Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Chemical Reactions & Equations - 2 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
(Page - 20)
Question 22:
(a) Explain, with an example, how the physical states of the reactants and products can be shown in a chemical equation.
(b) Balance the following equation and add state symbols :
Zn + HCl ——– > ZnCl2 + H2
(c) Convey the following information in the form of a balanced chemical equation :
“An aqueous solution of ferrous sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide to form a precipitate of ferrous hydroxide and sodium sulphate remains in solution.”
Solution :
(a) The physical states of the reactants and products are shown by putting the “state symbols”
in an equation.
For example: Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) —–> ZnSO4 (aq) + H2(g)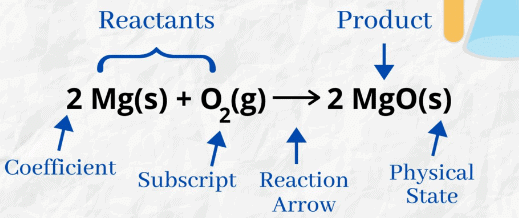 Showing physical state of reactants and productsb) Zn (s) + 2HCl(aq) —–> ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Showing physical state of reactants and productsb) Zn (s) + 2HCl(aq) —–> ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
(c) FeSO4(aq)+ 2NaOH (aq) —–> Fe(OH)2 (s) + Na2SO4(aq)
Question 23:
Write any two observations in an activity that may suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. Give an example in support of your answer.
Solution :
- Evolution of gas.
For example: When sodium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide gas is evolved. - Formation of a precipitate.
For example: When potassium iodide solution is added to a solution of lead nitrate, a yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed.
Question 24:
(a) Aluminium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid to form aluminium sulphate and water. Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
(b) Balance the following chemical equation :
MnO2 + HCl —–> MnCl2 + Cl2 + H2O
Solution :
(a) 2Al(OH)3+ 3H2SO4 —–> Al2(SO4)3+ 6H2O
(b) MnO2+ 4HCl —–> MnCl2+ Cl2 + 2H2O
Question 25:
Write the balanced equations for the following reactions, and add the state symbols (a) Magnesium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride, carbon dioxide, and water.
(b) Sodium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid to produce sodium sulphate and water.
Solution :
(a) MgCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) MgCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
(b) 2NaOH (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l)
Question 26:
Carbon monoxide reacts with hydrogen under certain conditions to form methanol (CH3OH). Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction indicating the physical states of reactants and product as well as the conditions under which this reaction takes place.
Solution :
CO (g) + 2H₂ (g) 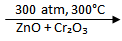 CH₃OH (l)
CH₃OH (l)
The conditions for this reaction to take place are a pressure of 300 atmospheres (written as 300 atm), a temperature of 300oC, and a catalyst which is a mixture of zinc oxide and chromium oxide (ZnO + CrO3).
Question 27:
(a) Potassium chlorate (KClO3) on heating forms potassium chloride and oxygen. Write a balanced equation
for this reaction and indicate the evolution of gas.
(b) Rewrite the following information in the form of a balanced chemical equation :
Magnesium burns in carbon dioxide to form magnesium oxide and carbon.
Solution :
(a) 2KClO3
(s) 2KCl (s) + 3O2 (g)
(b) 2Mg + CO2 —–> 2MgO + C
Question 28:
(a) Substitute formulae for names and balance the following equation :
Calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reaction: Sodium hydroxide solution reacts with a hydrochloric acid solution to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Solution :
(a) CaCO3+ 2HCl —–> CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
(b) NaOH (aq) + HCl(aq) —–> NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
Question 29:
Ammonia reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen and water. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. Add the state symbols for all the reactants and products.
Solution :
4NH3 (g)+ 3O2 (g) —–> 2N2 (g) + 6H2O (l)
Question 30:
Write a balanced chemical equation for the process of photosynthesis giving the physical states of all the substances involved and the conditions of the reaction.
Solution :
6CO2 (g) + 6H2OC6 —–> H12O6 (aq) + 6O2(g)
Carbon
dioxide Water
Glucose Oxygen
Question 31:
Translate the following statement into a chemical equation and then balance it :
Barium chloride solution reacts with aluminium sulphate solution to form a precipitate of barium sulphate and aluminium chloride solution.
Solution :
3BaCl2(aq) + Al2(SO4)3 (aq) —–> 3BaSO4 (s) + 2AlCl3(aq)
Question 32:
When potassium nitrate is heated, it decomposes into potassium nitrite and oxygen. Write a balanced equation for this reaction and add the state symbols of the reactants and products.
Solution :
2KNO3 (s) —–> 2KNO2 (s) + O2(g)
Question 33:
(a) What is meant by a chemical reaction? Explain with the help of an example.
(b) Give one example each of a chemical reaction characterized by :
- evolution of a gas
- change in colour
- formation of a precipitate
- change in temperature
- change in state.
Solution :
(a)Chemical reactions are the processes in which new substances with new properties are formed.
For example: When magnesium ribbon is heated, it burns in air to form a white powder called magnesium oxide.
(b)The chemical reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid.
- The chemical reaction between citric acid and purple coloured potassium permanganate solution is characterized by change in colour (from purple to
colourless). - The chemical reaction between potassium iodide and lead nitrate is characterized by the formation of a yellow precipitate of lead iodide.
- The reaction between quick lime and water to form slaked lime is characterized by a change in temperature.
(Page No. - 21)
Question 34:
(a) State the various characteristics of chemical reactions.
(b) State one characteristic each of the chemical reaction which takes place when :
- dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium carbonate
- lemon juice is added gradually to potassium permanganate solution
- dilute sulphuric acid is added to barium chloride solution
- quicklime is treated with water
- wax is burned in the form of a candle
Solution :
(a) The various characteristics of chemical reactions are:
- Evolution of a gas
- Formation of a precipitate
- Change in colour
- Change in temperature
- Change in state.
(b) Evolution of carbon dioxide gas
- Change in colour from purple to colourless
- Formation of white precipitate of barium sulphate
- Change in temperature
- Change in state from solid to liquid and gas.
Question 35:
(a) What do you understand by exothermic and endothermic reactions ?
(b) Give one example of an exothermic reaction and one of an endothermic reaction.
(c) Which of the following are endothermic reactions and which are exothermic reactions ?
- Burning of natural gas
- Photosynthesis
- Electrolysis of water
- Respiration
- Decomposition of calcium carbonate
Solution :
(a) Those reactions in which heat is evolved are known as exothermic reactions.
The reactions in which heat is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions.
(b) Example of exothermic reaction:
C (s) + O2 (g) —–> CO2 + Heat
Example of endothermic reaction:
N2 (g) + O2 (g) + Heat —–> 2NO (g)
(c) Endothermic reactions: Photosynthesis, Electrolysis of water, Decomposition of calcium carbonate.
Exothermic reactions: Burning of natural gas, Respiration.
Question 36:
One of the following does not happen during a chemical reaction This is :
(a) Breaking of old chemical bonds and formation of new chemical bonds
(b) Formation of new substances with entirely different properties
(c) Atoms of one element change into those of another element to form new products
(d) A rearrangement of atoms takes place to form new products
Ans: (c)
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer. Atoms of one element does not change into another element to form products but the bonds between these atom will break and form products and atoms are rearrange also.
Question 37:
Which one of the following does not involve a chemical reaction?
(a) Digestion of food in our body
(b) Process of respiration
(c) Burning of candle wax when heated
(d) Melting of candle wax on heating
Ans: (d)
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer. Wax changes its physical state on heating but not the properties so it does not involve any chemical change but involves physical change.
Question 38:
You are given the solution of lead nitrate. In order to obtain a yellow precipitate you should mix it with a solution of
(a) Potassium chloride
(b) Potassium nitride
(c) Potassium sulphide
(d) Potassium iodide
Ans: (d)
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer. When a solution of lead nitrate reacts with potassium iodide it gives yellow precipitate of lead iodide.
Question 39:
An acid which can decolourise purple coloured potassium permanganate solution is :
(a) Sulphuric acid
(b) Citric acid
(d) Carbonic acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Ans: (b)
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer. Reaction of purple-coloured potassium permanganate with citric acid is characterised by change in colour from purple to colourless.
Question 40:
The chemical reaction between the two substances is characterised by a change in colour from orange to green. These two substances are most likely to be:
(a) Potassium dichromate solution and sulphur dioxide
(b) Potassium permanganate solution and sulphur dioxide
(c) Potassium permanganate solution and lemon juice
(d) Potassium dichromate solution and carbon dioxide
Ans: (a)
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer. Reaction between potassium dichromate and sulphur dioxide is characterised by change in colour. The orange colour of acidified potassium dichromate will change into green by passing sulphur dioxide.
Question 41:
The chemical reaction between quicklime and water is characterised by:
(a) Evolution of hydrogen gas
(b) Formation of slaked lime precipitate
(c) Change in temperature of mixture
(d) Change in colour of the product
Ans: (c)
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer. Reaction of quicklime and water releases higher amount of energy and thus it is an exothermic reaction.
Question 42:
One of the following is an endothermic reaction. This is:
(a) Combination of carbon and oxygen to form carbon monoxide
(b) Combination of nitrogen and oxygen to form nitrogen monoxide
(c) Combination of glucose and oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water
(d) Combination of zinc and hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen
Ans: (b)
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer. When nitrogen and oxygen are heated at very high temperature they form nitrogen monoxide and it is a endothermic reaction.
Question 43:
Which of the following is not an endothermic reaction ?
(a) CaCO3→ CaO + CO2
(b) 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
(c) 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
(d) C6H12O6 + 6O2→ 6CO2 + 6H2O
Ans: (d)
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer. This is responsible for the respiration reaction in which glucose burns in oxygen to produce heat energy and thus an exothermic reaction.
Question 44:
One of the following is an exothermic reaction. This is:
(a) Electrolysis of water
(b) Conversion of limestone into quicklime
(c) Process of respiration
(d) Process of photosynthesis
Ans: (c)
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer. Respiration is an exothermic reaction as the heat energy is released which maintains our body temperature.
Question 45:
The chemical equations are balanced to satisfy one of the following laws in chemical reactions. This law is known as:
(a) Law of conservation of momentum
(b) Law of conservation of mass
(c) Law of conservation of motion
(d) Law of conservation of magnetism
Ans: (b)
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer. Equations are balanced when the mass of atoms of different element in reactants side equal to the products side.
(Page No. - 22)
Question 46:
When the solution of substance X is added to a solution of potassium iodide, then a yellow solid separates out from the solution.
(a) What do you think substance X is likely to be ?
(b) Name the substance which the yellow solid consists of.
(c) Which characteristic of chemical reactions is illustrated by this example ?
(d) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction which takes place. Mention the physical states of all the reactants and products involved in the chemical equation.
Solution :
(a) Lead nitrate.
(b) Lead iodide.
(c) Formation of a precipitate.
(d) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) —–> PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
Question 47:
When water is added gradually to a white solid X, a hissing sound is heard and a lot of heat is produced forming a product Y. A suspension of Y in water is applied to the walls of a house during white washing. A clear solution of Y is also used for testing carbon dioxide gas in the laboratory.
(a) What could be solid X ? Write its chemical formula.
(b) What could be product Y ? Write its chemical formula.
(c) What is the common name of the solution of Y which is used for testing carbon dioxide gas ?
(d) Write chemical equation of the reaction which takes place on adding water to solid X.
(e) Which characteristic of chemical reactions is illustrated by this example ?
Solution :
(a) Calcium oxide, CaO.
(b) Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2
(c) Lime water.
(d) CaO + H2O —–> Ca(OH)2
(e) Change in temperature.
Question 48:
When metal X is treated with a dilute acid Y, then a gas Z is evolved which burns readily by making a little explosion.
(a) Name any two metals which can behave like metal X.
(b) Name any two acids which can behave like acid Y.
(c) Name the gas Z.
(d) Is the gas Z lighter than or heavier than air ?
(e)Is the reaction between metal X and dilute acid Y exothermic or endothermic ?
(f) By taking a specific example of metal X and dilute acid Y, write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction which takes place. Also indicate physical states of all the reactants and products.
Solution :
(a) Zinc and Iron.
(b) Dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid.
(c) Hydrogen.
(d) Lighter than air.
(e) Exothermic.
(f) Suppose metal X is zinc (Zn) and acid Y is dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) ;
Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Question 49:
A solid substance P which is very hard is used in the construction of many buildings, especially flooring. When substance P is heated strongly, it decomposes to form another solid Q and a gas R is given out. Solid Q reacts with water with the release of a lot of heat to form a substance S. When gas R is passed into a clear solution of substance S, then a white precipitate of substance T is formed. The substance T has the same chemical composition as starting substance P.
(a) What is substance P ? Write its common name as well as chemical formula.
(b) What is substance Q ?
(c) What is gas R ?
(d) What is substance S ? What is its clear solution known as ?
(e) What is substance T ? Name any two natural forms in which substance T occurs in nature.
Solution :
(a) Calcium carbonate (limestone), CaCO3
(b) Calcium oxide, CaO
(c) Carbon dioxide, CO2
(d) Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2; Lime water.
(e) Calcium carbonate; Limestone and Marble.
Question 50:
A silvery-white metal X taken in the form of ribbon, when ignited, burns in air with a dazzling white flame to form a white powder Y. When water is added to powder Y, it dissolves partially to form another substance Z.
(a) What could metal X be ?
(b) What is powder Y ?
(c) With which substance metal X combines to form powder Y ?
(d) What is substance Z ? Name one domestic use of substance Z.
(e) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction which takes place when metal X burns in air to form powder Y.
Solution :
(a) Magnesium, Mg. Magnesium Ribbon(b) Magnesium oxide,MgO(c) Oxygen (of air),O2
Magnesium Ribbon(b) Magnesium oxide,MgO(c) Oxygen (of air),O2
(d) Magnesiumhydroxide, Mg(OH)2; Used as antacid to relieve indigestion
(e) 2Mg + O2 —–> 2MgO
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Chemical Reactions & Equations - 2 - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the different types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 2. How can we balance chemical equations? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of chemical equations in chemistry? |  |
| 4. What are some common examples of chemical reactions in everyday life? |  |
| 5. How do you identify a chemical reaction has occurred? |  |

















