NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physics Class 12 > Infographics: Electric Charges and Fields
Infographics: Electric Charges and Fields | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
The document Infographics: Electric Charges and Fields | Physics Class 12 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physics Class 12.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Infographics: Electric Charges and Fields - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are electric charges and how are they classified? |  |
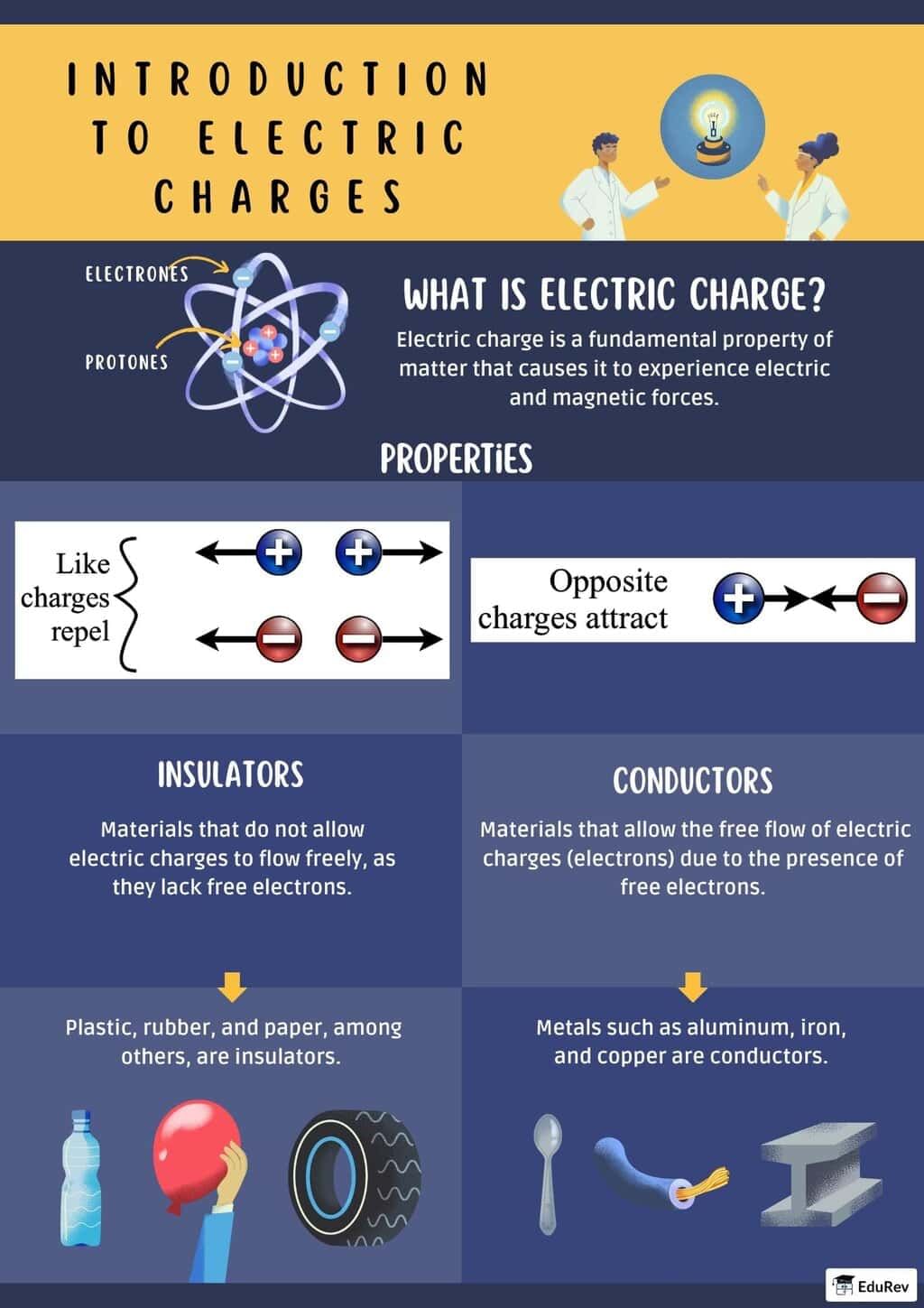
Ans. Electric charges are fundamental properties of matter that cause it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. They are classified into two types: positive and negative. Positive charges are carried by protons, while negative charges are carried by electrons. The interaction between these charges follows Coulomb's law, where opposite charges attract and like charges repel.
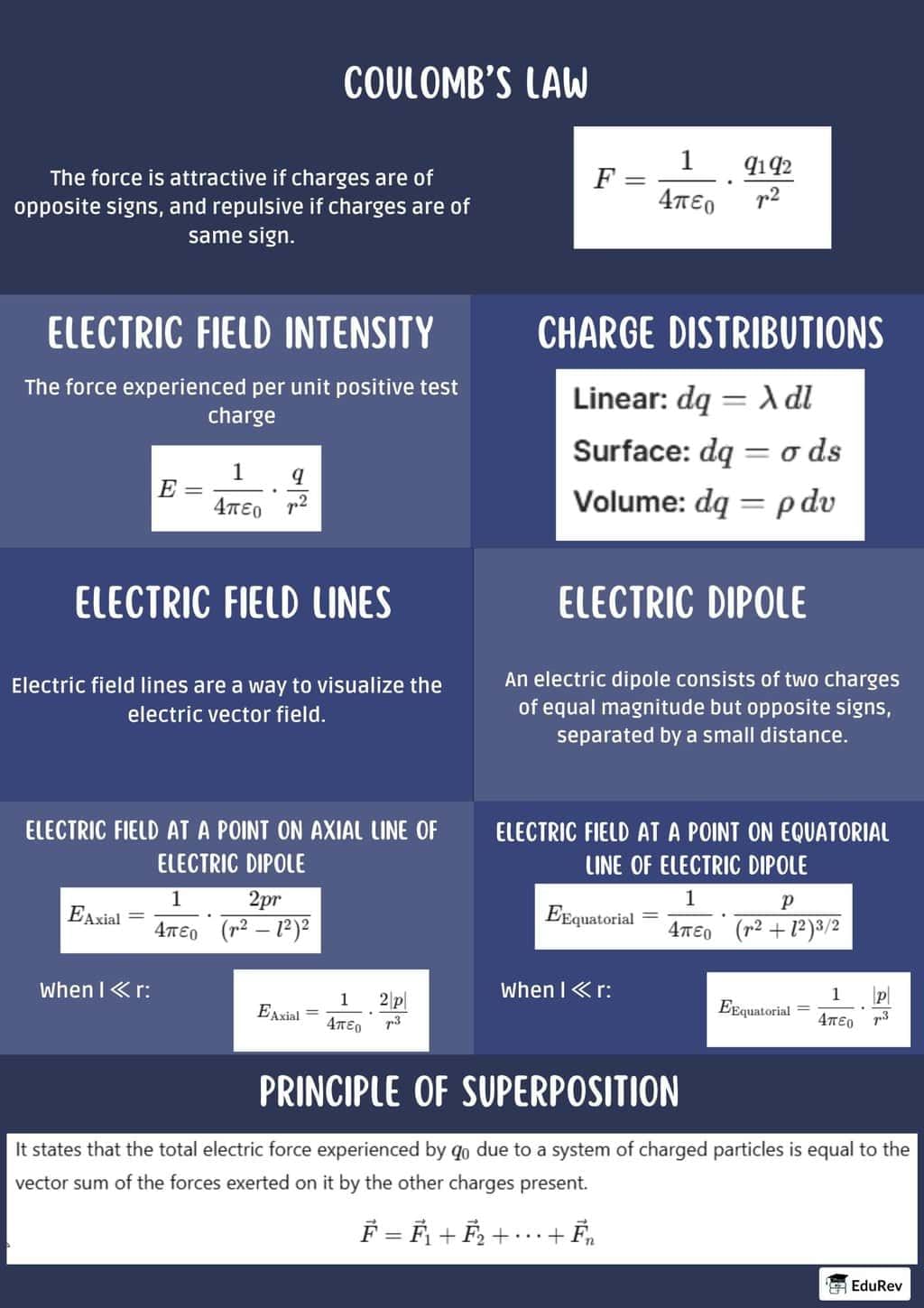
| 2. What is Coulomb's Law and how does it relate to electric fields? |  |
Ans. Coulomb's Law describes the force between two charged objects. It states that the force (F) between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges (q₁ and q₂) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between them: F = k * (q₁ * q₂) / r², where k is Coulomb's constant. This law helps define the electric field (E), which is the force per unit charge exerted on a positive test charge placed in the field.
| 3. What is the concept of an electric field and how is it represented? |  |
Ans. An electric field is a region around a charged object where other charges experience a force. It is represented by electric field lines, which indicate the direction of the field and its strength. The density of these lines represents the strength of the electric field; the closer the lines, the stronger the field. The electric field (E) can be calculated using E = F/q, where F is the force experienced by a charge q.
| 4. How do conductors and insulators differ in terms of electric charges? |  |
Ans. Conductors are materials that allow electric charges to flow freely through them, such as metals. They have a large number of free electrons that can move easily, allowing electrical current to pass. Insulators, on the other hand, do not allow charges to flow easily. Materials like rubber or glass have tightly bound electrons, which restrict the movement of electric charges, preventing current flow.
| 5. What role do electric fields play in electrostatics? |  |
Ans. In electrostatics, electric fields are crucial for understanding how charged objects interact with one another without moving. They provide a way to visualize the forces experienced by charges due to the presence of other charges. The study of electric fields allows us to calculate the potential energy and work done on charges in various configurations, aiding in the analysis of electrostatic problems.
Related Searches





















