Introduction of Photorespiration | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Photorespiration
Photorespiration is a plant metabolic process that primarily occurs in the cells of the leaves. It is considered a wasteful pathway that competes with photosynthesis, potentially impacting plant growth and productivity. This process is triggered under conditions where the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) is low and the concentration of oxygen (O2) is high.
What is Photorespiration?
Photorespiration is a metabolic process that occurs during the Calvin cycle, also known as the C2 Cycle. The enzyme RuBisCO plays a significant role in photorespiration. This process is particularly important in C3 plants as a mechanism to manage the inefficiencies of RuBisCO.
During photorespiration, oxygen (O2) is utilized, and carbon dioxide (CO2) is released in the presence of light. It shares similarities with the process of respiration, where O2 is consumed, and CO2 is produced.
Organelles involved in Photorespiration
Three cell organelles are implicated in photorespiration:
- Chloroplast
- Peroxisomes
- Mitochondria
Photorespiration is the Wasteful Product
- When the level of CO2 surrounding the cell drops, photorespiration is initiated.
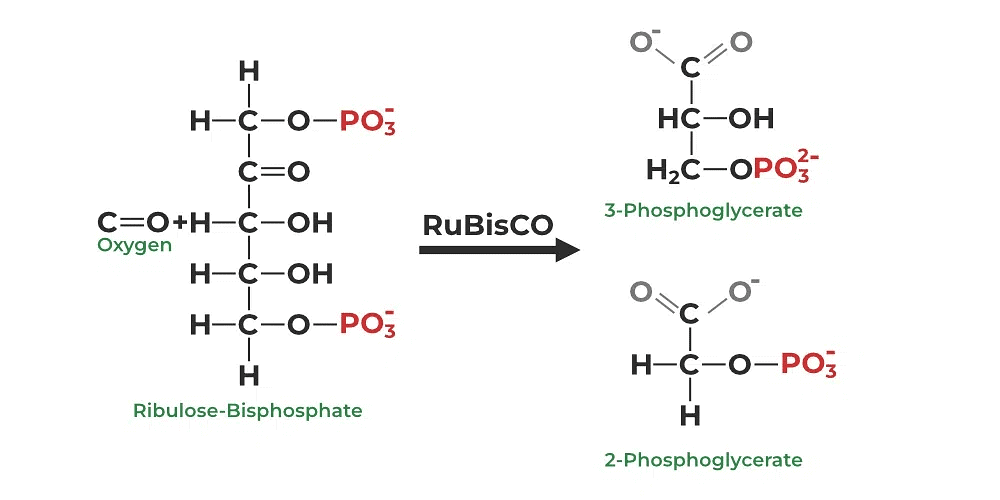
- Photorespiration commences with the oxygenation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate-carboxylase/oxygenase (RUBISCO), the key enzyme responsible for CO2 fixation in nearly all photosynthetic organisms.
- Phosphoglycerate produced in the presence of oxygen is recycled in the Calvin cycle amidst phosphoglycerate in the Photorespiratory pathway.
- This process consumes excess energy and diminishes the yields, with a portion of the previously fixed carbon being released as CO2.
- Consequently, photorespiration has often been viewed as an inefficient process.
- In photorespiration, oxygen binds with the enzyme Rubisco, yielding 3-Phosphoglycerate in a reduced setting and requiring substantial energy expenditure.
Factors influencing Photorespiration
- In submerged, stressful conditions, higher light intensity leads to increased photorespiration.
- Temperature plays a significant role in influencing photorespiration.
Benefits of Photorespiration
- Photorespiration contributes to plant defense mechanisms, enhancing their resilience.
- It aids in maintaining the redox balance within the cell.
Significance of Photorespiration
- Photorespiration acts as the opposite process of photosynthesis.
- It reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis.
- Photorespiration is an inefficient cycle since it does not produce ATP or NADPH.
|
150 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction of Photorespiration - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is photorespiration? |  |
| 2. Why does photorespiration occur? |  |
| 3. How does photorespiration affect plant growth? |  |
| 4. Can plants adapt to reduce photorespiration? |  |
| 5. What environmental factors can influence photorespiration? |  |
















