Introduction to Physical Geography - Physical Geography, UPSC, IAS. | Geography (Prelims) by Valor Academy PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to Physical Geography |

|
| Chapter - 1 |

|
| Chapter - 5 |

|
| Origin of Earth |

|
Introduction to Physical Geography
Chapter - 1
Earth in the Solar System
 While watching the night sky, you may notice various patterns formed by different groups of stars. These are called constellations. Ursa Major or Big Bear is one such constellation. One of the most easily recognizable constellations in the small bear or Saptarishi (Sapta-seven, rishi-sages). It is a group of seven stars that forms a part of the large Ursa Major Constellation.
While watching the night sky, you may notice various patterns formed by different groups of stars. These are called constellations. Ursa Major or Big Bear is one such constellation. One of the most easily recognizable constellations in the small bear or Saptarishi (Sapta-seven, rishi-sages). It is a group of seven stars that forms a part of the large Ursa Major Constellation.
In ancient times, people used to determine directions during the night with the help of stars. The North Star indicates the north direction. It is also called the Pole Star. It always remains in the same position in the sky. We can locate the position of the Pole Star with the Pole Star.
Some celestial bodies do not have their own heat and light. They are lit by the light of the stars. Such bodies are called planets. The word ‘planet’ comes from the Greek word “Planetai” which means ‘wonderers’.
The earth on which we live is a planet. It gets all its heat and light from the sun, which is our nearest star.
The moon that we see in the sky is a satellite. It is a companion of our earth and moves round it. Like our earth, there are eight other planets that get heat and light from the sun. Some of them have their moons too.
The Solar System
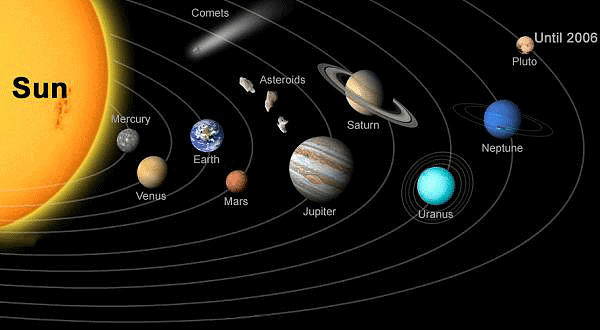
- The Sun, the nine planets (Pluto is not a planet now, considered as a dwarf planet) along with their satellites, the asteroids, the comets, the inter planetary dust, and the electrically charged gases called plasma, together make up the solar system.
- Our solar system consists of an average star we call it the Sun, the planets - Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. It also includes: the satellites of the planets: numerous comets, asteroids, and meteoroids; and the interplanetary medium.
- The Sun is an average star. It isn't the hottest, it isn't the coolest, it isn't the oldest. Nor is it brightest, biggest, etc.
- The Sun accounts for 99.85% of all the matter of the solar system.
- It is composed mainly of hydrogen and helium.
- Nuclear fusion in the core of the Sun is source of all its energy.
- The glowing surface of the Sun is called Photosphere.
- About it is red coloured Chromosphere and beyond it is Corona (visible during eclipses).
- The surface of the Sun changes continuously. Bright regions are called Plages and dark spots are called Sun spots which frequently form and disappear.
The Sun
- Our solar system's largest object is the sun. It is roughly 109 times the size of Earth.
- The Sun has a diameter of 1,392,000 kilometres. It comprises 99.8% of the mass of the solar system.
- The sun is a star with a surface temperature of 60000 degrees Celsius. It is largely made up of hydrogen gas, with a minor quantity of helium thrown in for good measure.
- The Sun is the solar system's closest star. It belongs to the Milky Way galaxy. It's thought to be more than 4 billion years old. The Sun is a yellow dwarf, a medium-sized star. As it rotates around the galaxy, the Sun spins gently on its axis.
- The Earth would be a dead sphere of rock and ice if it were not for the Sun. The Sun warms our globe, influences our weather, and provides energy to plants, which provides food and energy for life on Earth.
- The Sun's energy reaches the Earth and other planets in all directions. The planet absorbs less energy as it gets further away from the Sun.
- Distance from the Earth - 150 mn km.
Planets
- A planet must meet three criteria:
- It must orbit the Sun,
- It must be big enough for gravity to squash it into a round ball,
- It must have cleared other objects out of the way in its orbital neighbourhood.
- The Terrestrial Planets or Inner Planets are the four innermost planet in the solar system, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
- The Jovian Planets or Outer Planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune because they are all gigantic compared to Earth, and they have, gaseous nature.
- Mercury: It is the smallest and the closest planet to the Sun, without moon. Surface is full of craters.
- Venus: It is the second closest planet to the Sun, known as evening as well as morning star, rotates from east to west. It is the hottest planet. The atmosphere of venus is covered with thick clouds that strongly reflects sunlight.
- Earth: It is the third planet from the Sun with one moon. Perfect place for life. It consists of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other ingredient; envelops it. Moon is the only natural satellite of Earth.
- Mars: It is the fourth planet from the Sun with two moons (Phobos and Deimos).
- It is known as the Red Planet because iron minerals in the Martian soil oxidize, or rust, causing the soil and the dusty atmosphere to look red. The planet is characterised by volcanoes, canyon systems, river beds, crated terrains, and dune fields.
- Jupiter: It is the fifth planet, from the Its atmosphere is made up mostly of hydrogen (H2) and helium (He). It has the fastest rotational velocity completing one rotation in less than 10 hours. Jupiter has 67 known satellites and 4 Galilean moons. It has the biggest magnetosphere in the entire solar system.
- Saturn: It is the second-largest planet in the solar system and surrounded by rings like structures. These rings are made of primordial dust and ice particles. Moreover Saturn is a gaseous planet. The planet has 62 prominent moons among which the largest moon is Titan which is the second largest in the entire solar system.
- Uranus: It is the seventh planet from the Sun. One day on Uranus takes about 17 hours (the time it takes for Uranus to rotate or spin once). Uranus makes a complete orbit around the Sun (a year in Uranian time) in about 84 Earth years. It has 27 moons. It is characterised by usual magnetic and electric field.
- Neptune: It is the eighth planet from the Sun. Its atmosphere is made up mostly of hydrogen (H2), helium (He) and methane (CH4). Triton is its largest moon. It is having a earth-size blemish called as Green dark spot. It has 14 satellites among which Triton and Nereid are the prominent ones.
Note:
- Pluto (not a planet now.) It is now considered as a dwarf planet. It has slowest orbital velocity and hence, the longest year, Charon, is nearly half its size.
- Dwarf planet? A dwarf planet is a planetary ? mass object that is neither a planet nor a natural satellite. It shares its orbits around the sun with other objects such as asteroids or comets. It is massive enough for its shape to be in hydrostatic equilibrium under its own gravity, but has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit. The first 5 recognised dwarf planets are- ceres, Pluto, Eris, Haumea & Makemake.
- Light year: A light-year is a unit of astronomical distance. It is the distance that light can travel in one year. It is approximately 9.5 trillion kilometres (or about 6 trillion miles).
Interesting Facts:
- Saturn and Uranus have rings around them. These are belts of small debris. These rings may be seen from the earth with the help of powerful telescopes.
- Jupiter is the largest of all planets.
- All the nine planets revolve around the sun anti clockwise in elliptical paths known as Orbits.
- Except Venus and Uranus, all other planets rotate (on their own axes) in the same direction in which they revolve.
- Time to complete one revolution:
88 days - Mercury
255 days - Venus
365days, 6 hours - Earth (with speed100,000 km/hr).
11 years - Jupiter
164 years - Neptune
248 years - Pluto- On size Earth ranks 5th, in size and shape the earth is almost identical to Venus. Only Mercury and Venus have no satellite.
The Earth
- The earth is the third nearest planet to the Sun. In size, it is the fifth largest planet. It is slightly flattened at the poles. That is why, its shape is described as a Geoid. Geoid means an earth-like shape.
- Conditions favourable to support life are probably found only on the earth.
- The earth is neither too hot nor too cold.
- It has water and air, which are very essential for our survival. The air has life-supporting gases like oxygen.
- Because of these reasons, the earth is a unique planet in the solar system. From the outer space, the earth appears blue because its two-thirds surface is covered by water. It is, therefore, called a blue planet.
Moon
- Our earth has only one satellite, that is, the moon.
- Its diametre is only one-quarter that of the earth.
- It appears so big because it is nearer to our planet than other celestial bodies.
- The moon does not have conditions favourable for life.
- It has neither water nor air.
- It has mountains.
- Mass – 7.35 x 1022 kg.
- Its diameter is only 1/4th of that of the earth.
- Distance from earth – 385000 km.
- Circumference – 11,000 km
- Revolution time – 27.3 days
- Gravitational pull - 1/6 th of that of the Earth
- The moon revolves around the earth in about 27 days and 8 hours. It takes exactly the same time for it to complete one rotation about its axis. As such we always see only one side of the moon while the other side always remains away from us.
- The moon is very hot during the day and very cold during the night.
Note: Light travels at the speed of about 300,000 km per second. Yet, even with this speed, the light of the sun takes about eight minutes to reach the earth.
Asteroids
- Asteroids or Planetoids are rocky bodies up to 800 km in diameter, although most are much smaller in diameter less than a km, i.e. Asteroids are the minor planets which especially belong to the inner solar system.
- They orbit the Sun in the asteroid belt, which lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
Meteoroids
- The small pieces of rocks which move around the sun are called meteoroids. Sometimes these meteoroids come near the earth and tend to drop upon it.
- During this process due to friction with the air, they get heated up and burn.
- It causes a flash of light.
- Sometimes, a meteor without being completely burnt falls on the earth and creates a hollow.
Comets
- They are the smallest units of the cosmic bodies which is made up of frozen gases, rocks and dusts.
- The tail of the comet always points away from the Sun because of the force exerted by solar wind and the radiation pressure.
- The most common comet is Halley’s comet which is spotted every 76 years.
Note
- Star: A celestial body, having its own heat and light.
- Planet: A celestial body which revolves around the sun and receives heat and light from it.
- Satellite: A celestial body which revolves around a planet just as planet revolves around the sun. (So far 49 Satellite have been discovered).
Chapter - 5
Origin of Earth
Early Theories of Origin of Earth
 The major early theories of the earth’s origin are discussed below:
The major early theories of the earth’s origin are discussed below:
- Nebular Hypothesis: This theory was developed by Immanuel Kant and modified in 1796 by Pierre Laplace. According to this hypothesis, the planets were formed out of a cloud of material associated with a youthful sun, which was slowly rotating.
- In 1900, Chamberlain and Moulton considered that a wandering star approached the sun which resulted in the formation of a cigar-shaped extension of material that got separated from the solar surface. This separated material continued to revolve around the sun and slowly got condensed into planets.
- The binary theories considered a companion to be coexisting with the sun.
- In 1950, the Nebular Hypothesis was revised by Otto Schmidt (in Russia) and Carl Weizascar (in Germany). According to them, the sun was surrounded by a solar nebula consisting mainly of hydrogen and helium along with dust. The friction and collision of particles led to the formation of a disk-shaped cloud and planets were formed through the process of accretion.
Origin of Earth Modern Theories
Big Bang Theory
- The Big Bang Theory explains the origin of the universe. It is also called the expanding universe hypothesis.
- In 1927, Abbe Georges Lemaitre, a Belgian astronomer was the first to provide a theory on the origin of the Universe. It was Edwin Hubble who provided evidence that the universe is expanding.
- According to this theory, all matter that formed the universe existed in one point (tiny ball) called singularity having an unimaginable small volume, infinite temperature and infinite density.
- The great event of the big bang happened some 13.7 billion years ago. The tiny ball exploded which led to a huge expansion and this expansion continues even today. There was rapid expansion within fractions of a second after the bang. Thereafter, the expansion slowed down. With the expansion some of the energy was converted into matter. Within the first three minutes from the big bang event, the first atom began to form.
- Within 300,000 years from the big bang, temperature dropped down to 4500 K and gave rise to atomic matter. The majority of atoms formed were hydrogen, along with helium and traces of lithium. Huge clouds of these elements fused through gravity to form stars and galaxies.
- Once there were two theories for explaining the origin of the universe – the Big Bang theory and the Hoyle’s concept of steady state.
- The steady state theory considered the universe to be roughly the same at any point of time.
- However, with greater evidence becoming available about the expanding universe, the Big Bang theory was confirmed which proposes that the universe originated from a single violent explosion of a very minute amount (tiny ball) of matter of high density and temperature.
The Big Bang Theory considers the following stages in the development of the universe:
- In the beginning, all matter forming the universe existed in one place in the form of a “tiny ball” (singular atom) with an unimaginably small volume, infinite temperature and infinite density.
- At the Big Bang the “tiny ball” exploded violently. This led to a huge expansion. It is now generally accepted that the event of big bang took place 13.7 billion years before the present. The expansion continues even to the present day. As it grew, some energy was converted into matter. There was particularly rapid expansion within fractions of a second after the bang. Thereafter, the expansion has slowed down. Within first three minutes from the Big Bang event, the first atom began to form.
- Within 300,000 years from the Big Bang, temperature dropped to 4,500K and gave rise to atomic matter. The universe became transparent. The product of the moment of inertia and the angular velocity of a rotating body is called its angular momentum.
|
47 videos|185 docs|161 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Physical Geography - Physical Geography, UPSC, IAS. - Geography (Prelims) by Valor Academy
| 1. What is physical geography? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of physical geography? |  |
| 3. What are some key topics covered in physical geography? |  |
| 4. How does physical geography contribute to understanding climate change? |  |
| 5. How does physical geography influence human activities? |  |
















