate change have also caused crop failures and food shortages. Floods, droughts, and heatwaves are becoming more frequent and intense, which affects food production and increases food prices.
- Inefficient Supply Chain Networks:
- Inefficient supply chain networks, including inadequate transportation, storage, and distribution facilities, also contribute to food insecurity in India. This leads to higher prices for consumers and lower profits for farmers.
- Fragmented Landholdings:
- Fragmented landholdings, where farmers own small and scattered plots of land, make it difficult to adopt modern farming practices and technologies. This, in turn, affects food production and availability.
Way Forward
- Investing in Agriculture Production Systems and Research:
- The government should invest in modern agricultural research to increase agricultural production.
- Improving Storage Facilities and Transportation Networks:
- The government should develop adequate storage facilities to prevent post-harvest losses and robust transportation networks for distributing food products across the country to ensure supply-demand balance.
- Promoting Public-Private Partnerships:
- The government should promote partnerships between the public and private sectors to improve agricultural productivity and food availability.
- Encouraging Sustainable Agriculture Practices:
- The government should promote sustainable agriculture practices that preserve soil health and reduce the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers.
The document Indian Society and Social Issues: September 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly is a part of the UPSC Course Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
44 videos|5257 docs|1109 tests
|
Related Searches





















