Irodov Solutions: Kinetic Theory of Gases | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Q. 62. Modern vacuum pumps permit the pressures down to p = 4.10-15 atm to be reached at room temperatures. Assuming that the gas exhausted is nitrogen, find the number of its molecules per 1 cm3 and the mean distance between them at this pressure.
Solution. 62. From the formula p - n k T
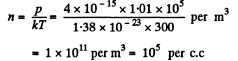
Mean distance between molecules
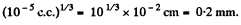
Q. 63. A vessel of volume V = 5.0 l contains m = 1.4 g of nitrogen at a temperature T = 1800 K. Find the gas pressure, taking into account that η = 30% of molecules are disassociated into atoms at this temperature.
Solution. 63. A fter dissociation each N2 molecule becomes two Adatoms and so contributes, 2 x 3 degrees of freedom. Thus the number of moles becomes
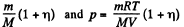
Here M is the molecular weight in grams of N2.
Q. 64. Under standard conditions the density of the helium and nitrogen mixture equals p = 0.60 g/l. Find the concentration of helium atoms in the given mixture.
Solution. 64. Let n1 = number density of He atoms, n2 = number density of N2 molecules
Then p = n1 m1 + n2 m2
where m1 = mass of He atom, m2 = mass of N2 molecule also p = (n1 + n2) kT
From these two equations we get
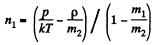
Q. 65. A parallel beam of nitrogen molecules moving with velocity v = 400 m/s impinges on a wall at an angle θ = 30° to its normal. The concentration of molecules in the beam n = 0.9.1019 cm-3. Find the pressure exerted by the beam on the wall assuming the molecules to scatter in accordance with the perfectly elastic collision law.
Solution. 65.
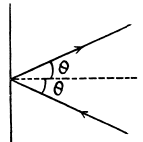
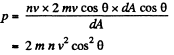
Q. 66. How many degrees of freedom have the gas molecules, if under standard conditions the gas density is p = 1.3 mg/cm3 and the velocity of sound propagation in it is v = 330 m/s.
Solution. 66. From the formula
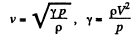
If i = number of degrees of freedom of the gas then
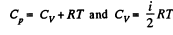
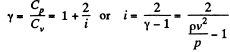
Q. 67. Determine the ratio of the sonic velocity v in a gas to the root mean square velocity of molecules of this gas, if the molecules are
(a) monatomic; (b) rigid diatomic.
Solution. 67. 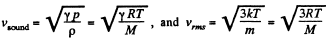
so, 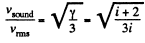
(a) For monoatomic gases i = 3
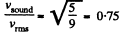
(b) For rigid diatomic molecules i = 5
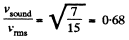
Q. 68. A gas consisting of N-atomic molecules has the temperature T at which all degrees of freedom (translational, rotational, and vibrational) are excited. Find the mean energy of molecules in such a gas. What fraction of this energy corresponds to that of translational motion?
Solution. 68. For a general noncollinear, nonplanar molecule
mean energy 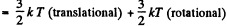 + (3N - 6) kT (vibrational)
+ (3N - 6) kT (vibrational)
= (3N - 3) kT per molecule
For linear molecules, mean energy  + kT (rotational) + (3 N - 5) kT (vibrational)
+ kT (rotational) + (3 N - 5) kT (vibrational)
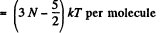
Translational energy is a fraction 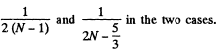
Q. 69. Suppose a gas is heated up to a temperature at which all degrees of freedom (translational, rotational, and vibrational) of its molecules are excited. Find the molar heat capacity of such a gas in the isochoric process, as well as the adiabatic exponent γ, if the gas consists of
(a) diatomic;
(b) linear N-atomic;
(c) network N-atomic molecules.
Solution. 69. (a) A diatomic molecule has 2 translational, 2 rotational and one vibrational degrees of freedom. The corresponding energy per mole is
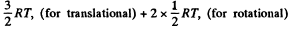

Thus, 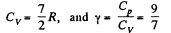
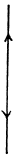
(b) For linear N - atomic molecules energy per mole
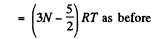
So, 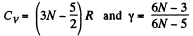
(c) For noncollinear N- atomic molecules
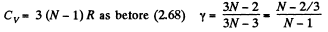
Q. 70. An ideal gas consisting of N-atomic molecules is expanded isobarically. Assuming that all degrees of freedom (translational, rotational, and vibrational) of the molecules are excited, find what fraction of heat transferred to the gas in this process is spent to perform the work of expansion. How high is this fraction in the case of a monatomic gas?
Solution. 70. In the isobaric process, work done is
A = pdv = RdT per mole.
On the other hand heat transferred Q = CpdT
Now Cp = (3N - 2) R for non-collinear molecules and 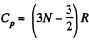 for linear molecules
for linear molecules
Thus 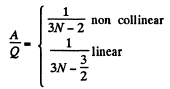
For monoatomic gases, 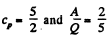
Q. 71. Find the molar mass and the number of degrees of freedom of molecules in a gas if its heat capacities are known: cv = 0.65 J/(g•K) and cp = 0.91 J/(g•K).
Solution. 71. Given specific heats cp, cv (per unit mass)
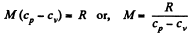
Also 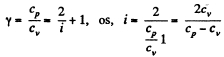
Q. 72. Find the number of degrees of freedom of molecules in a gas whose molar heat capacity
(a) at constant pressure is equal to Cp = 29 J/(mol.K);
(b) is equal to C = 29 J/(mol•K) in the process pT = const.
Solution. 72. 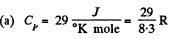
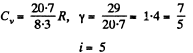
(b) In the process pT = const
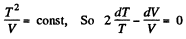
Thus 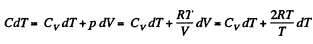
or 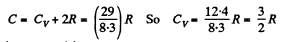
Hence i = 3 (monoatomic)
Q. 73. Find the adiabatic exponent γ for a mixture consisting of v1 moles of a monatomic gas and v2 moles of gas of rigid diatomic molecules.
Solution. 73. Obviously
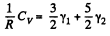
(Since a monoatomic gas has 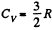 and a diatomic gas has
and a diatomic gas has 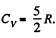 [The diatomic molecule is rigid so no vibration])
[The diatomic molecule is rigid so no vibration])
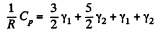
Hence 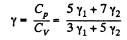
Q. 74. A thermally insulated vessel with gaseous nitrogen at a temperature t = 27°C moves with velocity v = 100 m/s. How much (in per cent) and in what way will the gas pressure change on a sudden stoppage of the vessel?
Solution. 74. The internal energy of the molecules are
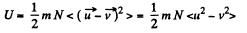
where 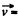 velocity of the vessel, N = number of molecules, each of mass m. When the vessel is stopped, internal energy becomes
velocity of the vessel, N = number of molecules, each of mass m. When the vessel is stopped, internal energy becomes 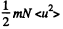
So there is an increase in internal energy of 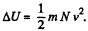 This will give rise to a rise in temperature of
This will give rise to a rise in temperature of
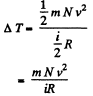
there being no flow of heat This change of temperature will lead to an excess pressure
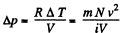
and finally 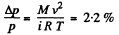
where M = molecular weight of N2 , i = number of degrees of freedom of N2
Q. 75. Calculate at the temperature t = 17°C:
(a) the root mean square velocity and the mean kinetic energy of an oxygen molecule in the process of translational motion;
(b) the root mean square velocity of a water droplet of diameter d = 0.10 μm suspended in the air.
Solution. 75. (a) From the equipartition theorem
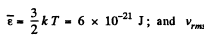
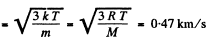
(b) In equilibrium the mean kinetic energy of the droplet will be equal to that of a molecule.
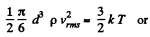
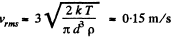
Q. 76. A gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of the molecules η = 1.50 times?
Solution. 76. 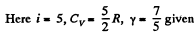
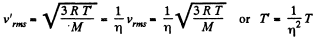
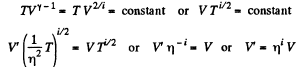
The gas must be expanded 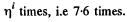
Q. 77. The mass m = 15 g of nitrogen is enclosed in a vessel at a temperature T = 300 K. What amount of heat has to be transferred to the gas to increase the root mean square velocity of its molecules η = 2.0 times?
Solution. 77. Here 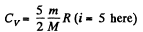
m = mass of the gas, M = molecular weight If vrms increases η times, the temperature will have increased η2 times. This will require (neglecting expansion of the vessels) a heat flow of amount
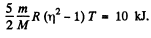
Q. 78. The temperature of a gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules is T = 300 K. Calculate the angular root mean square velocity of a rotating molecule if its moment of inertia is equal to I = 2.1.10-39 g• cm2.
Solution. 78. The root mean square angular velocity is given by
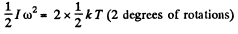
or 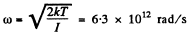
Q. 79. A gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules was initially under standard conditions. Then the gas was compressed adiabatically η = 5.0 times. Find the mean kinetic energy of a rotating molecule in the final state.
Solution. 79. Under compression, the temperature will rise
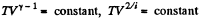
or, 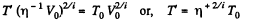
Q. 80. How will the rate of collisions of rigid diatomic molecules against the vessel's wall change, if the gas is expanded adiabatically η times?
Solution. 80. 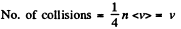
Now, 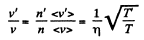
(When the gas is expanded η times, n decreases by a factor η). Also
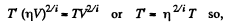
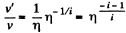
i.e. collisions decrease by a factor 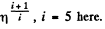
Q. 81. The volume of gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules was increased η = 2.0 times in a polytropic process with the molar heat capacity C = R. How many times will the rate of collisions of molecules against a vessel's wall be reduced as a result of this process?
Solution. 81. In a polytropic process pVn = constant., where n is called the polytropic index. For this process
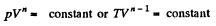
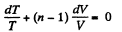
Then 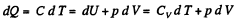
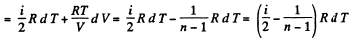
Now 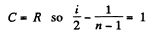
or, 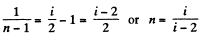
Now 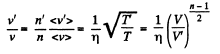
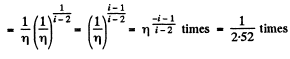
Q. 82. A gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules was expanded in a polytropic process so that the rate of collisions of the molecules against the vessel's wall did not change. Find the molar heat capacity of the gas in this process.
Solution. 82. If a is the polytropic index then
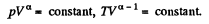
Now 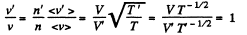
Hence 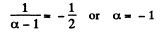
Then 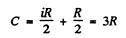
Q. 83. Calculate the most probable, the mean, and the root mean square velocities of a molecule of a gas whose density under standard atmospheric pressure is equal to p = 1.00 g/1.
Solution. 83.
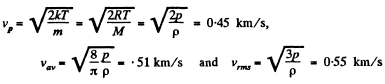
Q. 84. Find the fraction of gas molecules whose velocities differ by less than δη = 1.00% from the value of
(a) the most probable velocity;
(b) the root mean square velocity.
Solution. 84. (a) The formula is
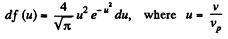
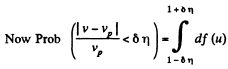
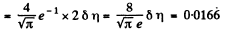
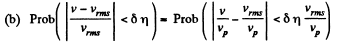
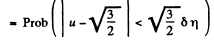
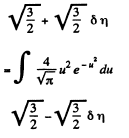
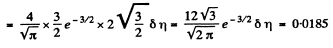
Q. 85. Determine the gas temperature at which
(a) the root mean square velocity of hydrogen molecules exceeds their most probable velocity by Δv = 400 m/s;
(b) the velocity distribution function F (v) for the oxygen molecules will have the maximum value at the velocity v = 420 m/s.
Solution. 85. 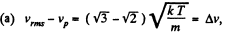
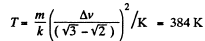
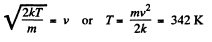
Q. 86. In the case of gaseous nitrogen find:
(a) the temperature at which the velocities of the molecules v1 = 300 m/s and v2 = 600 m/s are associated with equal values of the Maxwell distribution function F (v);
(b) the velocity of the molecules v at which the value of the Maxwell distribution function F (v) for the temperature T0 will be the same as that for the temperature η times higher
Solution. 86. (a) We have,
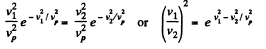
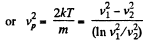
So 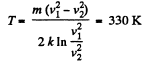
(b) 
Thus 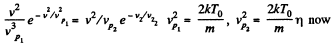
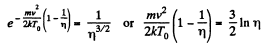
Thus 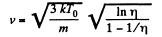
Q. 87. At what temperature of a nitrogen and oxygen mixture do the most probable velocities of nitrogen and oxygen molecules differ by Δv = 30 m/s?
Solution. 87. 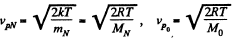
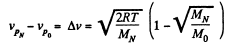
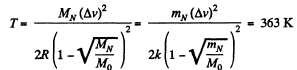
Q. 88. The temperature of a hydrogen and helium mixture is T = 300 K. At what value of the molecular velocity v will the Maxwell distribution function F (v) yield the same magnitude for both gases?
Solution. 88.
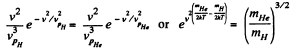
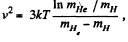 Putting the values we get v = 1.60 km/s
Putting the values we get v = 1.60 km/s
Q. 89. At what temperature of a gas will the number of molecules, whose velocities fall within the given interval from v to v + dv, be the greatest? The mass of each molecule is equal to m.
Solution. 89.
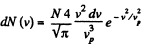
For a given range v to v + dv (i.e. given v and dv ) this is maximum when
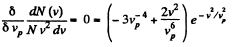
or, 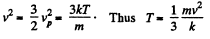
Q. 90. Find the fraction of molecules whose velocity projections on the x axis fall within the interval from vx to vx + dvx, while the moduli of perpendicular velocity components fall within the interval from v⊥ to v⊥ + dv⊥. The mass of each molecule is m, and the temperature is T.
Solution. 90. 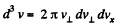
Thus 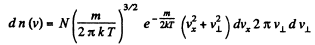
Q. 91. Using the Maxwell distribution function, calculate the mean velocity projection 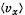 and the mean value of the modulus of this projection
and the mean value of the modulus of this projection 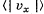 if the mass of each molecule is equal to m and the gas temperature is T.
if the mass of each molecule is equal to m and the gas temperature is T.
Solution. 91. 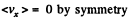
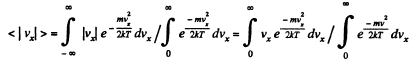
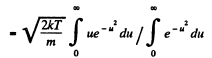
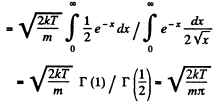
Q. 92. From the Maxwell distribution function find 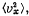 the mean value of the squared vx projection of the molecular velocity in a gas at a temperature T. The mass of each molecule is equal to m.
the mean value of the squared vx projection of the molecular velocity in a gas at a temperature T. The mass of each molecule is equal to m.
Solution. 92.
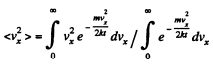
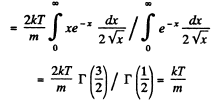
Q. 93. Making use of the Maxwell distribution function, calculate the number v of gas molecules reaching a unit area of a wall per unit time, if the concentration of molecules is equal to n, the temperature to T, and the mass of each molecule is m.
Solution. 93. Here vdA = No. of molecules hitting an area dA of the wall per second
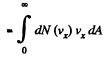
or, 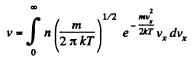
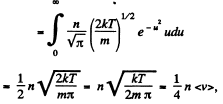
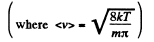
Q. 94. Using the Maxwell distribution function, determine the pressure exerted by gas on a wall, if the gas temperature is T and the concentration of molecules is n.
Solution. 94. 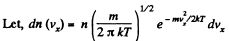
be the number of molecules per unit volume with x component of velocity in the range vx to vx + dvx
Then 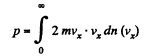
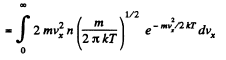
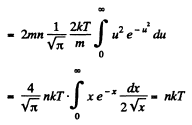
Q. 95. Making use of the Maxwell distribution function, find 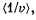 , the mean value of the reciprocal of the velocity of molecules in an ideal gas at a temperature T, if the mass of each molecule is equal to m. Compare the value obtained with the reciprocal of the mean velocity.
, the mean value of the reciprocal of the velocity of molecules in an ideal gas at a temperature T, if the mass of each molecule is equal to m. Compare the value obtained with the reciprocal of the mean velocity.
Solution. 95.
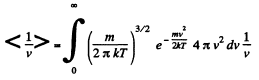
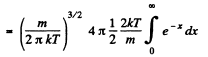
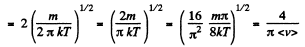
Q. 96. A gas consists of molecules of mass m and is at a temperature T. Making use of the Maxwell velocity distribution function, find the corresponding distribution of the molecules over the kinetic energies ε. Determine the most probable value of the kinetic energy εp. Does εp correspond to the most probable velocity?
Solution. 96. 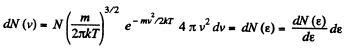
or, 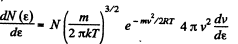
Now, 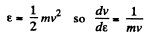
or, 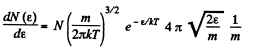
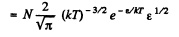
i.e. 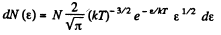
The most probable kinetic energy is given from
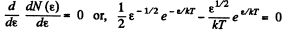
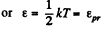
The corresponding velocity is 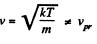
Q. 97. What fraction of monatomic molecules of a gas in a thermal equilibrium possesses kinetic energies differing from the mean value by δη = 1.0 % and less?
Solution. 97. The mean kinetic energy is
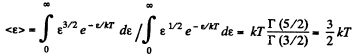
Thus
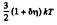
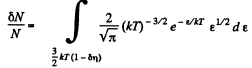
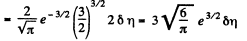
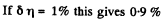
Q. 98. What fraction of molecules in a gas at a temperature T has the kinetic energy of translational motion exceeding ε0 if ε0 ≫ ≫kT?
Solution. 98. 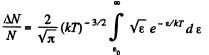
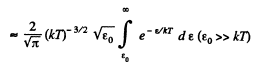
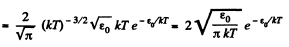
(In evaluating the integral, we have taken out 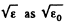 since the integral is dominated by the lower limit.)
since the integral is dominated by the lower limit.)
Q. 99. The velocity distribution of molecules in a beam coming out of a hole in a vessel is described by the function F (v)= A V3e-mv2/2hT, where T is the temperature of the gas in the vessel. Find the most probable values of
(a) the velocity of the molecules in the beam; compare the result obtained with the most probable velocity of the molecules in the vessel;
(b) the kinetic energy of the molecules in the beam.
Solution. 99. 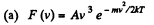
For the most probable value of the velocity
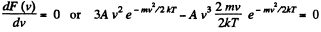
So, 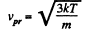
This should becom pared with the value 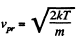 for the Maxwellian distribution.
for the Maxwellian distribution.
(b) In terms of eneigy, 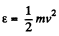
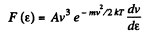
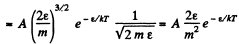
From this the probable eneigy comes out as follows : F' (ε) = 0 implies
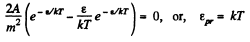
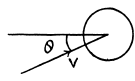
Q. 100. An ideal gas consisting of molecules of mass m with concentration n has a temperature T. Using the Maxwell distribution function, find the number of molecules reaching a unit area of a wall at the angles between θ and θ + dθ to its normal per unit time.
Solution. 100. The number of molecules reaching a unit area of wall at angle between θ and θ + dθ to its normal per unit time is
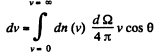
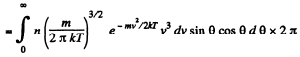
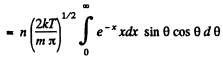
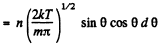
Q. 101. From the conditions of the foregoing problem find the number of molecules reaching a unit area of a wall with the velocities in the interval from v to v + dv per unit time.
Solution. 101. Similarly the number of molecules reaching the wall per unit area of the wall with velocities in the interval v to v + dv oer unit time is
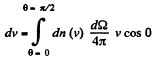
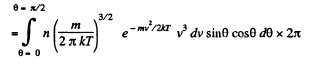
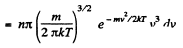
Q. 102. Find the force exerted on a particle by a uniform field if the concentrations of these particles at two levels separated by the distance Δh = 3.0 cm (along the field) differ by η = 2.0 times. The temperature of the system is equal to T = 280 K.
Solution. 102. If the force exerted is F then the law of variation of concentration with height reads
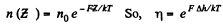
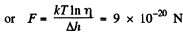
Q. 103. When examining the suspended gamboge droplets under a microscope, their average numbers in the layers separated by the distance h = 40 urrn were found to differ by η = 2.0 times. The environmental temperature is equal to T = 290 K. The diameter of the droplets is d = 0.40 μm, and their density exceeds that of the surrounding fluid by Δp = 0.20 g/cm3. Find Avogadro's number from these data.
Solution. 103. 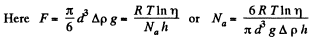
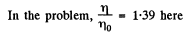
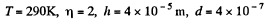
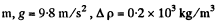
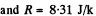
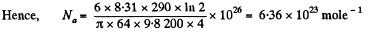
Q. 104. Suppose that η0 is the ratio of the molecular concentration of hydrogen to that of nitrogen at the Earth's surface, while η is the corresponding ratio at the height h = 3000 m. Find the ratio η/η0 at the temperature T = 280 K, assuming that the temperature and the free fall acceleration are independent of the height.
Solution. 104. 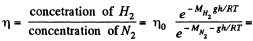
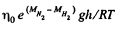
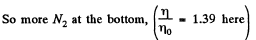
Q. 105. A tall vertical vessel contains a gas composed of two kinds of molecules of masses m1 and m2, with m2 > m1. The concentrations of these molecules at the bottom of the vessel are equal to n1 and n2 respectively, with n2 > n1. Assuming the temperature T and the free-fall acceleration g to be independent of the height, find the height at which the concentrations of these kinds of molecules are equal.
Solution. 105. 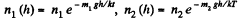
They are equal at a height h where 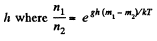
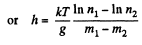
Q. 106. A very tall vertical cylinder contains carbon dioxide at a certain temperature T. Assuming the gravitational field to be uniform, find how the gas pressure on the bottom of the vessel will change when the gas temperature increases η times.
Solution. 106. At a temperature T the concentration n (z) varies with height according to
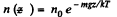
This means that the cylinder contains 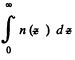
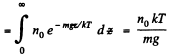
particles per unit area of the base. Clearly this cannot change. Thus n0 kT = p0 = pressure at the bottom of the cylinder must not change with change of temperature.
Q. 107. A very tall vertical cylinder contains a gas at a temperature T'. Assuming the gravitational field to be uniform, find the mean value of the potential energy of the gas molecules. Does this value depend on whether the gas consists of one kind of molecules or of several kinds?
Solution. 107.
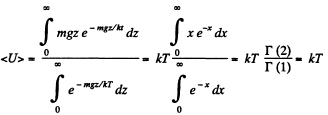
When there are many kinds of molecules, this formula holds for each kind and the average energy
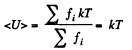
where fi α fractional concentration of each kind at the ground level.
Q. 108. A horizontal tube of length l = 100 cm closed from both ends is displaced lengthwise with a constant acceleration w. The tube contains argon at a temperature T = 330 K. At what value of w will the argon concentrations at the tube's ends differ by η = 1.0%?
Solution. 108. The constant acceleration is equivalent to a pseudo force wherein a concentration gradient is set up. Then
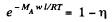
or 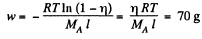
Q. 109. Find the mass of a mole of colloid particles if during their centrifuging with an angular velocity ω about a vertical axis the concentration of the particles at the distance r2 from the rotation axis is η times greater than that at the distance r1 ( in the same horizontal plane). The densities of the particles and the solvent are equal to p and to P0 respectively.
Solution. 109. In a centrifuge rotating with angular velocity co about an axis, there is a centrifugal acceleration ω2 r where r is the radial distance from the axis. In a fluid if there are suspended colloidal particles they experience an additional force. If m is the mass of each particle then its volume 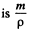 and the excess force on this particle is
and the excess force on this particle is 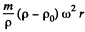 outward corresponding to a potential energy
outward corresponding to a potential energy 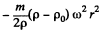
This gives rise to a concentration variation
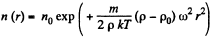
Thus 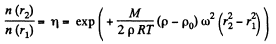
where 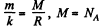 m is the molecular weight
m is the molecular weight
Thus 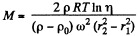
Q. 110. A horizontal tube with closed ends is rotated with a constant angular velocity ω about a vertical axis passing through one of its ends. The tube contains carbon dioxide at a temperature T = 300 K. The length of the tube is l = 100 cm. Find the value ω at which the ratio of molecular concentrations at the opposite ends of the tube is equal to η = 2.0.
Solution. 110. The potential energy associated with each molecule is : 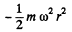
and there is a concentration variation
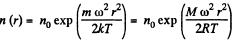
Thus 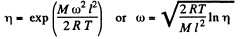
Using 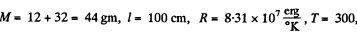
we get ω = 280 radians per second.
Q. 111. The potential energy of gas molecules in a certain central field depends on the distance r from the field's centre as U (r) = ar2, where a is a positive constant. The gas temperature is T, the concentration of molecules at the centre of the field is n0. Find:
(a) the number of molecules located at the distances between r and r + dr from the centre of the field;
(b) the most probable distance separating the molecules from the centre of the field;
(c) the fraction of molecules located in the spherical layer between r and r + dr;
(d) how many times the concentration of molecules in the centre of the field will change if the temperature decreases η times.
Solution. 111. 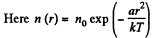
(a) The number of molecules located at the distance between r and r + dr is
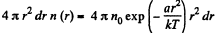
(b) 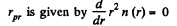
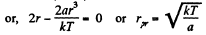
(c) The fraction of molecules lying between r and r + dr is
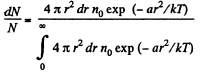
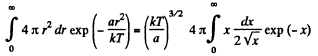
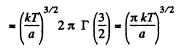
Thus 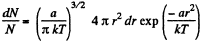
(d) 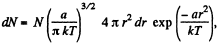
So 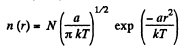
When T decreases η times (n0) = n0 will increase η3/2 times
Q. 112. From the conditions of the foregoing problem find:
(a) the number of molecules whose potential energy lies within the interval from U to U + dU;
(b) the most probable value of the potential energy of a molecule; compare this value with the potential energy of a molecule located at its most probable distance from the centre of the field.
Solution. 112. 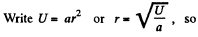
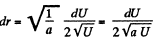
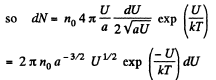
The most probable value of U is given by
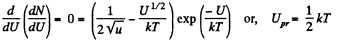
From Q.111 (b), the potential energy at the most probable distance is kT.
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Kinetic Theory of Gases - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the kinetic theory of gases? |  |
| 2. How does the kinetic theory of gases explain pressure? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between temperature and the kinetic energy of gas molecules? |  |
| 4. How does the kinetic theory of gases explain the expansion of gases when heated? |  |
| 5. Can the kinetic theory of gases explain the behavior of real gases? |  |

















