NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Infographics: Overall Process of Cellular Respiration
Infographics: Overall Process of Cellular Respiration | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
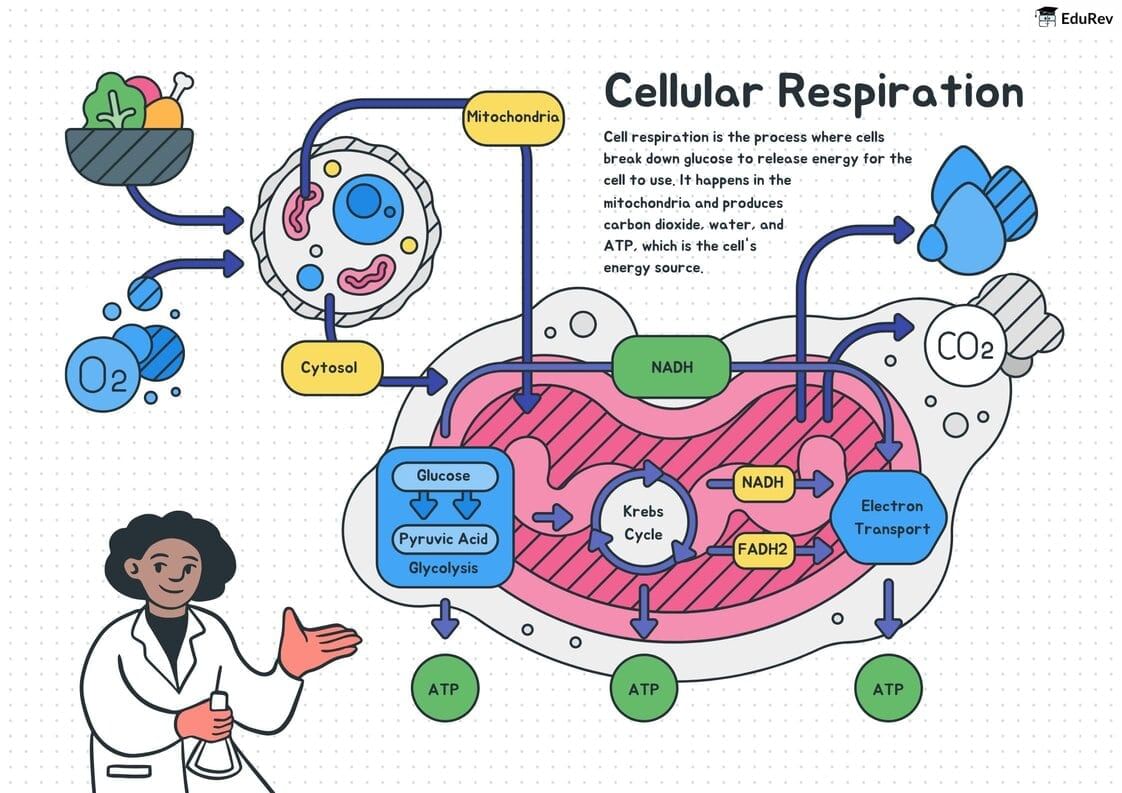
The document Infographics: Overall Process of Cellular Respiration | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
150 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Infographics: Overall Process of Cellular Respiration - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the overall process of cellular respiration? |  |
Ans. Cellular respiration is a biochemical process through which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water. It consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (or citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (which includes the electron transport chain). Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm, while the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation take place in the mitochondria.
| 2. What are the main products of cellular respiration? |  |
Ans. The main products of cellular respiration are adenosine triphosphate (ATP), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and water (H₂O). For each molecule of glucose that undergoes cellular respiration, approximately 36 to 38 ATP molecules are produced, along with 6 molecules of CO₂ and 6 molecules of H₂O.
| 3. How does glycolysis contribute to cellular respiration? |  |
Ans. Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration that occurs in the cytoplasm. It breaks down one molecule of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) into two molecules of pyruvate (C₃H₄O₃), producing a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules. This process does not require oxygen and serves as a crucial step for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
| 4. What role does the electron transport chain play in cellular respiration? |  |
Ans. The electron transport chain (ETC) is the final stage of cellular respiration, located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It utilizes electrons from NADH and FADH₂ (produced in previous stages) to create a proton gradient across the membrane. This gradient powers ATP synthesis through a process called chemiosmosis, ultimately leading to the production of about 28 to 34 ATP molecules.
| 5. Why is oxygen important for cellular respiration? |  |
Ans. Oxygen is essential for aerobic cellular respiration as it acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. It combines with electrons and protons to form water (H₂O). Without oxygen, the electron transport chain cannot function, leading to a decrease in ATP production and the reliance on anaerobic processes, which yield significantly less energy.
Related Searches
















