Introduction to Chemical Bonding | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Chemical Bonding |

|
| Types of Chemical Bonds |

|
| Important Theories on Chemical Bonding |

|
| Kossel’s theory of Chemical Bonding |

|
| Resonance in Chemical Bonding |

|
Chemical Bonding
The attractive force which holds various constituents (atom, ions, etc.) together and stabilizes them by the overall loss of energy is known as chemical bonding.
- Therefore, it can be understood that chemical compounds are reliant on the strength of the chemical bonds between their constituents.
- The stronger the bonding between the constituents, the more stable the resulting compound would be.
- Whenever matter interacts with another form of matter, a force is exerted on one by the other. When the forces are attractive in nature, the energy decreases.
- When the forces are repulsive in nature, the energy increases. The attractive force that binds two atoms together is known as the chemical bond.
Types of Chemical Bonds
Each element in-universe has a tendency to acquire stability (state of minimum energy). That is done by combining one atom with another leading to the formation of a compound.
- There are 5 primary types of chemical bonds which are formed by atoms or molecules to yield compounds.
- The type of chemical bonds formed vary in strength and properties and are formed from the loss, gain, or sharing of electrons between two atoms/molecules. These types of chemical bonds include:
- Ionic Bonds
- Covalent Bonds
- Hydrogen Bonds
- Polar Bonds
- Coordinate Bonds
1. Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding which involves a transfer of electrons from one atom or molecule to another.
- Here, an atom loses an electron which is in turn gained by another atom. When such an electron transfer takes place, one of the atoms develops a negative charge and is now called the anion. The other atom develops a positive charge and is called the cation.
- The ionic bond gains strength from the difference in charge between the two atoms, i.e. the greater the charge disparity between the cation and the anion, the stronger the ionic bond.
- So, Electron transfer gives rise to an ionic bond via the formation of anion and cation. Force of attraction is electrostatic interaction.
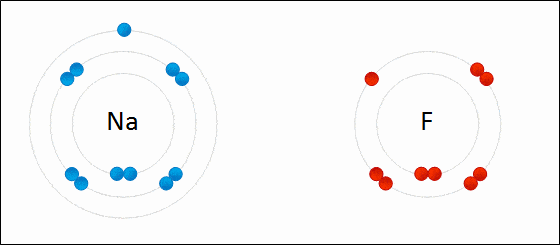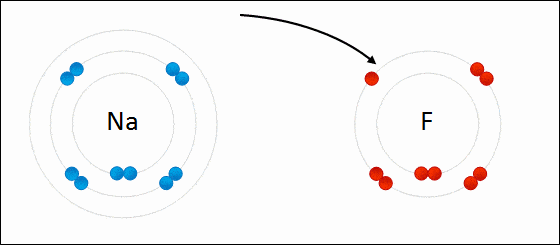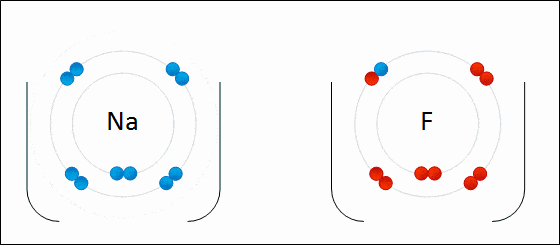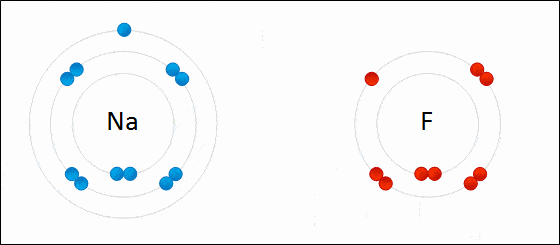 Ionic Bond
Ionic Bond
2. Covalent Bond
A covalent bond indicates the sharing of electrons between atoms.
- Compounds that contain carbon (also called organic compounds) commonly exhibit this type of chemical bonding.
- The pair of electrons which are shared by the two atoms now extend around the nuclei of atoms, leading to the creation of a molecule.
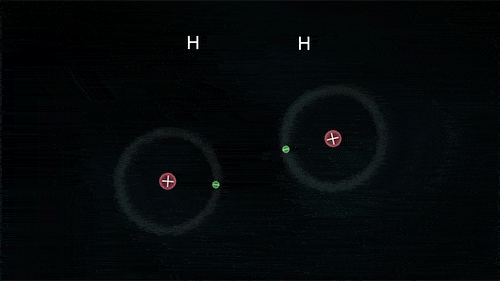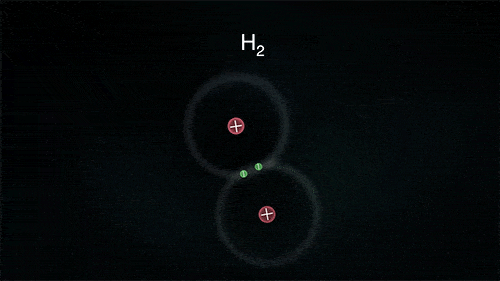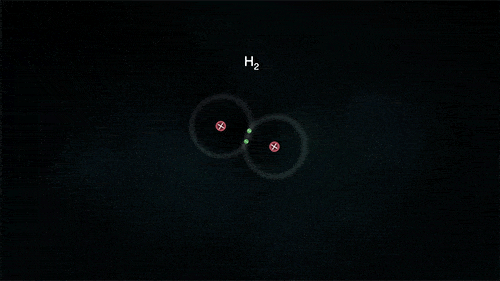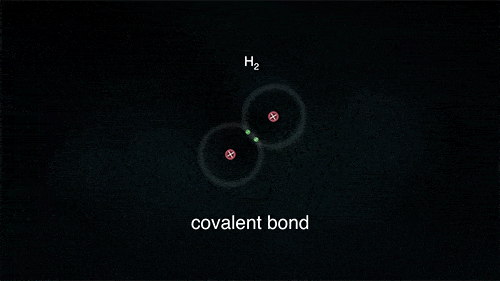 Covalent Bond
Covalent Bond
3. Hydrogen Bonding
It is a type of polar covalent bonding between oxygen and hydrogen wherein the hydrogen develops a partial positive charge.
- This implies that the electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative oxygen atom.
- This creates a tendency for the hydrogen to be attracted towards the negative charges of any neighboring atom.
- This type of chemical bonding is called a hydrogen bond and is responsible for many of the properties exhibited by water.
- Compared to ionic and covalent bonding, Hydrogen bonding is a weaker form of chemical bonding.
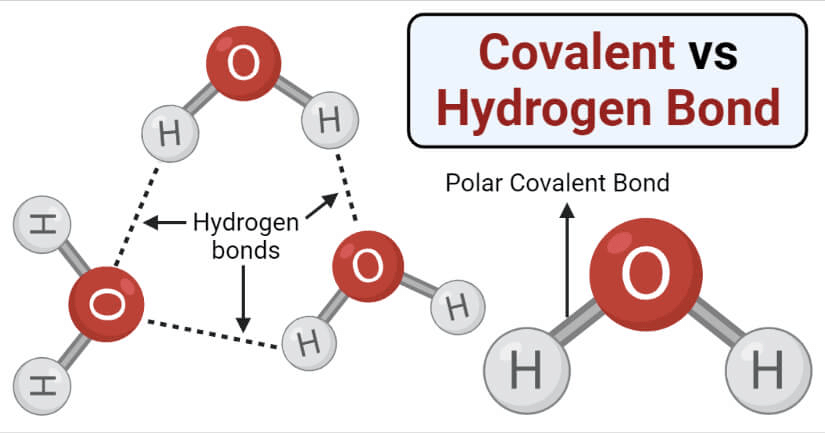
4. Polar Bonding
In Polar Covalent chemical bonding, electrons are shared unequally since the more electronegative atom pulls the electron pair closer to itself and away from the less electronegative atom.
- Water is an example of such a polar molecule.
- Covalent bonds can be either be Polar or Non-Polar in nature.
- A difference in charge arises in different areas of the atom due to the uneven spacing of the electrons between the atoms.
- One end of the molecule tends to be partially positively charged and the other end tends to be partially negatively charged.
5. Special Case: Coordinate Bond
The bond formed between two atoms in which contribution of an electron pair is made by one of them and the sharing is done by both.
For the formation of a coordinate bond, it is necessary to have at least one covalent bond in the compound.
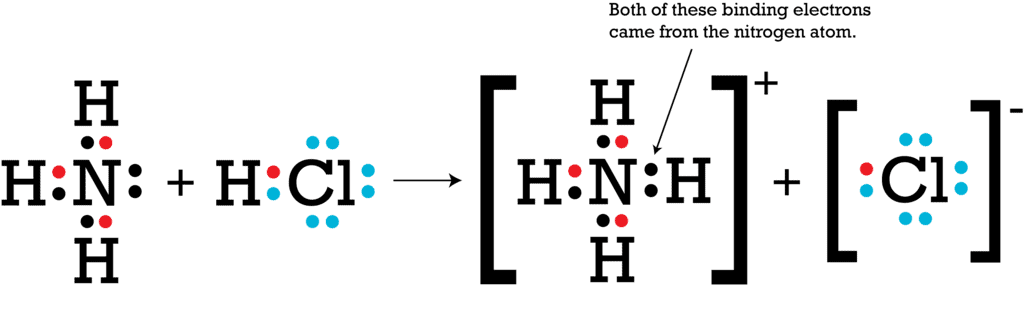 Coordinate Bond
Coordinate Bond
Important Theories on Chemical Bonding
Albrecht Kössel and Gilbert Lewis were the first to explain the formation of chemical bonds successfully in the year 1916. They explained chemical bonding on the basis of the inertness of noble gases.
1. Lewis Theory of Chemical Bonding & Octet Rule
Lewis's most important ideas were the rule of two (the electron pair), including the essential concept that a single bond consists of a pair of electrons shared between the valence shells of the two bonded atoms, and the rule of eight (the octet rule).
- An atom can be viewed as a positively charged ‘Kernel’ (the nucleus plus the inner electrons) and the outer shell.
- The outer shell can accommodate a maximum of eight electrons only.
- The eight electrons present in the outer shell occupy the corners of a cube that surround the ‘Kernel’.
- The atoms having an octet configuration, i.e. 8 electrons in the outermost shell, thus symbolize a stable configuration.
- Atoms can achieve this stable configuration by forming chemical bonds with other atoms. This chemical bond can be formed either by gaining or losing an electron(s) (NaCl, MgCl2) or in some cases due to the sharing of an electron (F2).
- Only the electrons present in the outer shell, also known as the valence electrons take part in the formation of chemical bonds. Gilbert Lewis used specific notations better known as Lewis symbols to represent these valence electrons.
- Generally, the valency of an element is either equal to the number of dots in the corresponding Lewis symbol or 8 minus the number of dots (or valence electrons).
Rules for Drawing Lewis Structures
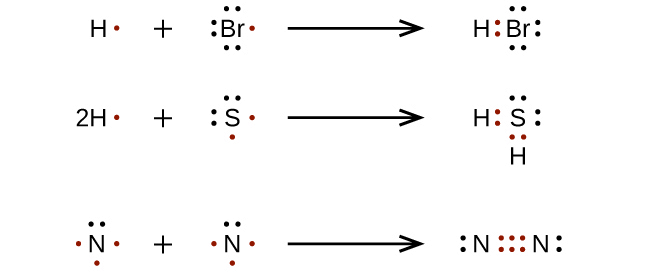
- Calculate n1 = no. of valence shell electrons of all atoms + no. of negative charge (if any) – no. of positive charge (if any)
- Calculate n2 = (no. of H-atom × 2) + (no. of atoms other than H-atoms × 8)
- Calculate n3 = n2 – n1 ⇒ no. of shared electrons.
i.e. No. of bonds =.......(a)
- Calculate n4 = n1 – n3 ⇒ no. of unshared electrons.
i.e. no. of lone pairs =.......(b)
Using the information (a) & (b) the structure is to be assigned as follows :
- Find out the central atom first (i.e. either least in number or more electropositive)
- Allocate the surrounding atoms around the central atom with the help of bonds available in (a).
- To fulfill the octet of each atom, utilize the lone pairs available in (b).
- Finally, calculate the formal charge for each atom and assign the atoms according to the formula given
F.C. (on an atom) = Valence shell electron of that atom – no. of bonds associated with it – no. of unshared electrons on it.
Formal Charge
- The formal charge is the charge which an atom would have if electron pairs were shared equally.
- Lewis structures with low formal charges typically have the lowest energy.
- Formal charge of an atom is the difference between the number of valence electrons in an isolated atom (i.e. free atom) and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in a Lewis structure.
- Example:
The Octet Rule
The octet rule dictates that atoms are most stable when their valence shells are filled with eight electrons.
- It is based on the observation that the atoms of the main group elements have a tendency to participate in chemical bonding in such a way that each atom of the resulting molecule has eight electrons in the valence shell.
- The octet rule is only applicable to the main group elements.
- The molecules of halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon are known to obey the octet rule. In general, the elements that obey this rule include the s-block elements and the p-block elements (except hydrogen, helium, and lithium).
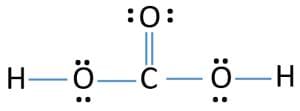
- The octet rule can be observed in the bonding between the carbon and oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule, as illustrated via a Lewis dot structure below.
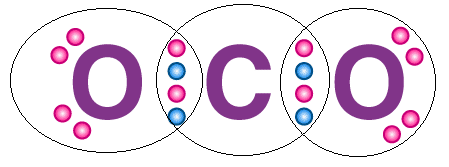 Complete octet of CO2
Complete octet of CO2
Deviation from the Octet Rule
- A number of cases are known where the combining species or atoms have less than eight (i.e. incomplete octet) or, more than eight (i.e. expansion of octet) electrons in the covalently bonded molecules.
Incomplete Octet
- In the molecules such as BeCl2, BCl3, and NO (: N g = O), the central atoms, i.e. Be, B and N bear four, six, and seven electrons respectively.
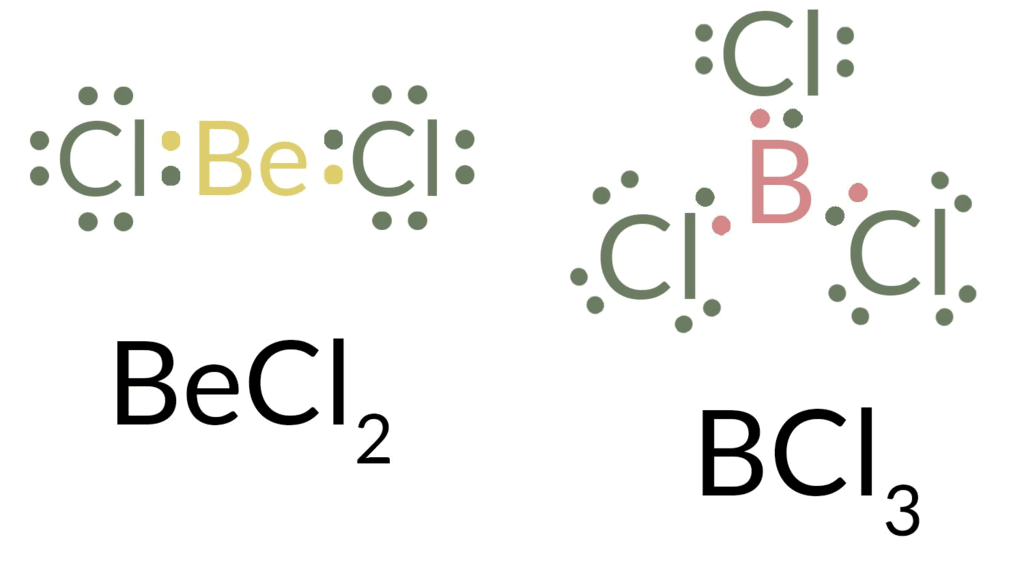
- Here it is noteworthy that other atoms except the central one in the above compounds follow the octet rule. As a matter of fact, a large number of compounds formed by Be (quartered), M (sextet) where M = B, Al, Ga are known to have incomplete octets.
- These compounds are very often referred to as electron-deficient compounds characterized by a profound tendency to receive back a lone pair (for Gr 13 or III-A elements, e.g. B, Al, Ga, etc.) or two lone pairs (for Gr 2 or II A elements, e.g. Be) to attain the octet. This is why the electron-deficient compounds act as Lewis acids.
Expansion of Octet
- In the compounds like PCl5, ClF3, SF6, SiF62– etc. the central elements, i.e. P, Cl, S, and Si, are bearing ten, ten, twelve, and twelve electrons respectively to display the expansion of octet.
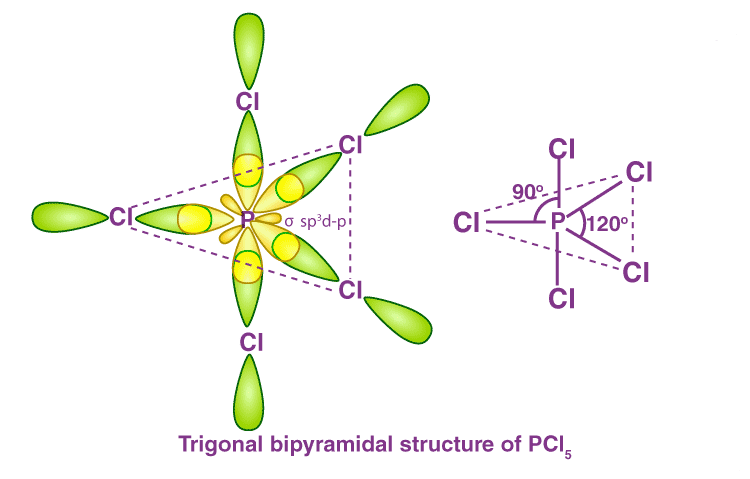
- Similarly, in OsF8, there are sixteen electrons around Os. Here also, except for the central atoms, all other atoms satisfy the octet rule.
Kossel’s theory of Chemical Bonding
- Noble gases separate the highly electronegative halogens and the highly electropositive alkali metals.
- Halogens can form negatively charged ions by gaining an electron. Whereas alkali metals can form positively charged ions by losing an electron.
- These negatively charged ions and positively charged ions have a noble gas configuration that is 8 electrons in the outermost shell. The general electronic configuration of noble gases (except helium) is given by ns2np6.
- As unlike charges attract each other these unlike charged particles are held together by a strong force of electrostatic attraction existing between them. For example, MgCl2, the magnesium ion, and chloride ions are held together by the force of electrostatic attraction. This kind of chemical bonding existing between two unlike charged particles is known as an electrovalent bond.
Explanation of Kossel Lewis Approach
In 1916 Kossel and Lewis succeeded in giving a successful explanation based upon the concept of an electronic configuration of noble gases about why atoms combine to form molecules.
- Atoms of noble gases have little or no tendency to combine with each other or with atoms of other elements. This means that these atoms must be having stable electronic configurations.
- Due to the stable configuration, the noble gas atoms neither have any tendency to gain or lose electrons and, therefore, their combining capacity or valency is zero.
- They are so inert that they even do not form diatomic molecules and exist as monoatomic gaseous atoms.
Resonance in Chemical Bonding
- In many molecules, the choice of atoms that are connected by multiple bonds is arbitrary. When several choices exist, all of them should be drawn.
- For example, as shown in Figure, three drawings (resonance structures or canonical forms) of CO32– are needed to show the double bond in each of the three possible C–O positions.
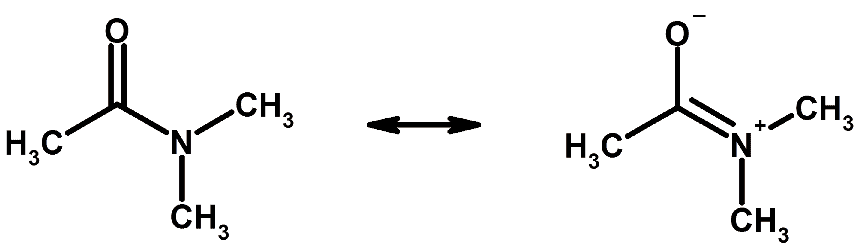 Example of resonance
Example of resonance - In fact, experimental evidence shows that all the C–O bonds are identical, with bond lengths (129 pm) between double-bond and single bond distances (116 and 143 pm, respectively); none of the drawings alone is adequate to describe the molecular structure, which is a combination of all three.
- Thus resonance signifies that there is more than one possible way in which the valence electrons can be placed in a Lewis structure. Note that in resonance structures such as those shown for CO32– in Figure, the electrons are drawn in different places but the atomic nuclei remain in fixed positions.
- The species CO32–, NO3–, and SO3 are isoelectronic (have the same electronic structure). Their Lewis diagram is identical, except for the identity of the central atom.
- When a molecule has several resonance structures, its overall electronic energy is lowered, making it more stable.
Bond Order
Bond order =
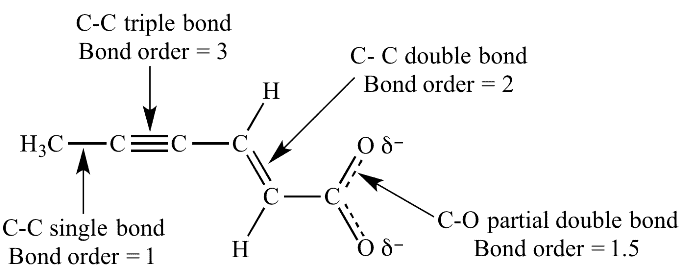
Resonance vs. Tautomerism
- The proposed canonical forms should not differ in the atomic arrangements. Only the position of the pi-electrons is changed from one position to another (generally the sigma-electrons do not get delocalized).
- Shifting of an atom leads to tautomerism, not resonance and such species are related through the equilibrium sign (
).
- Some examples of tautomerism are shown below:
(i) The nitrous acid may have two forms in equilibrium.The colored organic nitrites and some inorganic nitrites such as silver nitrite (pale yellow), mercurous nitrite (pale yellow) probably exist in nitro forms.
(ii) phosphorous acid (H3PO3) and hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) exist in tautomeric equilibria.H3PO3H3PO2(iii) Similarly, tautomerism in sulfurous acid is also reported. - All the examples of tautomerism cited above involve the shifting of a proton and this type of tautomerism is referred to as prototropic tautomerism which is very important in organic chemistry (e.g. keto-enol tautomerism.)
Important points in Resonance
- The canonical forms should have the same number of unpaired electrons.
- In the case of charge separation, if the adjacent atoms bear the same change then the electrostatic repulsion will destabilize the structure.
- The placement of opposite charges on the adjacent atoms stabilizes the system through electrostatic interaction.
- The canonical forms in which the negative charge resides on the electronegative atoms contribute more.
|
745 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Chemical Bonding - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the types of chemical bonds? |  |
| 2. What is Kossel’s theory of chemical bonding? |  |
| 3. What is resonance in chemical bonding? |  |
| 4. What are some important theories on chemical bonding? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding chemical bonding important in chemistry? |  |