Internal Security - 2 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Exercise PITCH Black |

|
| Exercise AL NAJAH-IV |

|
| MiG 21 |

|
| Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGM) |

|
| INS Vikrant: First Indigenous Aircraft Carrier |

|
| BrahMos Missiles |

|
Exercise PITCH Black
Why in news:
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to participate in Exercise Pitch Black, a biennial exercise hosted by the Australian Air Force, which also includes 16 other nations, including countries in the Quad partnership.
About:
- Hosted by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) every two years
- Aims to practice Offensive Counter Air (OCA) and Defensive Counter Air (DCA) combat in a simulated war environment
- Involves participation of 16 nations, including Quad partner countries
- Indian Air Force (IAF) to join the exercise
- First Pitch Black exercise was conducted in 1981 between RAAF units
Australia India Defence Relationship
Background:
- Australia and India share a long history of cooperation, including their shared experience during World War I.
- The defence relationship is supported by the 2006 Memorandum on Defence Cooperation and the 2009 Joint Declaration on Security Cooperation.
- The relationship covers various areas, such as strategic dialogues, coordination, and information exchanges, as well as military exercises involving ground, air, and maritime forces.
Strategic Dialogue:
- In June 2020, Australia and India decided to elevate their Secretaries 2+2 dialogue (Defence and Foreign Affairs) to the Ministerial level.
AUSINDEX:
- Australia and India are committed to enhancing maritime cooperation and have had AUSINDEX since 2015.
Shared Military Platform:
- India and Australia share a border with the Indian Ocean and are interested in maintaining freedom of navigation and trade.
- Australia recognizes India’s critical role in supporting security, stability, and prosperity in the Indian Ocean region.
IFC-IOR:
- Both countries are working together on the Information Fusion Centre - Indian Ocean Region initiative in Gurugram to boost maritime security and response through the exchange of information related to ships in the Indian Ocean Region.
Civil Nuclear Cooperation:
- A Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement was signed in September 2014, allowing uranium mining companies in Australia to supply uranium to India for civil use.
Other Military Exercises of India
- Malabar Exercise: Navies of India, USA, and Japan.
- JIMEX: India-Japan.
- Ex-Desert Knight 21: Bilateral air exercise between the Indian Air Force and the French air and Space Force.
- Indra Dhanush: Joint air force exercise between the Indian Air Force and the Royal Air Force of the United Kingdom.
- Exercise Pitch Black: India and Australia. The exercise focuses on practicing Defensive Counter Air combat and Offensive Counter Air Combat.
- AUSINDEX: Bilateral naval exercise between the Indian Navy and the Australian Navy.
- AUSTRAHIND: Bilateral army exercises.
- Dharma Guardian: Joint military exercise between India and Japan.
- Aviaindra: Joint air exercise between India and Russia.
- Nomadic Elephant: Joint exercise between India and Mongolia.
Exercise AL NAJAH-IV
Context:
- India and Oman will carry out a 13-day military exercise with a focus on counter-terror cooperation.
About Exercise AL NAJAH-IV:
- It is the fourth edition of India-Oman joint military exercise ‘AL NAJAH-IV’.
- The exercise is held between contingents of the Indian Army and the Royal Army of Oman.
- It will take place at the Foreign Training Node of Mahajan Field Firing Ranges.
- The previous edition of the exercise was held in Muscat in March 2019.
- The scope of the exercise includes professional interaction, mutual understanding of drills and procedures, the establishment of joint command and control structures, and elimination of terrorist threats.
Introduction to India-Oman Relations:
- Oman is a strategic partner of India in the Gulf.
- Both nations share close ties based on geography, history, and culture.
- India established an embassy in Oman in 1971.
History of the Ties:
- Oman was ruled by Sultan Qaboos bin Said al Said, who was a friend of India.
- Sultan Qaboos studied in India under the tutelage of former President Shankar Dayal Sharma.
- India and Oman share a strong bond due to their shared history and cultural ties.
Economic Ties:
- Oman has over 500,000 Indian nationals living there, making them the largest expatriate community in Oman.
- Bilateral trade between India and Oman stood at $4.5 billion in 2010.
- India is Oman’s second-largest destination for non-oil exports and fourth-largest source for Indian imports.
- India has considered constructing a 1,100-km-long underwater natural gas pipeline from Oman.
Defense Cooperation:
- Oman is the first Gulf nation to have formalized defense relations with India.
- Indian Navy has berthing rights in Oman and uses its ports as bases for conducting anti-piracy operations.
- India has secured access to the facilities at Duqm for the Indian Air Force and Navy.
- Bilateral exercises between India and Oman include Naseem al-Bahr.
Significance of Oman for India:
- Oman is India’s closest defense partner in the Gulf region.
- All three services of the Indian armed forces conduct regular bilateral exercises with Oman.
- Oman provides critical operational support to Indian naval deployments in the Arabian sea for anti-piracy missions.
Duqm Port and Its Strategic Imperative:
- India has secured access to the key Port of Duqm in Oman for military use and logistical support.
- Duqm is strategically located, in close proximity to the Chabahar port in Iran.
- India has deployed an attack submarine to this port in recent years.
Deterrent in Ties: Chinese Influence in Oman:
- China has cultivated close ties with Oman, and 92.99% of Oman’s oil exports go to China.
- Oman and China signed an agreement to establish an Oman-China Industrial Park at Duqm in 2016.
- China has been enhancing defense ties with Oman.
Way Forward
- India needs long-term energy partnerships with countries like Oman due to its rapidly growing energy demand.
- Oman’s Duqm Port is situated in the middle of international shipping lanes, providing opportunities for India to engage with Oman.
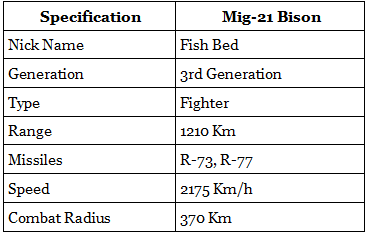
MiG 21
Introduction:
- A MiG-21 Bison aircraft of the Indian Air Force (IAF) crashed in Barmer, Rajasthan, killing the two pilots aboard the trainer version of the fighter aircraft.
Details about MiG-21 Bison crashes:
- Six MiG-21 Bison crashes in the last 20 months
- Five crashes in 2021 and one in 2022
MiG-21 Bison aircraft in service with IAF:
- Four squadrons of MiG-21 Bison aircraft currently in service in IAF
- Each squadron comprises 16-18 aircraft, including two trainer versions
Upgraded version of MiG-21 Bison:
- MiG-21 Bison is an upgraded version of the MiG-21bis
- MiG-21bis was first inducted into service in 1976
- MiG-21 FL, an older version of the aircraft, was phased out of IAF in 2013
- IAF received the first upgraded MiG-21 Bison in 2001 and the last in 2008
MiG-21 aircraft as backbone of IAF fleet:
- MiG-21 aircraft, with all its versions, formed the backbone of the fleet of fighter aircraft of the IAF
- Most versions were licence-produced in India
- More than 20 aircraft have crashed since 2010 and 38 aircraft crashed between 2003 and 2013 in a period of ten years
- High rate of accidents earned the aircraft the nickname of ‘Flying Coffin”
MiG-21 Bison aircraft specifications:
- MiG-21 Bison is a single engine, single seater multirole fighter aircraft of Russian origin
- It has a maximum speed of 2,230 km/hr and carries one 23mm twin-barrel cannon with four R-60 close combat missiles
- Described as the “back-bone” of the IAF
- India reportedly has 100 odd aircraft in its fleet
- This version of the MiG 21 — the last in a series of at least 15 variants — was flown for the first time in 1976
- MiG-21 Bison is described as an all-weather, multi-role fighter
- Inducted in the Indian Air Force in the early 1980s
MiG-21 Bison in global context:
- MiG21 variants have been flown by nearly 40 countries
- Former USSR began manufacturing these aircraft in the last 1950s
- Still has a reputation as the world’s best fighter jet, with some 11,000 aircraft produced
- Each has a life of up to 30 years.
Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGM)
Why in news:
- Recently, Laser-Guided Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGM) were successfully test-fired from Main Battle Tank (MBT) Arjun, a first for India.
- This all-indigenous missile employs a tandem High Explosive Anti-Tank (HEAT) warhead to defeat Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA) protected armoured vehicles.
- The ATGM has a multi-platform launch capability and is currently undergoing technical evaluation trials from the 120 mm rifled gun of MBT Arjun.
- With the trial, the ATGM’s capability to engage targets from minimum to maximum range has been established.
Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGM):
- Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGM) are guided missiles primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles.
- ATGMs range in size from shoulder-launched weapons, which can be transported by a single soldier, to larger tripod-mounted weapons, which require a squad or team to transport and fire, to vehicle and aircraft-mounted missile systems.
- The all-indigenous Laser Guided ATGM employs a tandem High Explosive Anti-Tank (HEAT) warhead to defeat Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA) protected armoured vehicles.
- The ATGM has been developed with a multi-platform launch capability.
HELINA Weapon System:
- HELINA (Helicopter-based NAG) is a third-generation fire and forget class Anti-tank Guided Missile (ATGM) system mounted on the Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH).
- The system has all-weather day and night capability and can defeat battle tanks with conventional armour as well as explosive reactive armour.
- The HELINA missile can engage targets both in direct hit mode as well as top attack mode.
- HELINA Weapon Systems is being inducted into the Indian Army (IA).
- A variant of the HELINA Weapon System called DHRUVASTRA is being inducted into the Indian Air Force (IAF).
INS Vikrant: First Indigenous Aircraft Carrier
Why in news:
- India's first indigenous aircraft carrier INS Vikrant was commissioned by the Prime Minister in Kochi.
- With INS Vikrant, India now has two aircraft carriers, the other one being INS Vikramaditya.
Unveiling of New Naval Ensign 'Nishaan':
- The Prime Minister also unveiled the new Naval Ensign 'Nishaan' during the commissioning of INS Vikrant.
- Naval Ensigns are flags that naval ships or formations bear to denote nationality.
- The current Indian Naval Ensign consists of a St. George's Cross - a red cross with a white background.
- In 2001, the George's Cross was replaced with the naval crest in the middle of the white flag while the Tricolour retained its place on the top left corner.
History of Indian Naval Ensign:
- The Indian Naval Ensign has changed multiple times since Independence.
- The current Indian Naval Ensign was adopted in 2001, replacing the St. George's Cross with the naval crest in the middle of the white flag.
Overview of INS Vikrant
- The name ‘INS Vikrant’ has been used previously for India’s first aircraft carrier acquired from the UK, which was decommissioned in 1997.
- INS Vikrant has been designed and developed by the Indian Navy's Warship Design Bureau and built by Cochin Shipyard Limited.
- It is the largest ship ever built-in maritime history of India, equipped with state-of-the-art automation features.
Operational Capability of INS Vikrant
- INS Vikrant can accommodate an air wing consisting of 30 aircraft, including fixed-wing and rotary aircraft.
- It is capable of undertaking various operations such as Air Interdiction, Anti-Surface Warfare, and Airborne Early Warning.
- The ship can operate MiG-29K fighter jets, Kamov-31, MH-60R multi-role helicopters, Advanced Light Helicopters, and Light Combat Aircraft.
Importance and Need for INS Vikrant:
- With INS Vikrant, India joins the elite group of nations that can design and build an aircraft carrier indigenously.
- It is an example of India’s ‘Atma Nirbhar Bharat’ and ‘Make in India Initiative’ with more than 76% indigenous content.
- The commissioning of INS Vikrant is significant amid India’s bid to be a net security provider in the Indian Ocean region and upholder of Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs) where it faces China.
- India needs at least three carriers considering the current geopolitical and strategic importance along the maritime domain.
- Naval forces can use INS Vikrant for dispensing humanitarian relief and disaster relief in peacetime.
Conclusion:
- India's stake in the IOR is greater than in the high Himalayas.
- The Navy shall be organized, trained, and equipped for the peacetime promotion of national security interests and prosperity of India and for prompt combat incidents to operations at Sea.
BrahMos Missiles
Why in news:
- The Ministry of Defense signed a contract to buy BrahMos missiles for the Indian Navy.
About:
- BrahMos is an Indo-Russian joint venture missile.
- It is a two-stage missile with a range of 290 km and a top speed of Mach 2.8.
- It can be launched from land, air, and sea with pinpoint accuracy.
- It operates on the "Fire and Forgets" principle.
Significance of the Deal:
- Induction of these missiles will significantly enhance the operational capability of the Indian Navy fleet.
- This contract will provide a boost to indigenous production of the critical weapon system.
- BrahMos missiles are expected to enhance ammunition with the active participation of indigenous industry.
Dual Role Capability:
- BrahMos missiles can be used for land as well as anti-ship attacks.
- All three variants are in service in the Indian armed forces.
Recent Developments:
- In April 2022, an anti-ship version of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile was successfully test-fired.
- In January 2022, an extended range sea-to-sea variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile was test fired from stealth guided missile destroyer INS Visakhapatnam.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|














