NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Infographics: Types of Plant Tissues
Infographics: Types of Plant Tissues | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
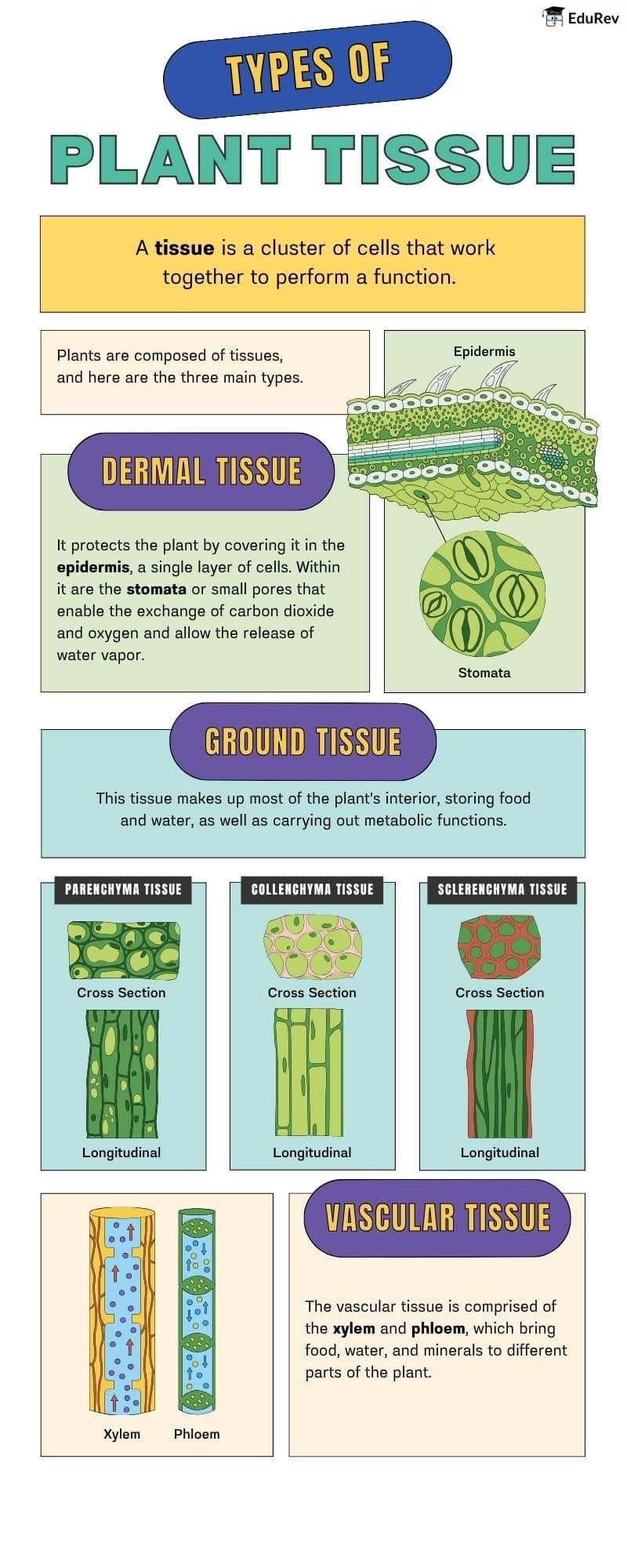
The document Infographics: Types of Plant Tissues | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
150 videos|398 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Infographics: Types of Plant Tissues - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main types of plant tissues? |  |
Ans. The main types of plant tissues are classified into two broad categories: meristematic tissues and permanent tissues. Meristematic tissues are undifferentiated cells found mainly at the tips of roots and shoots, responsible for the growth of the plant. Permanent tissues, on the other hand, are differentiated and serve specific functions. They can be further divided into simple tissues (such as parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma) and complex tissues (such as xylem and phloem).
| 2. What is the function of xylem in plants? |  |
Ans. Xylem is a type of complex tissue responsible for the conduction of water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. It also provides structural support due to the presence of lignin in its cell walls. Xylem consists of various cell types, including tracheids and vessel elements, which facilitate efficient water transport.
| 3. How does phloem differ from xylem in its function? |  |
Ans. Phloem is distinct from xylem in that it is responsible for the transportation of organic nutrients, particularly sugars produced during photosynthesis, from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Phloem consists of sieve elements and companion cells that work together to facilitate the flow of nutrients in a process known as translocation.
| 4. What is the role of meristematic tissue in plant growth? |  |
Ans. Meristematic tissue plays a crucial role in plant growth, as it contains undifferentiated cells that have the potential to divide and differentiate into various types of cells. This tissue is primarily located at the tips of roots (root apical meristem) and shoots (shoot apical meristem), allowing for continuous growth and development of the plant throughout its life.
| 5. Can you explain the differences between parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma? |  |
Ans. Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma are simple permanent tissues with distinct characteristics. Parenchyma cells are generally thin-walled and involved in storage, photosynthesis, and tissue repair. Collenchyma cells have unevenly thickened walls, providing flexible support to young stems and leaves. Sclerenchyma cells are thick-walled and provide rigid support, often found in mature plant parts; they can be further classified into fibers and sclereids.
Related Searches
















