Introduction to SI Units List | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The Base Units of SI |

|
| List of SI Derived Units |

|
| What is the meaning of SI Units? |

|
Introduction
Ensuring Consistency and Comparability
SI units play a vital role in scientific and technical research by providing a standardized framework for measuring physical quantities. By adhering to SI units, researchers across the globe can communicate their findings clearly, ensuring consistency and comparability in their work.
The International System of Units (SI)
The International System of Units, or SI, is a metric system adopted by every country as a global standard. Derived from the French term "Systeme International," SI consists of seven base units, which form the foundation for 22 derived units. These units span a vast range of magnitudes, from 10^(-24) to 10^24, and are expressed in fractional or standard quantities.
The Base Units of SI
The SI system relies on seven fundamental base units, each representing a distinct physical quantity. These base units act as the building blocks from which all other units are derived. Let's explore each base unit in detail:
Length (L) - Meter (m)
The meter is the base unit of length and serves as the fundamental measure for distance. It is approximately equal to 39.37 inches and acts as a reference point for smaller units such as centimeters and millimeters.
Time (T) - Second (s)
The second is the base unit of time and is defined as the duration of 9,192,631,770 oscillations of radiation emitted by a cesium-133 atom. It is an essential unit for measuring the continuous flow of existence.
Mass (M) - Kilogram (kg)
The kilogram is the base unit of mass. Originally, it was intended to be equal to the volume of 1,000 cubic centimeters of water, but it is slightly different in practice. The kilogram serves as the primary unit for quantifying the quantity of matter in an object.
Electric Current (I) - Ampere (A)
The ampere is the base unit of electric current and is defined by considering the constant value of the elementary charge. It enables the measurement of the flow of electric charge through a conductor.
Amount of Substance (N) - Mole (mol)
The mole is the base unit of amount of substance and is defined by the constant value of Avogadro's constant (6.02214076 × 1023). It represents the quantity of a substance that contains an exact number of elementary entities.
Thermodynamic Temperature (Θ) - Kelvin (K)
The kelvin is the base unit of thermodynamic temperature and is defined by the constant value of Boltzmann's constant (1.380649 × 10^(-23)). It provides a scale for measuring temperature based on the behavior of particles in a system.
Luminous Intensity (J) - Candela (cd)
The candela is the base unit of luminous intensity and is defined by the constant value of luminous efficacy. It quantifies the intensity of visible light emitted by a source in a particular direction.
List of SI Derived Units
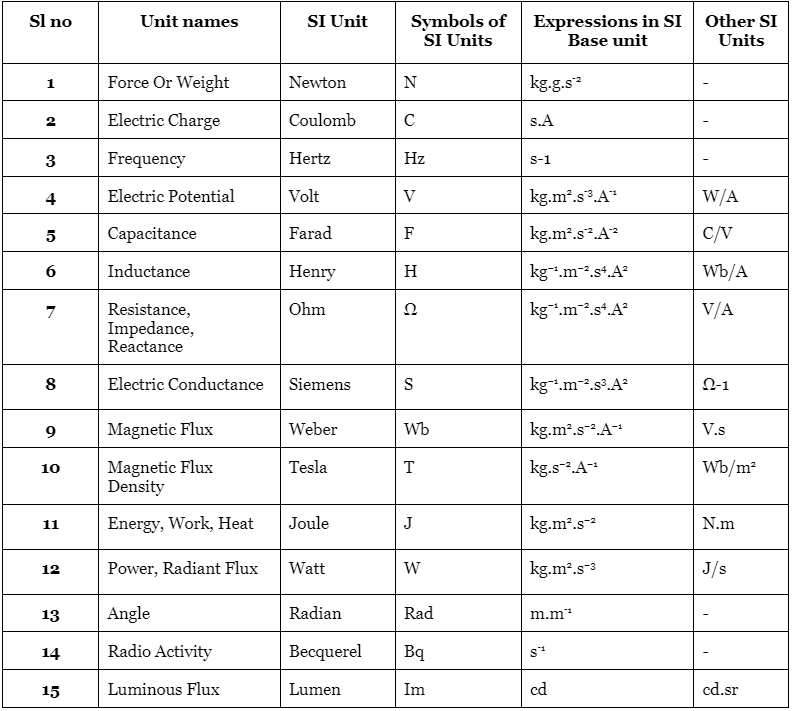
The following units are predominantly used in physics:
- The SI unit for velocity is meter per second (m/s).
- The SI unit for heat is the joule.
- The SI unit for momentum is kilogram meter per second (kg.m/s).
- The SI unit for magnetic field is the tesla.
Physics involves studying numerous numbers, terms, and quantities, which are expressed in various units. It is important to be familiar with both CGS (centimeter-gram-second) and SI (International System of Units) units to excel in physics. Understanding these units can provide a deeper comprehension of different topics, and they are presented in an interactive manner for easier understanding. By presenting the units in a concise format, the concepts can be retained for a longer duration.
Units of measurement for length, time, mass, and volume are as follows:
Length:
- The SI unit for length is the meter. It is defined as the distance traveled by light in 1/299792458 seconds.
- Other units of length include nanometers, millimeters, decimeters, centimeters, meters, and kilometers.
- Non-SI units of length include the yard, inch, and foot.
Time:
- The SI unit for time is the second. It is defined as the duration of 9192631770 vibrations of radiation corresponding to the transition between two hyperfine levels of the cesium-133 atom.
- Other units of time include the minute, hour, day, week, month, and year.
Mass:
- Mass is distinct from weight and refers to the quantity of matter in an object.
- The most commonly used units for mass are the gram and kilogram.
- Other units of mass include the milligram, decigram, centigram, decagram, hectogram, metric ton, and kilogram.
Volume:
- Volume is used to measure the capacity of an object.
- The SI unit for volume is the cubic meter (m³).
- Other commonly used units of volume exist as well.
Some Other Units Of Volume Are
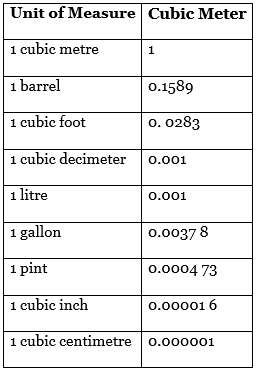
What is the meaning of SI Units?
SI Units, which stands for the International System of Units, is a globally recognized system of measurement. It is the sole system acknowledged on an international level and is used wherever the metric system is adopted. Additionally, it is widely employed in scientific research worldwide.
The SI system is based on seven fundamental units called Base SI Units. These include the second (for time), the meter (for length), the ampere (for electric current), the candela (for luminous intensity), the mole (for amount of substance), the kilogram (for mass), and the kelvin (for thermodynamic temperature).
In addition to the base units, there are 22 derived units known as Coherent Derived SI Units. These derived units are derived from the base units and serve various purposes in measurement.
The 22 Coherent Derived SI Units are as follows:
- Hertz (for frequency)
- Joule (for energy, work, heat)
- Pascal (for pressure, stress)
- Radian (for angle)
- Steradian (for solid angle)
- Coulomb (for electric charge)
- Newton (for force)
- Ohm (for electric resistance)
- Volt (for voltage)
- Farad (for electrical capacitance)
- Siemens (for electrical conductance)
- Tesla (for magnetic induction)
- Henry (for electrical inductance)
- Degree Celsius (for temperature relative to Kelvin)
- Weber (for magnetic flux)
- Gray (for absorbed dose of ionizing radiation)
- Lumen (for luminous flux)
- Lux (for illuminance)
- Becquerel (for radioactivity)
- Katal (for catalytic activity)
- Sievert (for equivalent dose of ionizing radiation)
These derived units are interconnected with and based on the seven base SI units.
Collectively, the seven base SI units and the 22 derived SI units form the International System of Units. This system is widely used worldwide for scientific research and is also employed in everyday measurements in most countries. For example, the meter and kilometer are commonly used for distance and length measurements, while miles are primarily used in a few countries.
|
1243 videos|2222 docs|849 tests
|




















