Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 7 (Old NCERT) > NCERT Summary: Inside Our Earth
Inside Our Earth Summary Class 7 Geography Chapter 2
Planet Earth
- The earth in which humans live is not absolute spherical in shape.
Interior of earth
- The earth is like onion which is made up of several layers.
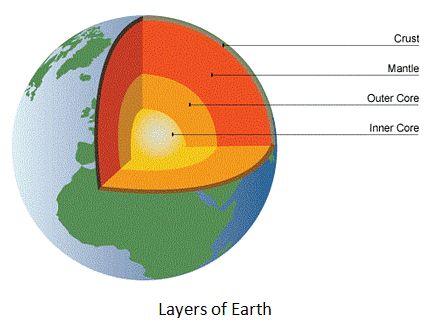
Crust
- The uppermost layer over the earth’s surface is called the crust.
- It is the thinnest of all the layers.
- It is 35 km thick on the landmass (continental masses) and only 5 km on the ocean floors.
- Main mineral constituents of the continental mass: Silica and Alumina.
- Thus, it is called sial (si-silica and al-alumina).
- The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium
- Thus, it is called sima (si-silica and ma-magnesium).
Mantle
- This layer extends up to a depth of 2900 km below the crust.
Core
- The innermost layer is the core.
- The radius of core is about 3500 km.
- It is mainly made up of nickel and iron.
- Thus, it is called nife (ni – nickel and fe – ferrous i.e. iron).
- The central core has very high temperature and pressure.
Question for NCERT Summary: Inside Our EarthTry yourself: What is the thinnest layer of the Earth?View Solution
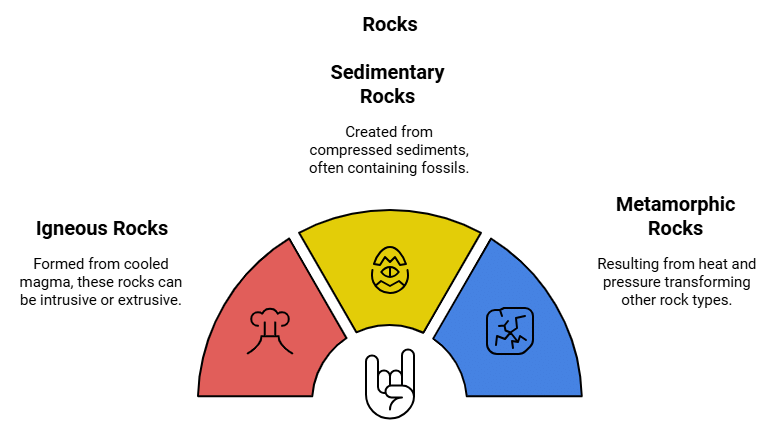
Rocks
- Any natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust is called a rock.
- It can be of different colour, size and texture.
- There are three major types of rocks:
- Igneous rocks
- Sedimentary rocks
- Metamorphic rocks
1. Igneous Rocks
- When the molten magma cools, it becomes solid and are called igneous rocks.
- They are also called primary rocks.
- There are two types of igneous rocks:
- Intrusive rocks
- Extrusive rocks
- When the molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid on the crust. These rocks are called extrusive igneous rocks.
- They have a very fine-grained structure.
- Example: Basalt. The Deccan plateau is made up of basalt rocks.
- When the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust giving formation of solid rocks are called intrusive igneous rocks.
- Since they cool down slowly they form large grains.
- Example: Granite. Grinding stones used to prepare paste/powder of spices and grains are made of granite.
2. Sedimentary Rocks
- Rocks roll down, crack, and hit each other and are broken down into small fragments which are called sediments.
- These sediments are transported and deposited by wind, water, etc. These loose sediments are compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks. These types of rocks are called sedimentary rocks. → Example: Sandstone is made from grains of sand.
- Sedimentary rocks may also contain fossils of plants, animals and other micro-organisms that once lived on them.
3. Metamorphic Rocks
- Under great heat and pressure, Igneous and sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks.
- Example: clay changes into slate and limestone into marble.
Use of Rocks
- Rocks are used for construction activities such as making buildings, roads.
- They are source of minerals which are useful for various purposes in daily life.
Rock Cycle
- The process of transformation of the rock from one to another is known as the rock cycle.
- It describes the changes among the three main type of rock i.e., Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic rocks.
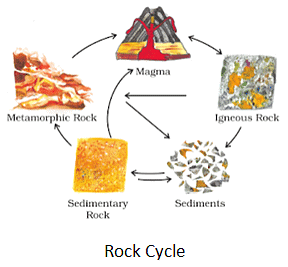
- When the molten magma cools; it solidifies to become igneous rock.
- These igneous rocks are broken down into small particles by various agents such as weathering, temperature, wind etc. and are transported and deposited to form sedimentary rocks.
- These smaller grains of rocks keep moving towards basins and lower regions and gradually form sedimentary rocks.
- When the igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to heat and pressure they change into metamorphic rocks.
- The metamorphic rocks which are still under great heat and pressure melt down to form molten magma.
- This molten magma again can cool down and solidify into igneous rocks.
Note: These processes take hundreds and thousands of years.
Question for NCERT Summary: Inside Our EarthTry yourself: What type of rock is formed when molten magma cools down deep inside the earth's crust?View Solution
Minerals
- Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition.
- These are very important for humans.
- For example, coal, natural gas and petroleum. They are also used in industries – iron, aluminium, gold, uranium, etc, in medicine, in fertilisers, etc.
The document Inside Our Earth Summary Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 is a part of the Class 7 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 7 (Old NCERT).
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
63 videos|371 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Inside Our Earth Summary Class 7 Geography Chapter 2
| 1. पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना क्या है? |  |
Ans. पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना मुख्यतः तीन भागों में बाँटी गई है: क्रस्ट (सतह), मेंटल (मध्य स्तर) और कोर (केंद्र)। क्रस्ट सबसे ऊपरी परत है, जिसमें महाद्वीपों और महासागरों का भूमि है। मेंटल उसके नीचे है, जो ठोस और तरल दोनों रूपों में उपस्थित होता है। कोर पृथ्वी का सबसे भीतरी भाग है, जो मुख्यतः लोहे और निकेल से बना है।
| 2. पृथ्वी के क्रस्ट की विशेषताएँ क्या हैं? |  |
Ans. पृथ्वी का क्रस्ट बहुत पतला होता है और इसकी मोटाई लगभग 5 से 70 किलोमीटर तक होती है। यह दो प्रकार का होता है: महाद्वीपीय क्रस्ट, जो मुख्यतः ग्रेनाइट से बना है, और महासागरीय क्रस्ट, जो बेसाल्ट से बना है। क्रस्ट में पृथ्वी के सभी जीवों और पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र का अस्तित्व है।
| 3. मेंटल की भूमिका क्या है? |  |
Ans. मेंटल पृथ्वी की आंतरिक गर्मी को बनाए रखता है और इसमें तापमान बढ़ता है। यह ठोस होते हुए भी, धीरे-धीरे बहता है, जिससे प्लेट विवर्तनिकी का निर्माण होता है। मेंटल में मैग्मा की उपस्थिति भी होती है, जो ज्वालामुखी विस्फोट का कारण बन सकती है।
| 4. पृथ्वी के कोर के बारे में क्या जानकारी है? |  |
Ans. पृथ्वी का कोर दो भागों में विभाजित होता है: बाहरी कोर और आंतरिक कोर। बाहरी कोर तरल अवस्था में है और इसमें लोहे और निकेल की उपस्थिति होती है। आंतरिक कोर ठोस है और अत्यधिक दबाव और तापमान के कारण यह ठोस बनता है। कोर पृथ्वी के मैग्नेटिक क्षेत्र का निर्माण करने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
| 5. पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना का अध्ययन क्यों आवश्यक है? |  |
Ans. पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना का अध्ययन हमें भूवैज्ञानिक प्रक्रियाओं, भूकंपों, ज्वालामुखी गतिविधियों और प्लेट टेक्टोनिक्स को समझने में मदद करता है। यह जानकारी प्राकृतिक आपदाओं के पूर्वानुमान करने में भी सहायक होती है, साथ ही यह पृथ्वी के विकास और उसके संसाधनों के प्रबंधन के लिए भी महत्वपूर्ण है।
Related Searches

















