Kurukshetra Summary: December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
Government Initiatives in Promoting Skill Development and Entrepreneurship

Bridging the Skill Gap
- India is dealing with a major issue known as a skill gap, especially in rural areas.
- A large part of the workforce in these regions lacks the necessary skills or is not adequately trained for modern jobs.
- The government is taking steps to solve this problem through various skill development programs led by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
These programs have specific goals, including:
- Improving the skills of workers to make them more suitable for available jobs.
- Providing training opportunities that meet the demands of the job market.
- Encouraging young people to gain valuable skills that will help them in their careers.
- Helping individuals in rural areas to find better job opportunities through skill enhancement.
Promoting Skill Development
- The MSDE is supported by several skill-centric organizations, including the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), which plays a vital role in:
- Providing certified skilling, upskilling, and reskilling courses.
- Delivering hands-on training and opportunities for international mobility.
- The NSDC collaborates with:
- Sector Skill Councils (SSCs).
- National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs).
- Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Other training partners to deliver a wide range of skill development programs across diverse sectors.
- The government’s efforts in promoting skill development extend to international collaborations, such as a recent agreement with Israel to provide skilled workers to address their workforce gap.
Fostering Entrepreneurship
In addition to skill development, the government focuses on strengthening the entrepreneurial ecosystem by:
- Creating a vibrant and inclusive entrepreneurial environment.
- Supporting aspiring and existing entrepreneurs across rural and urban areas, as well as marginalized communities.
- Promoting women’s entrepreneurship through targeted initiatives, mentorship programs, and improved access to finance.
Key Government Initiatives
- Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN): A program aimed at improving the lives of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups by providing skills training and entrepreneurship development. This is carried out by NIESBUD and IIE in partnership with TRIFED.
- Rashtriya Udyamita Vikas Pariyojana: This initiative focuses on beneficiaries of PM-SVANidhi, offering them classroom training and mentoring to boost their business skills.
- STRIVE Project: A program designed to encourage entrepreneurship among trainees and trainers in Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) and National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) through awareness programs, mentoring, and support.
- SANKALP Scheme: Aims to assist individuals in starting their own businesses, particularly those from marginalized communities. The support includes skill development, mentoring, incubation, and guidance.
- Entrepreneurship Development in Six Holy Cities: This initiative promotes business development and offers mentoring support to small businesses in six important temple towns.
- Capacity Building Programme for Fair Price Shop Owners: A program that helps Fair Price Shop (FPS) owners learn how to manage their stores effectively, adopting modern retail techniques.
- Establishing EDCs and ICs in Northeast Educational Institutions: Focuses on creating Entrepreneurship Development Centres (EDCs) and Incubation Centres (ICs) in schools and colleges throughout the Northeast region.
- Pradhan Mantri Dakshata Aur Kushalata Sampanna Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) Yojana: This program offers skill training for youth from Backward Classes, Scheduled Castes, and Safai Karamcharis.
- Solar Entrepreneurship Development: Trains entrepreneurs to become skilled in installing and maintaining solar PV systems as part of the PM-Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana.
- Entrepreneurship-cum-Skill Development Programmes: Provides training in traditional crafts and modern skills, including LED light repair and solar PV installation.
- Promoting Entrepreneurship among Jail Inmates: Offers support for developing business skills among jail inmates through capacity building, mentoring, and incubation support.
- Training of Trainers and ED Programme in Jan Shikshan Sansthans: Encourages an entrepreneurial mindset by providing capacity building, incubation support, mentoring, and guidance in Jan Shikshan Sansthans (JSSs).
- SFURTI Programme: Focuses on improving and modernizing traditional industries in India using a cluster-based approach.
- Entrepreneurship Awareness Programmes Supported by HUL: Works with Hindustan Unilever Ltd (HUL) to conduct programs that raise awareness about entrepreneurship for young people across India.
New Initiatives and Collaborations
- NITI Aayog’s Project SWAVALAMBINI: Aims to foster an entrepreneurial mindset among female students and provide resources for entrepreneurship.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan: Seeks to improve the socioeconomic conditions of tribal communities through skill development and entrepreneurship programs.
- Proposed MoU with the Ministry of Rural Development: Promotes skill development and entrepreneurship among Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and their members to enhance rural livelihoods.
Conclusion
India’s skill gap is being addressed through comprehensive government initiatives focusing on skill development and entrepreneurship. These efforts empower individuals, promote economic growth, and enhance global workforce competitiveness. Collaboration with international and domestic partners strengthens these programs, creating sustainable livelihoods and driving inclusive development.
Skilling India: Empowering the Workforce

India's Demographic Dividend
- India has one of the youngest populations in the world, which gives it a special chance to take advantage of its demographic dividend.
- The government is working on skill development to close the gap between what employers need and what workers can do.
Prime Minister's Internship Scheme 2024
- This program offers 12-month internships at the top 500 companies in India to connect education with industry needs.
- Eligibility: Indian citizens aged 21-24 who are not employed full-time or enrolled in full-time education.
- Benefits:
- Monthly payment of Rs. 5,000.
- One-time payment for incidentals.
- Insurance coverage and reimbursement for training costs.
Other Recent Initiatives
- Swiggy Skills Initiative: A partnership with Swiggy to provide job training for delivery partners.
- STRIVE Project: A program focused on encouraging entrepreneurship and providing mentorship in ITIs and NSTIs.
- PM-JANMAN Initiative: Aims to train and uplift vulnerable tribal communities.
- Training for Fair Price Shop Owners: Equipping 3,000 participants with entrepreneurship skills.
- SANKALP Scheme: Assists marginalized groups in starting their own businesses.
- Rashtriya Udyamita Vikas Pariyojana: Provides training and support for PM-SVANidhi beneficiaries.
- Entrepreneurship Development for Jail Inmates: Encourages business skills among inmates.
- Bijnor Kaushal Mahotsav: An event aimed at generating job opportunities for local youth.
Women Empowerment Initiatives
- Training programs in aspirational districts.
- Memorandum of Understanding with Visa to train 20,000 youth in tourism.
- Skill India Centre at Rashtrapati Bhawan established for training in-house staff.
Key Programs under Skill India Mission
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Offers short-term skill training.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendras (PMKK): Ensures quality training across India.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS): Focuses on non-literate and rural communities.
- Pradhan Mantri YUVA Yojana: Encourages entrepreneurship.
- Skill India Digital (SID): Uses AI tools for job matching and ongoing education.
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana: Helps traditional artisans modernize their skills.
Latest Achievements and Initiatives
- Revised Model Skill Loan Scheme: Loan limits increased from Rs. 1.5 lakh to Rs. 7.5 lakh for advanced skill courses.
- World Youth Skills Day: Celebrated the 10th year of the Skill India Mission.
- Apprenticeship Training:
- Currently, 7.46 lakh apprentices are in training.
- In the current financial year, 2.77 lakh are participating.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): Over Rs. 122.36 crore given as apprentice stipends in the past four months.
Indian Institute of Skills (IIS)
- Aims to prepare a workforce suitable for Industry 4.0.
- Focuses on areas like factory automation, digital manufacturing, AI, and data analytics.
- Offers short courses in partnership with companies like Fanuc India and Taj Skyline.
Comprehensive Ecosystem for Rural Women Entrepreneurship
Untapped Potential of Rural Women
- Rural women possess entrepreneurial skills, resilience, and perseverance.
- Women’s contribution to GDP is low, underscoring the need to promote rural women’s entrepreneurship.
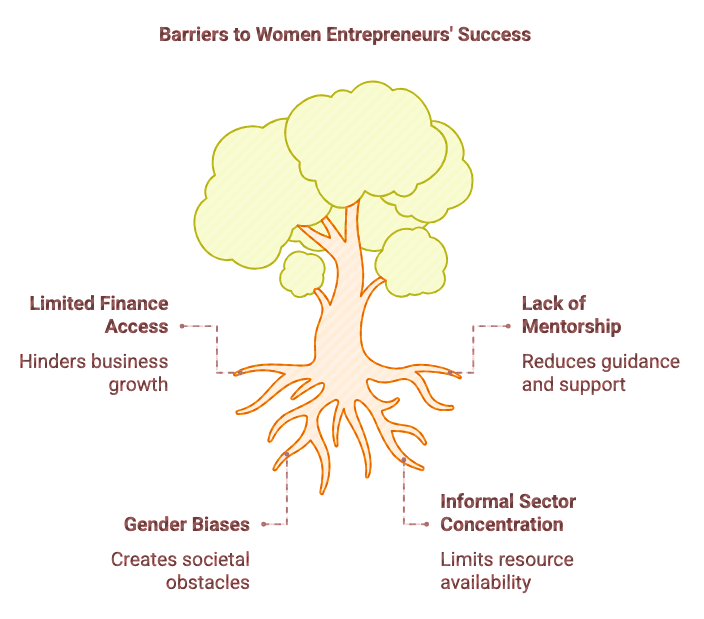
Challenges Faced by Women Entrepreneurs
Government Schemes for Rural Women Entrepreneurship
- Skill Upgradation & Mahila Coir Yojana (MCY): Focuses on skill development for coir industry artisans with stipends and unit setup support.
- Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP): Helps SHG members establish non-farm enterprises to stimulate economic growth.
- Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP): Empowers women in agriculture with enhanced productivity and resource access.
- Mahila Shakti Kendra (MSK): Offers skill development, employment assistance, and digital literacy for rural women.
- Women Enterprise Development Scheme (WED): Provides financial aid for North Eastern Region women entrepreneurs.
- Annapurna Yojana: Offers loans for women in the food service sector to meet working capital needs.
- Mudra Yojana Loans for Women Entrepreneurs: Provides micro-credit and special provisions for small women entrepreneurs.
- Start-Up India Initiative: Encourages startups with 46% of recognized startups having at least one woman director.
Addressing Loopholes in Existing Schemes
- Lack of awareness and promotion among beneficiaries.
- Overemphasis on financial and skill development support, neglecting market linkages and mentorship.
- Limited targeted schemes for rural women entrepreneurs.
- Neglect of sectors like services and the digital economy.
- Partial online access to schemes with unfriendly user interfaces.
Recommendations for Improvement
- Create comprehensive schemes covering entrepreneurship promotion, business support, market linkages, finance, and mentoring.
- Ensure a smooth user journey from registration to benefit availing.
- Enhance online access with improved user interfaces, multilingual content, and regional language support.
- Provide physical or assisted access for women with limited digital literacy.
- Collect gender-disaggregated data to monitor scheme performance by sector and region.
- Support formalization of women-owned informal enterprises by assisting with licenses and paperwork.
Conclusion
Empowering rural women entrepreneurs is key to economic growth. Addressing existing scheme gaps and fostering inclusivity will unlock the untapped potential of women in driving sustainable development.
Building a Skilled Workforce in Rural India

Importance of Skilling in Rural India
- Skilling plays a crucial role in rural development by providing better job opportunities and reducing migration to urban areas.
- It fosters entrepreneurship among rural youth, enabling them to contribute to local economies.
- Targeted programs like DDU-GKY and RSETI have demonstrated encouraging results in enhancing rural livelihoods.
India’s Demographic Dividend
- India has a young population, with 65% under the age of 35, presenting a significant opportunity to harness its demographic dividend.
- Skilling is essential to prepare this young workforce for the demands of a modern economy.
- Despite improvements in employability, a large portion of the workforce still lacks critical skills.
Government Initiatives for Skilling
- Prime Minister’s Package for Skilling and Employment: This initiative aims to skill 20 lakh youth and upgrade 1,000 ITIs across the country.
- National Policy on Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (NPSDE): This policy focuses on bridging skill gaps, improving industry engagement, and expanding apprenticeship opportunities.
- Skill India Mission (SIM): This mission equips Indian youth with industry-relevant skills through schemes like PMKVY, JSS, NAPS, and CTS.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Since its inception, PMKVY has trained 1.42 crore individuals in various skill domains.
- Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS): This scheme provides vocational training through over 15,000 ITIs, with increasing participation of women.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS): JSS targets non-literates and marginalized groups, offering skill training to empower these communities.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS): NAPS supports over 32 lakh apprentices, promoting on-the-job training with increasing participation from women.
- Entrepreneurship Training: Institutions like NIESBUD and IIE have provided entrepreneurial training to numerous beneficiaries.
- Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH): SIDH facilitates access to skilling, credit, and employment through AI/ML integration.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY): This placement-linked program mandates a 70% minimum placement rate for trained candidates.
- Rural Self Employment Training Institutes (RSETIs): RSETIs offer free skill training and credit assistance to rural youth for self-employment.
Partnering with Industry for Skilling
- The Skill India Mission collaborates with industries through NSDC-driven partnerships to support skill development, reskilling, and upskilling.
- The government aligns skilling programs with market demands by collaborating with industries and prioritizing future-ready job roles.
Skilling India at Global Standards
- India is expanding its global skilling footprint through initiatives like Skill India International Centers (SIICs).
- Partnerships with countries such as Australia, Germany, Japan, and the UK focus on aligning skilling with international standards.
- Migration and Mobility Agreements with several countries support skilling aligned with global demands.
Impact of Skill Development Initiatives
- These initiatives have contributed to reducing unemployment rates and increasing wages in rural areas.
- The focus on skilling has led to the growth of rural industries and created employment opportunities in the hinterlands.
Conclusion
- Skilling programs are crucial for rural development and the effective utilization of India’s demographic dividend.
- Continued investment and innovative strategies are needed to ensure long-term economic growth and inclusivity in rural areas.
Skilling the Youth through Technology

The Importance of Skilling in the Digital Age
- India faces the challenge of preparing its youth for a competitive, digital-first world.
- Skilling is crucial for improving job prospects, productivity, and adaptability in a rapidly changing global economy.
- Technology plays a vital role in skilling by providing scalability, accessibility, and customization.
Government Initiatives for Technology-Driven Skilling
- Digital India Campaign: Enhances digital literacy and infrastructure, creating the foundation for online skilling.
- Skill India Mission: Aligns vocational training programs with the demands of the 21st-century economy.
- Atal Innovation Mission: Introduces students to emerging technologies through Atal Tinkering Labs.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Focuses on short-term skilling programs that integrate digital tools.
Budget 2024-25 Initiatives
- The Union Budget 2024-25 outlines a strategy for education, employment, and skills development.
- It includes an internship program at leading companies to enhance employability.
- Increased funding has been allocated for the National Apprenticeship Training Scheme.
- The budget proposes the enhancement of 1,000 ITIs to align with modern skilling requirements.
Challenges and Way Forward
- The percentage of the formally skilled workforce in India remains low despite these initiatives.
- There is a pressing need for continuous learning and upskilling to meet evolving industry demands.
- Addressing the digital divide is crucial to ensure equitable access to skilling opportunities.
- India must focus on training programs that develop future-ready skills to harness its demographic dividend effectively.
Specific Courses for Technological Development
Several courses can help students develop skills in emerging technologies, including: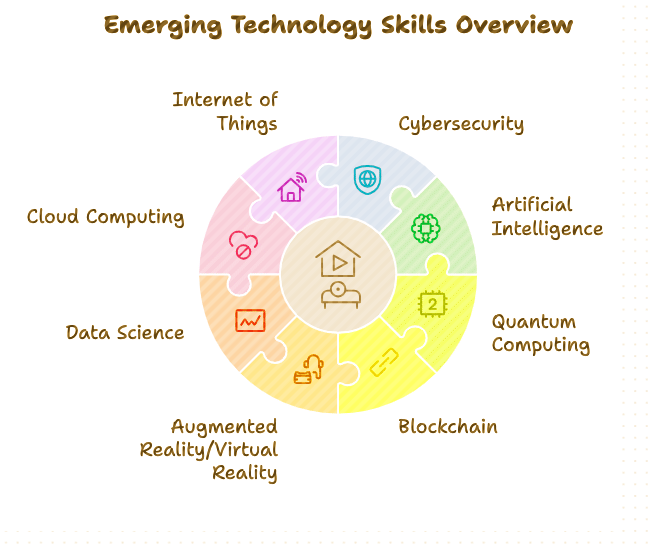
Conclusion
Skilling youth through technology is essential for India’s future. Technology must be leveraged to provide accessible, scalable, and industry-aligned training programs. Collaboration among the government, commercial sector, and educational institutions is crucial to empower India’s youth in a rapidly changing global economy.
Skilled Farmers: Bright Future of Indian Agriculture
The Need for Skilled Farmers
- Despite India's long-standing role as an agricultural nation, farming and farmers are often seen as lacking training and skills.
- The Green Revolution increased crop production but also caused issues such as soil degradation and groundwater depletion.
- To overcome these problems and ensure food security, it is important to create a farming community that is both skilled and focused on business.
Importance of Skill Development in Agriculture
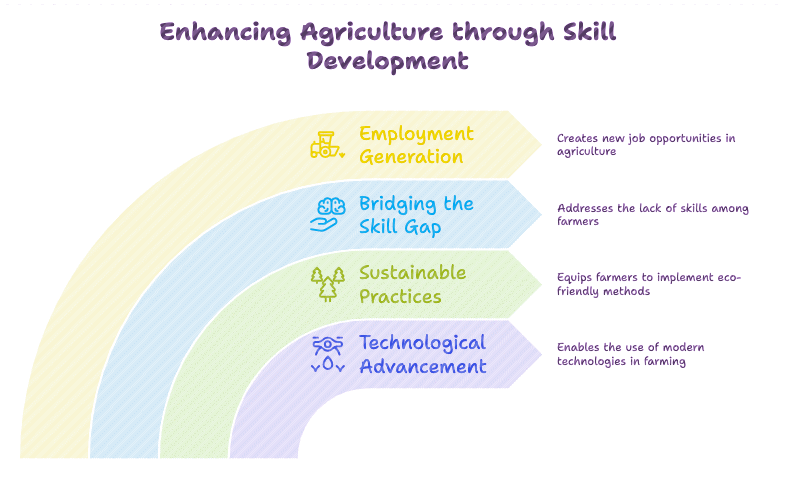
Government Programs for Skill Development in Agriculture
- Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP): Helps women farmers gain skills and resources to improve their work.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM): Aims to improve livelihoods and develop skills for people living in rural areas.
- PM Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprise (PMFME): Supports and helps small food processing businesses to become official.
- Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SHAM): Promotes the use of machines in farming by providing skill training.
- National Beekeeping and Honey Mission: Encourages beekeeping as a way for people to earn money.
- Agricultural Technology Management Agency (ATMA): Supports a farmer-friendly system for sharing agricultural knowledge and advice.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Offers training to farmers to improve their skills in various agricultural topics.
- National Skill Development Mission: Runs skill training programs for young people and farmers in rural areas.
- Skill Training for Rural Youth (STRY): Enhances the knowledge of rural youth in farming and related areas.
- Centers of Excellence (CoE): Provides specialized training to farmers on different types of horticultural crops.
- Per Drop More Crop (PDMC): Conducts training and awareness programs for farmers about efficient irrigation methods.
- Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM): Focuses on building skills for using machinery in farming.
- Drone Training for Women SHGs: Offers training for women’s self-help groups on how to operate drones for farming.
- Food Processing Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP): Provides training on food processing for farmers and self-help groups.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM): Delivers training on various farming practices, including drone operation, natural farming, and managing livestock.
Collaboration between Government and Private Sector
- The private sector, through agri start-up companies, is also contributing to skill development in agriculture.
- Collaboration between the government and the private sector is crucial for effective skill development and ensuring the bright future of Indian agriculture.
Conclusion
Developing skilled farmers is vital to address challenges like climate change and food security. Government and private sector collaboration ensures the growth of modern agriculture and promotes income generation through skill development.
Skill and Entrepreneurial Ecosystem in India

- Skill development and entrepreneurship are crucial for India to maximize its social and economic benefits.
- The Indian government emphasizes skill development and entrepreneurship through initiatives like “Skilled India”, “Make in India”, and “Start-up India”.
- The evolving job market and advancements in technology necessitate continuous skilling, reskilling, upskilling, and lifelong learning.
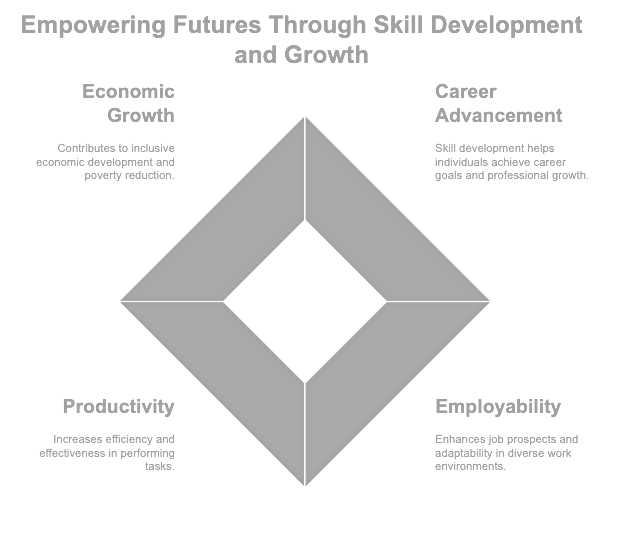
The Significance of Skill Development
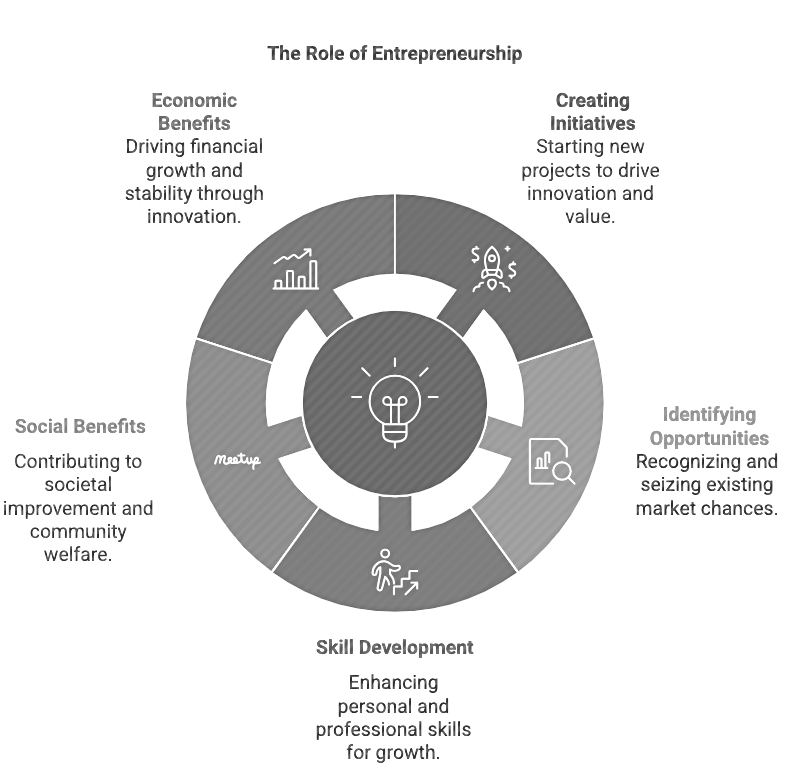
The Role of Entrepreneurship
Government Initiatives for Skill Development
The Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) coordinates skill development efforts across India with the following objectives:
- Enabling individual economic gains and social mobility.
- Creating a learner-centric and demand-driven skills market.
- Facilitating aspirational employment and entrepreneurship generation.
- Improving overall productivity for enterprises.
- Catalyzing economic growth.
National Education Policy (NEP) 2020
- NEP 2020 emphasizes the integration of skill education programs into mainstream education, promoting a flexible and multidisciplinary approach.
- It aims to bridge the gap between education and employment by exposing students to a wide range of work opportunities and skill development courses.
Bridging the Skills Gap
- NEP 2020 aims to remove the societal stigma associated with skill education and provide multiple pathways for students to explore their interests and career options.
- Skill modules are introduced early in the school curriculum, and students can choose skill development courses aligned with industry standards.
- Various states have adopted innovative approaches to skill education, such as establishing incubation centers and integrating skill development into the curriculum.
Schemes of Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Provides free short-duration skill training programs and monetary rewards to encourage skill development. Over 1.48 crore people have been trained/oriented under this scheme.
- Skill India Mission: An umbrella scheme encompassing various skilling programs to empower youth with industry-relevant skills and improve productivity.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS): Provides vocational training and skill development to non-literates and school dropouts, with a focus on women and marginalized communities. Around 26.4 lakh people have been trained under this scheme.
- Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS): Provides long-term training through a network of ITIs to ensure a steady flow of skilled workers in different trades. Over 79.5 lakh people have been trained under this scheme.
- Advanced Vocational Training Scheme (AVTS): Offers short-term modular courses and tailor-made programs to meet specific industry requirements.
- Vocational Training Programme for Women: Focuses on providing skill training to women and creating employment opportunities for them.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme: Promotes apprenticeship training and increases the engagement of apprentices in industries. Approximately 30 lakh apprentices have been engaged in training.
- SANKALP (Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion): Improves short-term skill training qualitatively and quantitatively, strengthens institutions, and promotes market connectivity and inclusion.
- Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH): A unified platform for skilling, education, employment, and entrepreneurship, providing access to training programs, courses, and government services.
- PM VISHWAKARMA: Aims to upskill traditional artisans and provide them with credit support for business expansion.
- Skill Loan Scheme: Offers institutional credit to individuals for skill development courses aligned with the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF).
Entrepreneurship Development
- Startup India Programme: Launched to build a strong ecosystem for nurturing innovation and startups, driving economic growth, and generating employment opportunities.
- BHASKAR (Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry): A one-stop digital platform for connecting and collaborating with diverse stakeholders in the startup ecosystem.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Provides micro-credit and loans to micro-enterprises engaged in non-farm sectors, including activities allied to agriculture.
Conclusion
India’s skilled workforce percentage is low, but initiatives like MSDE’s Vision 2025 present opportunities for skill development and entrepreneurship. Addressing challenges such as social acceptability, labor laws, and infrastructure is crucial to making India the Skill Capital of the World.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|





















