Influence of Man on Ecology & Environment | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
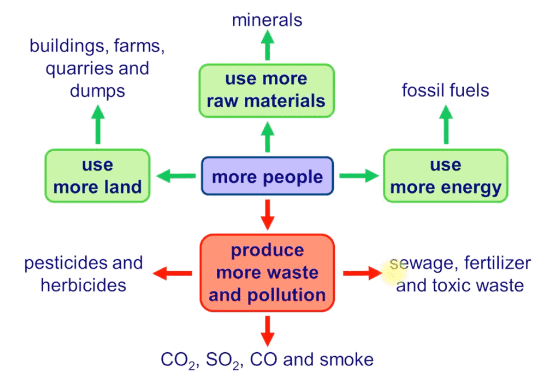
The relationship between humans and their natural environment is multifaceted, as humans are both influenced by and have the capacity to alter their surroundings. This dynamic has evolved over time, with human beings increasingly able to modify their physical environment to better suit their needs.
- While the human impact on the environment has accelerated exponentially since the Industrial Revolution, humans have been contributing to environmental change for roughly 40,000 years, dating back to the late Pleistocene ice age. Although the primary goal of these alterations was to enhance living conditions, some of these changes have resulted in significant long-term problems, while others have led to disastrous consequences for both nature and humanity.
- Some of the ways humans have inadvertently altered the environment include climate change, landform modifications, soil degradation, and ecosystem disruption. These changes have occurred through various means, such as overpopulation, pollution, burning fossil fuels, and deforestation. As a result, we are now facing issues like climate change, soil erosion, poor air quality, and water pollution.
- Such negative impacts have far-reaching effects on human behavior and can lead to mass migrations or conflicts over access to clean water. In summary, the complex relationship between humans and their natural environment has led to both intended and unintended consequences, and it is crucial to recognize and address these issues in order to ensure a sustainable future for both humanity and the planet.
Modification of Landforms
- Human activities, such as mining, quarrying, deforestation, introducing non-native plants and animals, using agricultural machinery, constructing roads, and overgrazing, have significantly impacted landforms, leading to increased erosion and deposition. These activities can either directly alter the landscape or indirectly affect natural processes like wind and water action.
- Indirect effects are more common and often occur unintentionally or as a side effect of another activity. Intentional attempts to influence landform processes, like building coastal groynes or reforestation, tend to be costly and limited in their scope. Overall, human actions have had profound consequences on landforms and the environment.
Direct Alteration of Landforms
- Human activities have a significant impact on the shape of landforms through actions such as excavation, land reclamation from the sea, and land subsidence caused by mining. These activities have increased substantially since the Industrial Revolution, owing to the development of powerful machinery and explosives for moving materials. The term "land scarification" is sometimes used to describe the disturbances caused by the extraction of mineral resources, which can create open-pit mines, quarries, and sand and gravel pits.
- Strip-mining is one of the most destructive examples of human-induced landform alteration. Other visible examples of man-made landforms include waste heaps from mining and quarrying, such as coal tips. Many of these structures are unstable from a geomorphological perspective, which can lead to various forms of mass movement. For instance, when heavy rainfall saturates these waste heaps, they can become prone to sliding and flowing, producing sediment that obstructs stream channels.
Indirect Effects: Slopes and Rivers
- The most significant impact humans have on landforms is related to the interference with natural vegetation, especially when clearing forests for agriculture. There is a strong correlation between the amount of vegetation cover and erosion rates on hillsides, which in turn affects the sediment levels in streams.
- Having a stable vegetation cover is crucial for regulating natural erosion. Vegetation helps protect the ground from direct raindrop impact, absorbs some of the runoff, and increases the cohesiveness of the slope. When vegetation is removed, the surface loses its plant litter, which leads to a decline in soil structure, cohesion, and porosity. As a result, multiple narrow rills and gullies can form on hillsides, which is a common indication of humans' indirect influence on slopes.
- Changing the vegetation on slopes also has a significant impact on nearby rivers. It affects both the rivers' discharge and sediment supply by altering the infiltration and runoff on slopes. Therefore, it is essential to consider the consequences of modifying natural vegetation on slopes and rivers when planning land use and agriculture.
Wind Deflation
- Wind deflation, or the process of land erosion caused by wind, is a phenomenon that can have disastrous consequences on the environment, as demonstrated by the Dust Bowl in the Great Plains region of the United States during the 1930s. This event serves as a prime example of how human activities can lead to significant land erosion. The Great Plains were initially grasslands with rich brown and chestnut soils, but overgrazing and ploughing contributed to the eventual catastrophe that forced many farmers to abandon their land.
- An increase in wheat cultivation during the early 1930s was followed by a series of droughts. This combination led to the soil being depleted of its natural nutrients, making it susceptible to severe deflation and the drifting of soil particles, which had devastating effects on the region. However, the Dust Bowl is not the only instance of such an occurrence. Areas bordering today's hot deserts, like the Thar Desert in Pakistan and India, and the Egyptian Desert, also experience significant wind deflation caused by grazing animals.
Coastal Erosion and Deposition
- Human activities have minimal influence on the natural forces that control waves, tides, and currents. However, humans have impacted coastal erosion and deposition through the construction of various structures and the removal of beach materials for purposes like ballast or construction.
- As a result, engineers have been compelled to build structures such as groynes, breakwaters, and seawalls to counteract marine erosion. Despite their effectiveness, these structures are not only costly to construct and maintain, but they can also inadvertently exacerbate erosion in other areas by preventing it in one location.
Modification of the Atmosphere
Over the past few decades, the global heat balance has experienced significant changes, leading to the question of whether human-induced atmospheric pollution is a contributing factor. It is clear that pollution has had noticeable local impacts on the atmosphere.Human-induced atmospheric changes can be classified into three main categories:
- The addition of solid and gaseous substances that are not typically present in the atmosphere, also known as pollutants.
- Alterations in the ratios of the natural component gases found in the atmosphere.
- Modifications to the Earth's surface that can influence the atmosphere in various ways.
Pollutants in the Atmosphere:
- Atmospheric pollution is a significant issue, especially for those living in urban areas. Pollutants in the atmosphere include particulate matter, such as solid and liquid particles, as well as gaseous substances like sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2, NO3), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrocarbon compounds. However, pollution is not limited to cities; it can also stem from isolated industrial activities, mining, and quarrying, which release large amounts of mineral dust into the air. Additionally, man-made forest and grass fires, as well as bonfires, can contribute to particulate pollution during certain times of the year.
- Once these primary pollutants enter the atmosphere, they undergo various chemical reactions, generating a secondary group of pollutants. For instance, sulfur dioxide (SO2) reacts with oxygen and water droplets in the air to form sulfuric acid, which is harmful to organic tissues and highly corrosive. Sunlight also plays a role in producing pollutants through photochemical reactions. An example of this is the formation of ozone (O3) when sunlight interacts with nitrogen oxides and organic compounds. Ethylene, another toxic chemical, is also produced by photochemical action.
- Atmospheric pollution has numerous detrimental effects on plant and animal life, including humans. Many pollutants irritate the eyes and pose a threat to the respiratory system.
Changes in Atmospheric Gas Levels:
- Among the main natural gases present in the atmosphere, oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are the most significant from an environmental perspective. This is because they are deeply connected to the biochemical cycles between the atmosphere and the Earth's surface. While nitrogen makes up around 80% of the atmosphere, its non-reactive nature means it plays a smaller role in these processes. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are naturally introduced into the atmosphere through "out gassing" from the Earth's interior. Plants play a crucial role in removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it as coal and other fossil organic materials.
- Prior to the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric carbon dioxide levels were approximately 290 parts per million. However, in the past century, this number has increased by about 40% to 400 ppm, primarily due to human use of fossil fuels. It has been proposed that, unlike the effect of solid particles, an increase in carbon dioxide levels may lead to a rise in atmospheric temperature since the gas absorbs long-wave radiation.
- Moreover, the widespread burning of hydrocarbon fuels by humans necessitates a large amount of oxygen to be removed from the atmosphere and transformed into carbon dioxide and water vapor. This could potentially cause a reduction in atmospheric oxygen levels, which may negatively impact animal life.
- Changes in water vapor levels, caused by human activities such as combustion and modifications to vegetation cover, could theoretically have a significant impact on global radiation and heat balances, similar to the effect of altered carbon dioxide levels. However, water vapor content varies greatly between locations, making it challenging to measure global changes.
Alterations to the Earth’s Surface:
- Changes to the Earth's surface, such as deforestation, agricultural practices, and urbanization, significantly impact meteorological processes near the ground. These human activities can influence the rate of evapotranspiration, which is the process by which water is transferred from the land to the atmosphere by evaporation and plant transpiration. For example, when a forest is completely removed, the rate of transpiration decreases, and less water is returned to the atmosphere in the form of vapor.
- Another crucial effect of surface alterations is the modification of temperature characteristics in the atmosphere close to the ground. Urban areas with dense construction can develop their own "heat islands" during calm summer nights, where temperatures are higher than in surrounding areas.
- Lastly, changes to the Earth's surface can also impact wind patterns. Trees and hedges can act as windbreakers, reducing wind speed and subsequently decreasing evaporation rates and carbon dioxide exchange near the ground. Overall, human activities that alter the Earth's surface have significant consequences for local and global climates.
Modification of Ecosystems
- The advent of agriculture brought about significant changes to ecosystems, both evident and subtle. Over time, humans have become more adept at altering ecosystems to cultivate the desired crops. In doing so, they have inadvertently simplified ecosystems, disrupted nutrient cycles, introduced non-native species, eliminated certain species, and caused pollution.
- It is only in recent years that people have become more aware of the repercussions of modifying ecosystems.
Simplification:
- In general, human activities tend to simplify ecosystems, as humans often aim to direct energy and resources within these systems towards their own needs. This usually involves promoting the growth of specific species that are beneficial to humans while trying to get rid of other species considered as weeds or pests. Consequently, this leads to a decrease in species diversity, sometimes even resulting in ecosystems with just one dominant species.
- The extent of ecosystem simplification varies depending on the location and the human activities involved. In areas where only hunter-gatherers reside, human impact may actually add another layer to the food chain. In contrast, primitive shifting agriculture in tropical rainforests causes only temporary simplification, as cultivated plots are abandoned after a few years. However, ecosystems subjected to grazing activities are simplified to a much larger degree.
- This simplification of ecosystems can have negative consequences, such as increased vulnerability to diseases, pests, and parasites. For example, a field of wheat or a herd of cows consisting of only one species is more likely to experience the spread of diseases and pests.
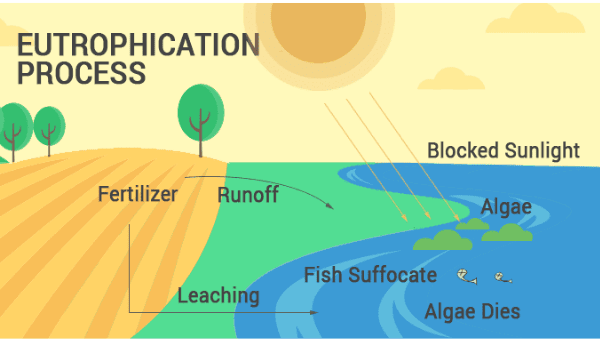
Eutrophication:
- Eutrophication is a process that occurs when chemical fertilizers are used on land, leading to an excess of elements like nitrate being added to the soil. Although many elements in fertilizers are absorbed by the soil, nitrates are not, and they are released into rivers and lakes at a faster rate than they can be broken down by denitrifying agents in the soil. As nitrates are soluble, they easily leach into water bodies.
- The increased presence of nitrates in water bodies promotes the rapid growth of plants, algae, and other phytoplankton. This enrichment of the aquatic ecosystem with nutrients, which leads to increased productivity, is called eutrophication. However, when this process becomes extreme, it can have detrimental effects on the environment.
- As plants and organisms grow rapidly due to eutrophication, they also die and decompose at an accelerated rate. This high rate of decomposition consumes oxygen in the water, eventually depleting oxygen levels to the point where aquatic life cannot survive. One notable example of severe eutrophication is Lake Erie in North America, where significant amounts of decaying organic matter have accumulated along large stretches of the shoreline, resulting in detrimental effects on the lake's ecosystem.
Effect on Individual Species:
- The impact of human activities on the environment has led to the extinction or decline of numerous plant and animal species. This is often not caused by direct hunting or elimination, but rather by habitat disruption and fragmentation. Many species, particularly large predators, need vast specialized habitats to breed and hunt, and the fragmentation of these habitats due to human interference has often had catastrophic consequences. For example, the marsh harrier, a large bird of prey found in reed beds and fens, has suffered greatly from this.
- On the other hand, the introduction of non-native species into ecosystems, whether accidentally or intentionally, has also had significant effects on the environment. Some plants and animals, due to their high genetic adaptability and rapid reproduction rates, can outcompete native species and disrupt the ecosystem's balance.
- Naturally, ecosystems maintain an ecological equilibrium. However, as human influence on the environment grows, the balance of these ecosystems is being disrupted, leading to signs of instability or decreasing efficiency in many of them. This can be seen in the degradation of once fertile agricultural or grazing lands due to overuse, the reduction of species when secondary forests replace primary forests, a general decrease in biological productivity, and an increase in pollution.
Positive Effects of Human Activities
- Human activities don't always negatively impact the environment. Whenever you recycle materials like paper, plastic, or metal, or clean up litter from the streets, you're making a positive contribution to the ecosystem. Many individuals are also dedicating their time and effort to large-scale projects aimed at improving the environment.
- For instance, in 2011, a 16-year-old inventor named Boyan Slat developed a device capable of removing plastic from the ocean. He later established The Ocean Cleanup project, which utilizes this technology to tackle ocean pollution. The project aims to remove half of the plastic found in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch within five years.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between humans and their natural environment is complex and dynamic, with human activities significantly impacting landforms, the atmosphere, and ecosystems. While some actions have led to environmental degradation and disruption, increased awareness and efforts to address these issues are contributing to positive changes. It is crucial for humanity to recognize and address the consequences of our actions on the environment in order to ensure a sustainable future for both humans and the planet.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Influence of Man on Ecology & Environment
What are some of the main ways humans have inadvertently altered the environment?
Some of the main ways humans have inadvertently altered the environment include climate change, landform modifications, soil degradation, and ecosystem disruption. These changes have occurred through various means, such as overpopulation, pollution, burning fossil fuels, and deforestation.
How do human activities impact landforms and contribute to erosion and deposition?
Human activities such as mining, quarrying, deforestation, introducing non-native plants and animals, using agricultural machinery, constructing roads, and overgrazing have significantly impacted landforms, leading to increased erosion and deposition. These activities can either directly alter the landscape or indirectly affect natural processes like wind and water action.
What is eutrophication, and how does it negatively affect aquatic ecosystems?
Eutrophication is a process that occurs when chemical fertilizers are used on land, leading to an excess of elements like nitrates being added to the soil. These nitrates can leach into water bodies, promoting the rapid growth of plants, algae, and other phytoplankton. When this process becomes extreme, it can have detrimental effects on the environment, including the depletion of oxygen levels in water bodies, which can lead to the death of aquatic life.
How do human activities affect the atmosphere and contribute to climate change?
Human activities can contribute to climate change by adding pollutants to the atmosphere, altering the ratios of natural component gases, and modifying the Earth's surface. One of the most significant contributors to climate change is the burning of fossil fuels, which releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to increased greenhouse gas concentrations and global warming.
What are some positive effects of human activities on the environment?
Positive effects of human activities on the environment include recycling materials like paper, plastic, or metal, cleaning up litter from streets, and participating in large-scale projects aimed at improving the environment, such as The Ocean Cleanup project, which utilizes technology to remove plastic from the ocean.
|
304 videos|717 docs|259 tests
|
FAQs on Influence of Man on Ecology & Environment - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. How do human activities modify landforms? |  |
| 2. What are the indirect effects of human activities on slopes and rivers? |  |
| 3. How do human activities modify the atmosphere? |  |
| 4. What are some positive effects of human activities on the environment? |  |
| 5. How do human activities influence the ecology and environment? |  |
















