International Relations - 2 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Iran Nuclear Deal Talks |

|
| Indian Uzbekistan Relations |

|
| India Maldives Relations |

|
| Critical Minerals Alliance |

|
| Kyrgyzstan-Tajikistan Conflict |

|
| India - Saudi Arabia Relations |

|
Iran Nuclear Deal Talks
In their latest meeting, officials from Iran and other countries gathered in Vienna to discuss the revival of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), which is also referred to as the 2015 nuclear deal. This marked the first time they have met since March 2022.
What is the Iran Nuclear Deal?
- Overview: The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) aims to ensure that Iran's nuclear program remains peaceful in exchange for lifting of sanctions.
- Signatories: The JCPOA was signed by Iran, the US, Russia, France, China, the United Kingdom, Germany, and the European Union.
- Iran's obligations: Under the deal, Iran agreed to reduce its stores of centrifuges, enriched uranium, and heavy-water, which are all essential for developing nuclear weapons. Iran also agreed to allow inspectors from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to access its nuclear sites.
Issues
- US withdrawal: The US withdrew from the JCPOA in 2018 under the former President Donald Trump and reimposed sanctions on Iran.
- Iran's backtracking: Due to the US sanctions, Iran failed to meet its obligations under the JCPOA, including exceeding the uranium enrichment rate of 3.67%, reaching 20% in early 2021, and even crossing the 60% threshold, which is getting closer to the 90% needed for making a bomb.
- Opposition: Israel and Saudi Arabia opposed the JCPOA, with Israel rejecting it altogether and Saudi Arabia expressing its concern for regional security.
What is the significance of JCPOA for India?
- Enhance regional connectivity: Lifting of sanctions could revive India's interest in Chabahar and Bandar Abbas ports, along with other regional connectivity plans. This will help India neutralize China's presence in the Gwadar port, Pakistan. India's interest in the International North-South Transit Corridor (INSTC), which runs through Iran, and will improve connectivity with five Central Asian republics, may also get a boost.
- Energy security: Under the US Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA), India has been forced to reduce oil imports from Iran to zero. Restoring ties between the US and Iran could help India to procure cheap Iranian oil, which will aid in energy security.
Way Forward
- US considerations: The US needs to consider not only Iran's nuclear program but also its aggressive behavior in the region. Additionally, it must recognize the new multipolar world where unilateral leadership is no longer guaranteed.
- Iran's considerations: Iran must consider the evolving dynamics in the Middle East as Israel has recalibrated its relations with several Arab countries in recent years.
Indian Uzbekistan Relations
Context:
- Union Minister for Commerce & Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, and Textile emphasized the importance of India-Uzbekistan relations in India's vision of an integrated extended neighborhood.
- The year 2022 is significant for India-Uzbekistan relations as both nations are celebrating 30 years of diplomatic relations.
- The Union Minister made these remarks while addressing the 13th session of the India-Uzbekistan Inter-governmental Commission (IGC) held in New Delhi.
India-Uzbekistan Relations: Areas of Cooperation
- The Minister highlighted the need to identify new drivers for ambitious growth in bilateral trade between India and Uzbekistan.
- He emphasized the importance of an integrated approach for regional connectivity and cooperation.
- The Minister underlined seven emerging areas of cooperation between India and Uzbekistan, which are:
- Digital Payments
- Space Cooperation
- Agri and Dairy
- Pharma
- Gems and Jewellery
- MSME
- Inter-regional cooperation
- Despite the challenges posed by Covid-19, interactions and trade have increased between the two nations in recent years.
- The bilateral trade between India and Uzbekistan increased from $247 million in 2019-20 to $342 million in 2021-22, representing a growth of 38.5%.
Historical Background:
- India recognized Uzbekistan's state sovereignty after its independence and signed the protocol on establishment of diplomatic relations in Tashkent on 18 March 1992.
Virtual Summit:
- In December 2020, a Virtual Summit was held between the Prime Minister of India and President Mirziyoyev of Uzbekistan.
- Bilateral relations now cover a wider range of issues including political, strategic, defence and security, trade and investment, energy, agriculture, S&T, education, and people-to-people ties.
Bilateral Mechanisms:
- Regular high-level visits/meetings, regional exchanges, parliamentary exchanges, bilateral and multilateral mechanisms, national coordination committees, inter-governmental commission, foreign office consultations, joint working group on counter-terrorism, India-Central Asia Business Council, India-Central Asia Dialogue.
Defence and Security Cooperation:
- The first-ever joint military exercise 'Dustlik' between India and Uzbekistan was inaugurated by the Raksha Mantri in 2019.
- India has assisted in setting up an India Room at the Armed Forces Academy of Uzbekistan in Tashkent.
- India and Uzbekistan share common perspectives on security issues including terrorism, trans-national organized crime, illegal trafficking, and smuggling.
Bilateral Trade and Investments:
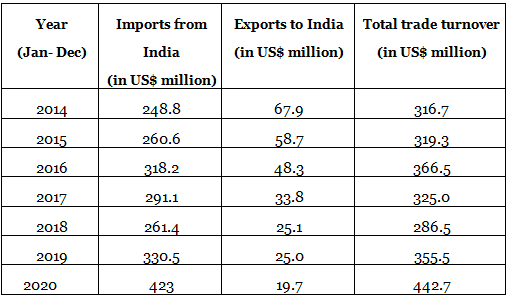
- Bilateral trade is well below potential at about USD 442 million (as per Uzbek statistics).
- India's major exports to Uzbekistan are pharmaceutical products, mechanical equipment, vehicle parts, services, optical instruments, and equipment.
- India's imports from Uzbekistan consist mainly of fruit and vegetable products, services, fertilizers, juice products and extracts, and lubricants.
Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) and Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT)
- Joint Statement in September 2019 to set up a joint feasibility study for a PTA
- BIT under negotiation between both countries
Development Assistance:
- Line of Credit Agreement for USD 200 million for construction of affordable housing and social infrastructure projects
- Joint Centre for Information Technology and India-Uzbekistan Entrepreneurship Development Centre (EDC)
- India offered grant assistance for High Impact Community Development Projects
Education and Culture:
- Uzbekistan sending candidates under the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) programme since 1993
- Indian Study Centre established at Samarkand State University
- Growing interest in co-production and organization of film festivals; Indian films, actors, and songs popular
- Regular visits of cultural troupes from both sides
Diaspora:
- Around 1800 Indian nationals living in Uzbekistan
- Mostly involved in pharmaceutical and hospitality businesses, teaching, and oil and gas sector
Bilateral Relations and Exchanges:
- India was one of the first countries to recognize the state sovereignty of Uzbekistan
- Virtual Summit held between PM and President Mirziyoyev in December 2020
- Regular High Level visits/meetings, Regional Exchanges, Parliamentary Exchanges
- Bilateral and multilateral Mechanisms
- National Coordination Committees
- Inter-Governmental Commission
- Foreign Office Consultations
- Joint Working Group on Counter Terrorism
- India-Central Asia Business Council
- India- Central Asia Dialogue
Defence and Security Cooperation:
- First-ever joint military exercise 'Dustlik' held in 2019
- India assisted in setting up an India Room at the Armed Forces Academy of Uzbekistan
- Common perspectives on security issues including terrorism, trans-national organized crime, illegal trafficking, and smuggling
Bilateral Trade and Investments:
- Bilateral trade at USD 442 million (as per Uzbek statistics)
- Major items of India's exports are pharmaceutical products, mechanical equipment, vehicle parts, services, optical instruments and equipment
- India's import from Uzbekistan consist largely of fruit and vegetable products, services, fertilizers, juice products and extracts, and lubricants.
India Maldives Relations
Why in news:
- Indian PM held talks with Maldives President during the latter's visit to India.
- PM stressed the significance of defense and security cooperation between India and Maldives.
- Importance of maintaining peace and stability in the Indian Ocean highlighted due to threats of transnational crime, terrorism, and drug trafficking.
Outcomes of Bilateral Talks between India and Maldives
Security Cooperation:
- India will provide assistance to counter the threats of transnational crime, terrorism and drug trafficking in the Indian Ocean region
- 24 vehicles and one naval boat to be given to Maldives Security Force
- India to help train Maldives' security personnel
- India to cooperate in building police facilities in 61 islands of Maldives
Greater Male Connectivity Project:
- India-funded USD 500 million project welcomed by both leaders
- Both leaders participated in virtual ceremony of “pouring of the first concrete”
- Project includes grant and concessional loan support from India
Agreements Signed:
- Six agreements signed to expand cooperation in various areas including cybersecurity, capacity building, housing, disaster management and infrastructure development
- India to provide USD 100 million financial aid to help Maldives complete certain infrastructure projects.
India-Maldives Relations
Overview:
- India and Maldives share a close relationship due to geographical proximity, cultural affinities, and economic interdependence. India has always been a major player in the Maldives, helping it in various development projects and maintaining security and stability in the region.
Achievements
- Security Partnership:
- India and Maldives have been working closely to counter the threats of transnational crime, terrorism, and drug trafficking in the Indian Ocean region. In this regard, India has provided the Maldives Security Force with 24 vehicles and a naval boat, and has also helped in training the island-nation's security personnel. India has also cooperated in building police facilities in 61 islands of Maldives.
- Rehabilitation Centre:
- India has built a drug detoxification and rehabilitation centre in Addu with Indian assistance, which is one of 20 high impact community development projects being implemented by India in areas such as healthcare, education, fisheries, tourism, sports and culture.
- Economic Cooperation:
- India is Maldives' second-largest trading partner, and the two countries have been working to expand cooperation in various sectors. The Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP), a USD 500 million project funded by India, has been signed by Afcons, an Indian company, and is the largest-ever infrastructure project in Maldives. India has also announced USD 100 million financial aid to help the island-nation complete certain infrastructure projects.
Challenges
- Political Instability:
- India's major concern has been the impact of political instability in the neighbourhood on its security and development. The arrest of Maldives' opposition leader Mohamed Nasheed on terrorism charges in 2015 and the consequent political crisis have posed a real diplomatic test for India's neighbourhood policy.
- Radicalisation:
- The number of Maldivians drawn towards terrorist groups like the Islamic State (IS) and Pakistan-based jihadist groups has been increasing in the past decade, raising the possibility of Pakistan based terror groups using remote Maldivian islands as a launch pad for terror attacks against India and Indian interests.
- China Angle:
- China's strategic presence in the Maldives has increased, and the country has emerged as an important 'pearl' in China's “String of Pearls” construct in South Asia. This has been a concern for India due to the uncertain dynamics of Sino-Indian relations, and the Maldives using the China card to bargain with India.
Overall, India and Maldives have been working together to overcome these challenges and strengthen their relationship in various fields.
Way Forward for India-Maldives Relations
Importance of Vigilance:
- India must not become complacent about its position and must remain attentive to developments in the Maldives.
Role in Indo-Pacific Security:
- India must play a key role in the Indo-Pacific security space to ensure regional security in South Asia and surrounding maritime boundaries.
Response to Extra-Regional Powers:
- The Indo-Pacific security space has been developed as a response to the growth of extra-regional powers, particularly China, in India's maritime sphere of influence.
'India Out' Campaign:
- Currently, the 'India Out' campaign has limited support but the Indian government cannot take this for granted.
Handling Domestic Issues:
- If issues raised by supporters of the 'India Out' campaign are not handled carefully and India is unable to convince Maldivians of its intentions behind projects on the island nation, the campaign may change the domestic political situation in the Maldives and may have an impact on India's relationship with the country.
Critical Minerals Alliance
Why in news:
- Indian Government is worried about not being included in the Minerals Security Partnership.
- The Minerals Security Partnership is a new partnership led by the US to secure supply chains of critical minerals and reduce dependence on China.
- The partnership aims to ensure the availability of critical minerals, which are crucial for clean energy and other advanced technologies.
- The demand for these minerals is projected to grow significantly in the coming decades, highlighting the importance of securing their supply chains.
Critical Minerals and the Minerals Security Partnership
Introduction:
- Critical minerals are essential elements used in modern technologies and are at risk of supply chain disruptions. The Minerals Security Partnership is a US-led initiative aimed at securing the supply chains of critical minerals.
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical minerals are used in various applications, including mobile phones, computers, batteries, electric vehicles, and green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Aerospace, communications, and defense industries also rely on several critical minerals as they are used in manufacturing fighter jets, drones, radio sets, and other critical equipment. Cobalt, nickel, lithium, and rare earth minerals are some of the major critical minerals.
Significance of Critical Minerals:
- As countries transition towards clean energy and digital economy, critical resources are vital to fuel this change. Any supply shock can severely imperil the economy and strategic autonomy of a country that is over-dependent on others to procure critical minerals.
What is Minerals Security Partnership (MSP)?
- The Minerals Security Partnership is an initiative by the United States aimed at bolstering critical mineral supply chains. It includes the partnership of several countries, including Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Sweden, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the European Commission.
Objective of MSP:
- The objective of MSP is to ensure that critical minerals are produced, processed, and recycled in a manner that supports the ability of countries to realize the full economic development benefit of their geological endowments. The partnership focuses on the supply chains of minerals such as cobalt, nickel, lithium, and rare earth minerals.
Significance of MSP:
- The Minerals Security Partnership will help catalyze investment from governments and the private sector for strategic opportunities across the full value chain that adhere to the highest environmental, social, and governance standards.
India's Concerns with Exclusion from MSP
Supply of Critical Minerals:
- India's growth strategy relies on the shift to electric vehicles and electronics manufacturing.
- This underscores the need to secure the supply of critical minerals.
- Rare earth elements (REE) are essential in this shift.
Dependency on Other Countries:
- India has some REE such as Lanthanum, Cerium, Neodymium, Praseodymium, and Samarium.
- However, REE classified as heavy (HREE) such as Dysprosium, Terbium, and Europium are not available in extractable quantity in India.
- India would require support from other countries for such elements.
Technology Status:
- Experts say that India lacks the technology and expertise in extracting and processing REE.
- Countries like Australia, Canada, and Japan have reserves and technology in this area.
Implications of Exclusion from MSP:
- Exclusion from the MSP could result in a lack of access to critical minerals for India's growth strategy.
- India's dependence on other countries for critical minerals could compromise its energy security and economic growth.
India's Efforts to Secure Critical Minerals
Lithium Agreement:
- In 2020, India signed an agreement with an Argentinian firm to jointly prospect lithium.
- Argentina has the third-largest reserves of lithium in the world.
- The agreement was made through a newly floated state-owned company.
India-Australia Critical Minerals Investment Partnership:
- India and Australia have partnered to strengthen their supply chains for critical minerals.
- Australia has the resources to help India meet the growing demand for critical minerals.
- This partnership will support India's ambitions to lower emissions and boost its space and defense industries.
- Critical minerals will also be essential in the manufacture of solar panels, batteries, and electric vehicles.
Implications of India's Efforts:
- India's efforts to secure critical minerals will help reduce its dependence on other countries.
- These efforts will strengthen India's energy security and promote its economic growth.
- Increased access to critical minerals will also support India's transition to a more sustainable economy.
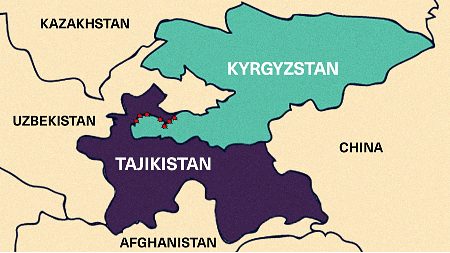
Kyrgyzstan-Tajikistan Conflict
Why in news:
Factors Behind the Kyrgyzstan-Tajikistan Clash
Historical Legacy:
- The current clashes between Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan have their roots in pre- and post-Soviet era legacies.
- The borders of the two republics were demarcated during Joseph Stalin's leadership.
- The creation of the Soviet Union saw the redistribution of livestock to collective and state farms, which disrupted existing resource-sharing arrangements.
Common Rights over Natural Resources:
- Historically, the Kyrgyz and Tajik populations shared common rights over natural resources.
- This was disrupted by Soviet-era policies.
Present Tussle:
- Recent incidents saw groups from both sides planting trees in disputed areas and engaging in physical confrontations.
- The Ferghana Valley remains a site of struggle, with Tajiks, Kyrgyz, and Uzbeks sharing the region.
- Conflicts arise every year during the crucial irrigation period due to the shared water channels between the two countries.
- Approximately 471 kilometers of the 971 kilometers of the border territory remain in dispute.
- Leaders of both countries have contributed to the conflict by displacing nomadic communities to stabilize internal dynamics and legitimize their power.
Implications of the Clash:
- The border clashes between the two countries have resulted in loss of lives and injuries.
- The ongoing conflict has disrupted the lives and livelihoods of communities on both sides of the border.
- The conflict highlights the need for a resolution to the border disputes to ensure peace and stability in the region.
India-Tajikistan Relations: A Overview
Cooperation in International Forums:
- Tajikistan extended support for India’s candidature for a non-permanent seat in the United Nation Security Council for the term 2021-22.
- Tajikistan strongly supported India's membership in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO).
- India supported Tajikistan's candidature to the United Nations' Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) and accession to WTO in March 2013.
Development & Aid Partnership:
- India provided a grant of USD 0.6 million for the commissioning of an Information and Technology Centre (Bedil Centre) in 2006.
- India completed a project for setting up computer labs in 37 schools in Tajikistan in August 2016.
- India provided humanitarian assistance in the form of cash and vaccines after floods and the outbreak of Polio in Tajikistan.
- Tajikistan has been a beneficiary of the Indian Technical & Economic Cooperation Programme (ITEC) since the establishment of the Indian embassy in Dushanbe in 1994.
Trade & Economic Relation:
- Indian exports to Tajikistan include pharmaceuticals, medical preparations, cane or beet sugar, tea, handicraft, and machinery.
- Tajikistan's market for Indian pharmaceutical products is approximately 25%.
Cultural & People-to-People Relation:
- Deep rooted historical and cultural linkages between the two countries have expanded and widened their relationship to a new level.
- Cooperation between the two countries encompasses all aspects of human endeavour with a special focus on military and defence ties.
- The Swami Vivekananda Cultural Centre in Dushanbe offers courses in Kathak & Tabla, Sanskrit, and Hindi language classes.
- In 2020, Tajikistan participated in the 'My Life My Yoga' video blogging competition.
Strategic:
- India has an airbase at a place called Ayni, about thirty kilometres from Dushanbe, which developed into an Indian Air Force (IAF) base known as Gissar Military Aerodrome (GMA).
Way forward
- Agree upon a common map to resolve the dispute.
- Involve elders from both communities to resolve the conflict, as historically they have been effective in resolving disputes.
- In addition, it is recommended that the international community take steps to help resolve the conflict by engaging with the warring groups and encouraging dialogue towards a peaceful solution.
India - Saudi Arabia Relations
Why in news:
- India and Saudi Arabia have been engaging in discussions to finalize a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT) that would allow both countries to seek formal assistance from one another during investigations into criminal cases.
India's MLATs with other countries and Saudi Arabia's status
India's MLATs:
- India has signed MLATs with 45 countries.
- India is in talks to finalise MLATs with Italy and Germany.
Saudi Arabia's Status:
- Saudi Arabia does not have an MLAT or any other bilateral agreement with India to facilitate investigations related to criminal cases.
- India is in talks with Saudi Arabia to sign an MLAT for formal assistance in such investigations.
What is Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT)?
- MLAT is a mechanism of gathering and exchanging information among countries to enforce public or criminal laws.
- Ministry of Home Affairs is India's Central Authority for mutual legal assistance requests.
- It ensures cooperation between countries for the prevention, suppression, investigation, and prosecution of crime.
Significance of MLAT:
- The signing of MLAT would enable India and Saudi Arabia to obtain formal assistance in investigations related to criminal cases.
- MLATs are used to send a formal request for investigation in foreign countries for evidence collection and examination of witnesses.
- The treaty helps in getting a conviction for an accused in a court of law based on evidence gathered through mutual agreement.
- In the past, Saudi Arabia has deported several terror suspects on India's request, indicating the potential impact of a formal MLAT between the two countries.
India-Saudi Arabia Bilateral Relations
Political Relations:
- Diplomatic relations between India and Saudi Arabia were established in 1947.
- The Delhi Declaration signed in 2006 during King Abdullah's visit to India boosted bilateral ties.
Commercial Relations:
- Saudi Arabia is India's fourth-largest trade partner and a significant source of energy.
- In FY22, bilateral trade was valued at US$29.28 billion.
Cultural Relations:
- India participated in the 32nd Saudi National Festival of Heritage and Culture in 2018 as a guest of honour.
- Yoga was recognized as a sports activity in Saudi Arabia.
Military Exercise:
- AL - Mohed AL - Hindi is the first naval exercise between India and Saudi Arabia.
Diaspora:
- The Indian community in Saudi Arabia is the largest expatriate community, with around 2.2 million Indians.
Need for Cooperation:
- Saudi Arabia's position on the developments in Afghanistan is significant, as several countries in the Gulf region, including Qatar and Iran, play a role in the country's development.
- Economic reform programs in Saudi Arabia require India's economic and technological assistance.
- Saudi Arabia plays an essential role in India's energy security, while India is a vital partner in Saudi Arabia's food security.
- Saudi investment of around $100 billion is in the pipeline in areas ranging from energy, refining, petrochemicals and infrastructure to agriculture, minerals and mining.
- India's expertise in fighting threats like Houthi militias could be imparted to Saudi Arabia by enhancing joint military training programs.
Challenges:
- The politics of the Middle East is complex and multidimensional, requiring a collective and united effort.
- The Saudi Arabia-Turkey rivalry could create problems for India.
- India is yet to balance its ties with Iran on the one hand and Saudi Arabia and the United States on the other.
Future Prospects:
- The defence collaboration between India and Saudi Arabia is progressing swiftly amid the fast-changing dynamics in the Gulf region.
- This will not only strengthen the bilateral partnership but also improve the security situation in the Indian Ocean Region.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|



















