NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physics Class 11 > Infographics: Motion in a Plane
Infographics: Motion in a Plane | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
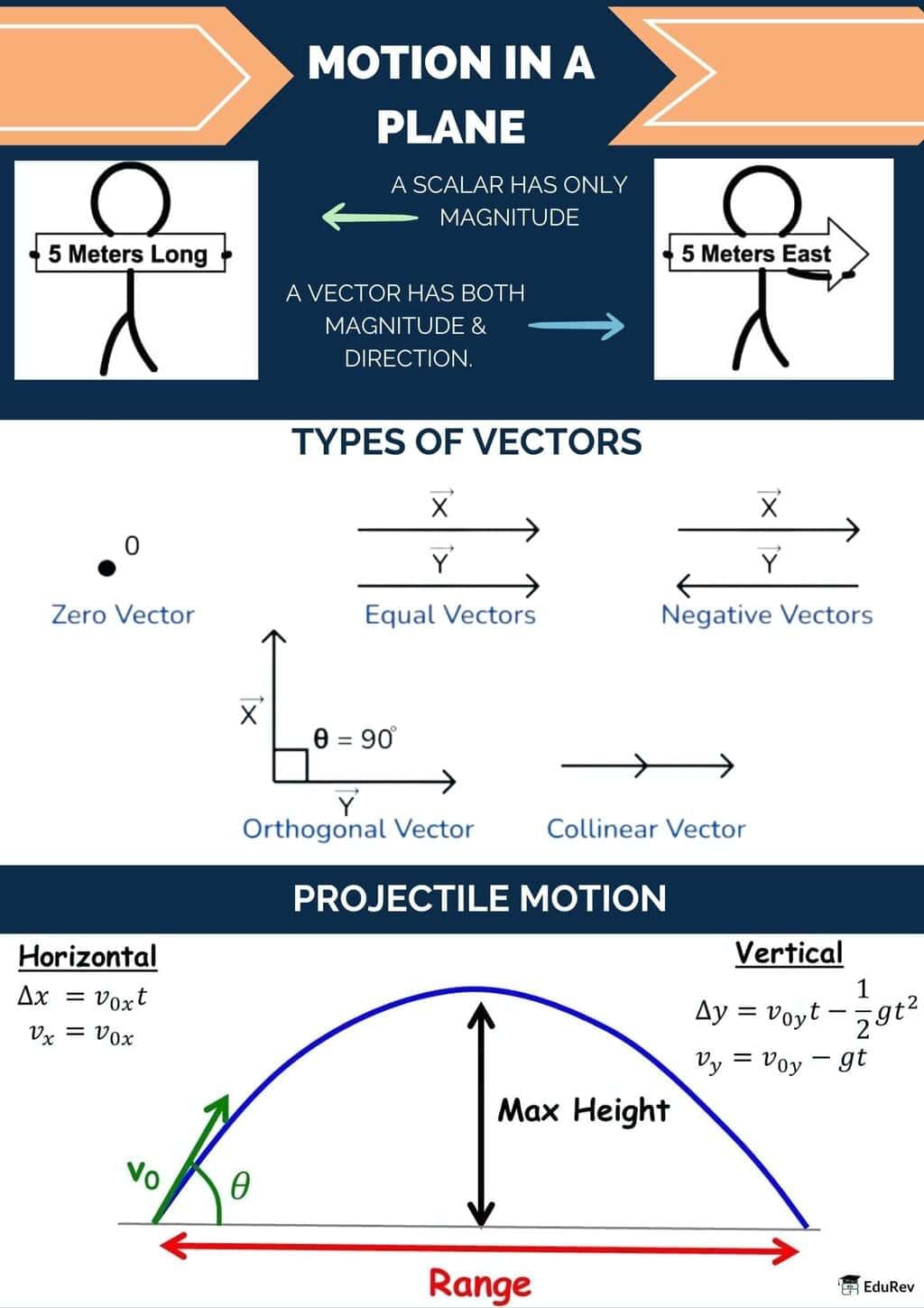
The document Infographics: Motion in a Plane | Physics Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physics Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Infographics: Motion in a Plane - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is motion in a plane and how is it different from motion in a straight line? |  |
Ans. Motion in a plane refers to the movement of an object in two dimensions, meaning it can move in both the x and y axes simultaneously. This contrasts with motion in a straight line, where the object moves along a single dimension (one axis). In a plane, the position of the object is described using coordinates, and various factors such as velocity and acceleration can be represented as vectors with both magnitude and direction.
| 2. What are the key equations of motion applicable to motion in a plane? |  |
Ans. The key equations of motion for objects moving in a plane include:
1. v = u + at, where v is final velocity, u is initial velocity, a is acceleration, and t is time.
2. s = ut + 1/2 at², where s represents displacement.
3. v² = u² + 2as.
These equations can be applied in both horizontal and vertical directions, and they help in determining various parameters of the motion.
| 3. How do we calculate the resultant velocity of an object moving in two dimensions? |  |
Ans. To calculate the resultant velocity of an object moving in two dimensions, we must first break down the velocity into its components along the x and y axes. If the velocities are represented as V₁ in the x-direction and V₂ in the y-direction, the resultant velocity V can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem:
V = √(V₁² + V₂²).
The direction of the resultant can be found using the tangent function: θ = tan⁻¹(V₂/V₁), where θ is the angle of the resultant relative to the x-axis.
| 4. What role do vectors play in understanding motion in a plane? |  |
Ans. Vectors are crucial in understanding motion in a plane as they provide both magnitude and direction for quantities such as displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Unlike scalar quantities that only have magnitude, vectors allow us to analyze how an object moves across two dimensions. By using vector addition, we can combine motions occurring in different directions and accurately describe the overall motion of the object.
| 5. How can projectile motion be classified under motion in a plane? |  |
Ans. Projectile motion is a specific type of motion in a plane where an object is thrown into the air and moves under the influence of gravity. It can be analyzed as two independent motions: horizontal motion (constant velocity) and vertical motion (uniformly accelerated motion due to gravity). The trajectory of a projectile can be predicted using kinematic equations, and the path it follows is typically parabolic. Understanding this concept is vital in many applications, including sports and engineering.
Related Searches
















